Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for GS LANSOPRAZOLE DR
✉ Email this page to a colleague
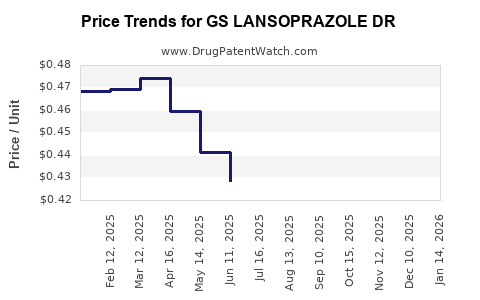
Average Pharmacy Cost for GS LANSOPRAZOLE DR
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS LANSOPRAZOLE DR 15 MG CAP | 00113-1114-01 | 0.42362 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GS LANSOPRAZOLE DR 15 MG CAP | 00113-1114-02 | 0.42362 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GS LANSOPRAZOLE DR 15 MG CAP | 00113-1114-03 | 0.42362 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GS LANSOPRAZOLE DR 15 MG CAP | 00113-1114-03 | 0.43495 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| GS LANSOPRAZOLE DR 15 MG CAP | 00113-1114-02 | 0.43495 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| GS LANSOPRAZOLE DR 15 MG CAP | 00113-1114-01 | 0.43495 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| GS LANSOPRAZOLE DR 15 MG CAP | 00113-1114-01 | 0.44583 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for GS Lansoprazole DR
Introduction
GSK’s GS Lansoprazole DR (delayed-release formulation) emerges as a significant entrant into the proton pump inhibitor (PPI) segment, primarily treating gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), gastric ulcers, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. As the healthcare landscape shifts towards targeted therapies with improved safety profiles, understanding its market dynamics and pricing trajectory becomes essential for stakeholders, including pharmaceutical companies, investors, and healthcare providers.
Market Overview and Competitive Landscape
Segment Dynamics
PPIs dominate the global acid suppression market, with key players including Pfizer (originally with omeprazole), AstraZeneca (omeprazole and esomeprazole), and Takeda (lansoprazole). The segment’s growth is propelled by rising GERD prevalence—approximately 20% in the U.S. (source: ACG) — and increasing awareness regarding acid-related disorders.
GS Lansoprazole DR’s patented delayed-release formulation aims to enhance bioavailability and minimize food interactions, which could offer clinical benefits over earlier formulations. Moreover, the shift towards genericization of older PPIs pressures branded drugs to defend market share through differentiation, pharmacokinetic advantages, or combination offerings.
Regulatory and Developer Strategy
GSK’s strategic positioning emphasizes developing next-generation formulations with improved efficacy and safety, capitalizing on PLIVA's manufacturing capacity for cost competitiveness. Regulatory approvals from key markets, such as the FDA and EMA, serve as critical enablers for market penetration.
Market Size and Penetration Potential
Current Market Size
The global proton pump inhibitor market was valued at approximately USD 11 billion in 2022, with expected compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 4% until 2027 (source: MarketsandMarkets). Lansoprazole accounts for about 15-20% of the PPI market share, translating to roughly USD 2–2.2 billion.
Target Markets and Adoption
Main markets include the US, Europe, and emerging economies in Asia-Pacific. The US alone accounts for roughly 40% of global PPI sales, driven both by prescription and OTC channels. GSK’s introduction of GS Lansoprazole DR aims to secure early adoption through physician preference and insurer acceptance of its superior pharmacokinetic profile, especially in formulations aimed at managing complex gastric conditions.
Competitive Advantages and Barriers
- Clinical Benefits: Improved acid suppression and fewer food interactions may promote greater clinician preference.
- Patent and Exclusivity: Patent protection or exclusivity periods are critical; existing patents on conventional lansoprazole may limit initial market share, but likely expire within 5–7 years.
- Generics: The availability of low-cost generics poses significant price pressure, potentially impacting GSK’s pricing strategy.
Pricing Strategy and Projections
Historical Pricing Trends
Historically, branded PPIs like Nexium (esomeprazole) have commanded 20-30% premium over generics, but pricing has plummeted upon patent expiry. Initial launch prices for branded lansoprazole ranged from USD 250 to USD 300 per month (per patient, in the US).
Projected Price Path
Given the competitive landscape and patent expirations, GSK’s GS Lansoprazole DR is expected to follow a phased price decline:
- Year 1-2: Premium pricing maintained at 20–30% over generic lansoprazole, especially in branded segments aimed at refractory GERD or complex cases.
- Year 3-5: Entry of generics and biosimilars lead to price erosion, with expected reductions of 30–50%. GSK might adopt a value-based pricing model, emphasizing clinical benefits.
- Beyond Year 5: Margin compression to USD 50–100 per month aligns GSK with generic prices, unless pharmacoeconomic data supports premium positioning.
Factors Influencing Price Trends
- Patent Landscape: Patent expirations or litigation outcomes will dictate initial pricing strategies.
- Regulatory Approvals and Indications: Expanded labels, especially for difficult-to-treat populations, justify higher prices.
- Market Penetration and Volume: Higher volume sales may offset lower unit prices.
- Reimbursement Policies: Greater insurance coverage and formulary inclusion will influence achievable prices.
Forecasting Market Penetration and Revenue
Assuming GSK captures 15%–25% of the global lansoprazole market within 3–5 years, revenue projections could range from USD 300 million to USD 600 million annually. High-volume markets like the US and Europe represent substantial revenue potential, especially with strategic partnerships and marketing.
Example Scenario:
- Market share: 20% in the global PPI market.
- Average patient treatment cost: USD 250/month.
- Patients treated: 1 million globally within the target niche.
- Annual Revenue: USD 250 12 1 million * 20% = USD 600 million.
Adjustments to these estimates depend on actual market entry timing, marketing effectiveness, pricing, regulatory environment, and competitive response.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Outlook
Successful regulatory approval in major markets sets the foundation for competitive positioning. GSK can leverage cost-effective manufacturing and differentiated delivery systems to secure favorable reimbursement terms, emphasizing superior safety and efficacy profiles.
In the US, formularies often prefer branded drugs with demonstrated clinical advantages, providing room for premium pricing. Conversely, cost-containment policies in European and emerging markets may pressure prices downward, favoring widespread generic adoption.
Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges
- Patent Cliffs: The expiration of patents on existing lansoprazole formulations will intensify price competition.
- Generic Competition: Established low-cost generics will exert downward pressure on brand pricing.
- Market Penetration: Achieving significant market share requires overcoming entrenched competitor brands and clinician preferences.
Opportunities
- Formulation Advantages: GSK’s DR formulation may unlock niche markets or specialized indications.
- Expanded Indications: Label expansions into Zollinger-Ellison or refractory GERD could justify premium pricing.
- Healthcare Trends: Growing focus on personalized medicine and combination therapies could create avenues for strategic partnerships.
Key Takeaways
- GSK’s GS Lansoprazole DR is positioned for moderate to high growth, provided it demonstrates clinical benefits over existing PPIs.
- Initial pricing is likely to be premium in key markets, but rapid erosion is expected upon patent expiration and generic entry.
- Market penetration will depend heavily on regulatory success, clinician adoption, and reimbursement strategies.
- The overall market remains highly competitive, but differentiated formulations and expanded indications can sustain profitability.
- Long-term revenue prospects hinge on strategic lifecycle management, including patent protection, line extensions, and positioning within niche therapeutic areas.
FAQs
1. When is GS Lansoprazole DR expected to gain regulatory approval in major markets?
Regulatory timelines depend on data submissions and review processes. GSK’s current timelines suggest approval within the next 12-24 months, assuming successful clinical trial results and regulatory submission.
2. How will patent expiration influence pricing strategies for GS Lansoprazole DR?
Patent expiration typically leads to significant price reductions due to generic competition. GSK will likely pursue lifecycle management strategies—such as formulations with improved pharmacokinetics or combination therapies—to sustain higher pricing beyond patent expiry.
3. What differentiates GS Lansoprazole DR from existing lansoprazole products?
Its delayed-release formulation aims to optimize pharmacokinetics, reduce food interactions, and potentially improve symptom control. These advantages could justify premium pricing and clinician preference.
4. How significant is the impact of generics on the projected revenue of GS Lansoprazole DR?
Generics exert substantial downward pressure on brand pricing and volume. The initial premium price may diminish within 3-5 years post-launch, emphasizing the need for early market penetration and indication expansion.
5. What are the key regulatory hurdles for GS Lansoprazole DR?
Ensuring bioequivalence, demonstrating clinical safety and efficacy, and navigating patent landscapes are primary hurdles. Additionally, gaining approval for broader indications can expand the market but may require further clinical studies.
Sources:
[1] MarketsandMarkets (2022). Proton Pump Inhibitors Market Report.
[2] American College of Gastroenterology (2020). GERD Prevalence Data.
[3] GSK Corporate Reports (2023). Pipeline and Regulatory Updates.
[4] IMS Health. (2021). Global PPI Market Trends.
[5] FDA and EMA Regulatory Guidelines for PPIs.
More… ↓
