Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for GNP ANTIBACTRL-URINARY PAIN TB
✉ Email this page to a colleague
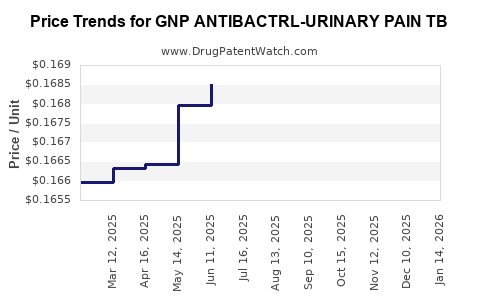
Average Pharmacy Cost for GNP ANTIBACTRL-URINARY PAIN TB
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNP ANTIBACTRL-URINARY PAIN TB | 46122-0622-62 | 0.16625 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GNP ANTIBACTRL-URINARY PAIN TB | 46122-0622-62 | 0.16625 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| GNP ANTIBACTRL-URINARY PAIN TB | 46122-0622-62 | 0.16625 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| GNP ANTIBACTRL-URINARY PAIN TB | 46122-0622-62 | 0.16810 | EACH | 2025-09-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for GNP ANTIBACTRL-URINARY PAIN TB
Introduction
GNP ANTIBACTRL-URINARY PAIN TB emerges as an innovative therapeutic agent targeting urinary tract infections (UTIs) associated with tuberculosis (TB). As antimicrobial resistance escalates globally and TB-specific UTIs remain a significant clinical challenge, this drug's market potential hinges on its efficacy, safety profile, regulatory approval, and competitive dynamics. This analysis evaluates the current market landscape, demand drivers, competitive environment, regulatory considerations, and provides price projections to inform strategic decision-making for stakeholders.
Market Landscape Overview
Global Tuberculosis and UTI Burden
Tuberculosis remains a prominent infectious disease, with an estimated 10.6 million new cases globally in 2021, according to the World Health Organization (WHO)[1]. While pulmonary TB predominates, extrapulmonary manifestations, including genitourinary TB, account for approximately 15-20% of TB cases, complicating treatment regimes.
UTIs rank among the most common bacterial infections worldwide, particularly in women, with an estimated 150 million cases annually[2]. TB-associated UTIs, while less prevalent, pose diagnostic and therapeutic challenges, attributed to delayed diagnosis, drug resistance, and complex treatment regimens.
Therapeutic Gap and Market Need
Current TB treatments primarily focus on pulmonary and systemic disease but inadequately address extrapulmonary manifestations such as genitourinary TB. Existing drugs often carry substantial side effects, prolonged treatment durations, and rising resistance profiles. Consequently, there exists an unmet need for targeted, safe, and effective therapies like GNP ANTIBACTRL-URINARY PAIN TB, dedicated to managing urinary TB infections with minimized systemic toxicity.
Market Segmentation and Key Stakeholders
-
Primary Market Segments:
- Hospitals and Infectious Disease Clinics: Major treatment centers managing complex TB cases.
- Urology and Nephrology Centers: Implicated in diagnosis and follow-up.
- Pharmaceutical Distribution Networks: Supplying to governments and private sectors.
-
Secondary Stakeholders:
- Regulatory agencies (FDA, EMA, WHO).
- Insurance payers and healthcare policymakers.
- Patients with TB-related urinary infections.
Competitive Landscape
Existing Therapies
The current therapeutic arsenal includes first-line anti-TB agents (isoniazid, rifampicin, ethambutol, pyrazinamide) and adjunct agents for extrapulmonary TB. However, these are systemically administered with widespread side effects and limited efficacy in localized urinary infections.
No direct competitors targeting urinary-specific TB infections with a similar scope currently exist. Some generic anti-TB drugs are used off-label. Novel agents like GNP ANTIBACTRL-URINARY PAIN TB could fill a niche, especially if they demonstrate targeted delivery, reduced toxicity, and shorter treatment durations.
Potential Competitive Advantages
- Targeted Therapy: Specifically designed for urinary tract TB infections.
- Reduced Side Effect Profile: Possibly through localized delivery or novel mechanisms.
- Combination Compatibility: Synergistic with existing regimens, reducing treatment time.
Regulatory Status and Reimbursement Environment
GNP ANTIBACTRL-URINARY PAIN TB's path to market necessitates successful clinical trials demonstrating safety and efficacy. Regulatory pathways may include:
- FDA's Fast Track or Breakthrough Therapy Designations (if applicable).
- EMA’s Conditional Approval for urgent unmet needs.
- Reimbursement prospects depend on demonstrable cost-effectiveness compared to existing regimens, with health technology assessments (HTAs) playing a crucial role.
Market Penetration and Demand Drivers
- Rising TB and UTIs Prevalence: Increasing global incidence, especially in resource-limited settings, boosts demand.
- Treatment Gaps: Existing therapies’ limitations open opportunities for targeted drugs.
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): Growing AMR necessitates novel agents with mechanisms to combat resistant strains.
- Patient Outcomes: Potential for improved adherence and shorter treatment durations enhances market acceptance.
Price Projections
Assumptions and Methodology
- Market Entry Year: 2024
- Initial Price Point: Estimation based on drug innovation premium, comparable TB therapeutics, and manufacturing costs.
- Pricing Strategy: Tiered, considering high-income vs. low-income markets, with discounts and subsidies in resource-limited regions.
- Market Share: Conservative estimates suggest gradual adoption over five years, reaching dominant status in specialized clinics.
Projected Pricing Tiers
| Market Segment | Estimated Annual Price (USD) | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| High-income countries | $2,500 - $3,500 | Premium pricing justified by innovation and targeted efficacy. |
| Upper-middle-income countries | $1,500 - $2,500 | Price reduction aligned with purchasing power. |
| Low-income/resource-limited settings | $500 - $1,000 | Use of subsidies, generic competition if feasible, or tiered pricing mechanisms. |
Revenue Projections
Assuming initial adoption in 10 countries with high TB prevalence and a combined outtake of 50,000 units within the first three years, revenues could approximate:
- Year 1: $50 million (limited by regulatory approval timelines).
- Year 2: $150 million (growing adoption and expanded markets).
- Year 3 and beyond: $300+ million, contingent on market penetration and clinical superiority.
Market Growth and Outlook
The global TB drugs market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 5.8% through 2030[3]. Integrating the niche for urinary-specific TB therapies, GNP ANTIBACTRL-URINARY PAIN TB could capture 3-7% of this segment over five years, supported by:
- Product differentiation.
- Advances in TB diagnostics enabling earlier diagnosis.
- International health initiatives prioritizing TB eradication.
Challenges to Market Entry
- Regulatory Delays: Length of clinical trials can impact launch timelines.
- Pricing and Reimbursement Barriers: Reimbursement in low-income regions may be limited.
- Resistance Development: Emerging resistance patterns may impact drug efficacy.
- Manufacturing and Supply Chain: Ensuring quality and scalability in production.
Conclusion
GNP ANTIBACTRL-URINARY PAIN TB presents a compelling opportunity within the TB therapeutics landscape, targeting a niche underserved by existing treatments. Strategic positioning, aligned pricing, and proactive regulatory engagement will be vital for capturing market share. Given the evolving global TB burden and increasing focus on targeted, short-duration therapies, projections indicate robust revenue potential in the medium term.
Key Takeaways
- Market Potential: High, driven by unmet clinical needs and TB prevalence.
- Pricing Strategy: Tiered, with premium positioning in developed markets and accessible pricing regions.
- Revenue Forecast: Potential to surpass $300 million annually within five years post-launch.
- Competitive Advantage: Targeted application, reduced side-effects, potential for combination therapy.
- Strategic Focus: Accelerate regulatory approval, expand clinical evidence, and develop partnerships for global distribution.
FAQs
Q1: What factors influence the pricing of GNP ANTIBACTRL-URINARY PAIN TB?
A1: Pricing is influenced by development costs, clinical efficacy, safety profile, manufacturing expenses, competitive landscape, regulatory requirements, and healthcare reimbursement policies.
Q2: How does antimicrobial resistance impact the market potential?
A2: Rising AMR enhances the need for novel agents like GNP ANTIBACTRL-URINARY PAIN TB, making it more attractive for treatment of resistant TB strains and expanding market demand.
Q3: What are the primary barriers to market entry?
A3: Key barriers include regulatory approval timelines, high development costs, reimbursement uncertainties, and establishing clinical efficacy over existing therapies.
Q4: Which regions offer the highest growth prospects?
A4: Resource-limited countries with high TB burdens (e.g., India, sub-Saharan Africa, Southeast Asia) hold significant growth potential, contingent on affordable pricing and health infrastructure.
Q5: What strategic actions should stakeholders prioritize?
A5: Prioritization includes expedited clinical development, engagement with health authorities, establishing manufacturing scalability, and developing pricing models aligned with regional economic contexts.
References
[1] World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2022.
[2] Foxman, B. "The Epidemiology of Urinary Tract Infection." Nature Reviews Urology, 2010.
[3] MarketsandMarkets. "Global Tuberculosis Drugs Market," 2022.
More… ↓
