Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for GLIPIZIDE-METFORMIN
✉ Email this page to a colleague
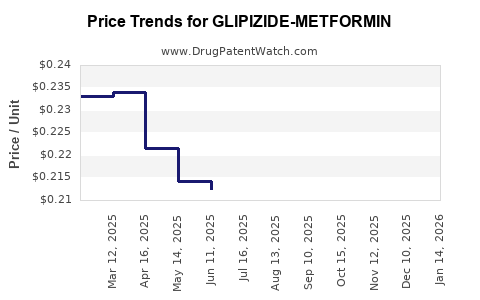
Average Pharmacy Cost for GLIPIZIDE-METFORMIN
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLIPIZIDE-METFORMIN 2.5-250 MG | 68382-0184-01 | 0.17727 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GLIPIZIDE-METFORMIN 2.5-500 MG | 00093-7456-01 | 0.30713 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GLIPIZIDE-METFORMIN 2.5-250 MG | 62135-0731-60 | 0.17727 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GLIPIZIDE-METFORMIN 2.5-500 MG | 23155-0116-01 | 0.30713 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GLIPIZIDE-METFORMIN 2.5-250 MG | 00093-7455-01 | 0.17727 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GLIPIZIDE-METFORMIN 5-500 MG | 68382-0186-01 | 0.22083 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Glipizide-Metformin
Introduction
Glipizide-Metformin combination drugs represent a significant segment within the diabetes management market, particularly for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This fixed-dose combination (FDC) links an insulin sensitizer, metformin, with a sulfonylurea, glipizide, offering enhanced glycemic control with simplified dosing. This analysis evaluates current market dynamics, competitive landscape, regulatory environment, and provides price projections grounded in industry trends.
Market Overview
Global Market Size and Growth
The global diabetes pharmacotherapy market, valued at approximately USD 54 billion in 2022, is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6-8% through 2030 [1]. Within this, the oral antidiabetic segment, including fixed-dose combinations (FDCs), accounts for nearly 70% of prescriptions, driven by patient compliance and cost-effectiveness.
Prevalence and Epidemiology
T2DM afflicts over 400 million people worldwide, projected to reach 700 million by 2045 [2]. The increasing burden fuels sustained demand for adjunct therapies such as Glipizide-Metformin. Notably, the adoption of FDCs hinges on medical guidelines favoring combination approaches, especially in patients requiring intensified glycemic control.
Market Penetration of Fixed-Dose Combinations
FDCs like Glipizide-Metformin streamline treatment regimens. The segment’s penetration is robust in emerging markets (e.g., India, China), where affordability and patient adherence are critical. Western markets exhibit cautious uptake due to concerns over fixed dosing flexibility and side effects, yet the trend is shifting with newer formulations.
Competitive Landscape
Key Players
- AstraZeneca (Synjardy, Janumet)
- Eli Lilly (Humalog Mix)
- Generic Manufacturers (multiple, including Cipla, Sun Pharma)
Market leaders predominantly offer metformin-based FDCs, with Glipizide-Metformin available as generics and under patent by various manufacturers. While no dominant branded product currently monopolizes this segment, generics compete intensely on price.
Patent and Regulatory Environment
Several formulations of Glipizide-Metformin are now off-patent, leading to increased generic competition. Regulatory authorities, including the FDA and EMA, approve multiple versions, further amplifying market availability and price pressure.
Innovation and Pipeline
Emerging formulations focus on extended-release (XR) versions and combining additional agents like DPP-4 inhibitors, aiming for improved safety and efficacy. However, Glipizide-Metformin remains a staple due to its proven efficacy and low cost.
Price Dynamics
Current Pricing Trends
The price of Glipizide-Metformin varies substantially across regions:
-
United States: Primarily generics, with wholesale acquisition costs (WAC) around USD 10-20 for a month's supply.
-
India: Highly affordable, averaging INR 100-200 (~USD 1.30-2.60) per month due to local manufacturing and generic proliferation.
-
Europe: Prices tend to fall between USD 15-30 per month, influenced by regulatory controls and insurance coverage.
Pricing is subject to insurance formularies, payer negotiations, and market competition, which exert downward pressure especially in highly commoditized markets.
Price Projections
Short-term (1-3 years):
-
Price Stability: Given patent expirations and intense generic competition, prices are expected to remain stable or decline marginally by 5-10%. The low-cost nature of generics limits significant hikes.
-
Market Penetration Impact: As market share for combination drugs increases, especially in emerging economies, economies of scale could further depress unit prices.
Medium- to Long-term (4-10 years):
-
Emerging Market Dynamics: Continued expansion in markets like Africa and Southeast Asia may drive prices even lower, assuming regulatory and manufacturing efficiencies.
-
Innovation Influence: Introduction of newer, patent-protected formulations (e.g., XR formulations, combination with SGLT2 inhibitors) could maintain premium pricing in developed markets, but these remain a niche compared to generics.
-
Potential Price Stabilization Factors: Patent extensions or formulations with improved safety profiles may temporarily elevate prices, but the overall trend favors affordability due to the high availability of generics.
Regulatory and Market Drivers
-
Off-Patent Status: The expiration of patents in major markets fosters aggressive generic entry, constraining prices.
-
Guideline Recommendations: Clinical guidelines favor FDCs for combinatorial efficacy and regimen simplicity, bolstering demand.
-
Government Pricing Policies: Many countries implement price caps or reference pricing, further influencing the downward trajectory.
-
Globally Growing Diabetes Population: Sustained demand supports trading stability; however, market saturation and price competition remain challenges.
Implications for Stakeholders
-
Manufacturers: Focus on optimizing production efficiency to sustain margins amidst price pressures.
-
Healthcare Providers: Benefit from affordable options, increasing treatment adherence.
-
Patients: Gain access to cost-effective therapies, improving disease control.
-
Investors: Should monitor patent cliff timelines and emerging formulations that could disrupt current pricing dynamics.
Key Takeaways
-
The global Glipizide-Metformin market is characterized by high competition and declining prices driven by generic proliferation.
-
Price projections suggest stability or slight decreases over the next 3 years, with more significant reductions in markets where generics dominate.
-
The expanding diabetes prevalence ensures enduring demand, but market saturation and price competition are pressing concerns for manufacturers.
-
Innovation remains a key differentiator; however, cost considerations dominate, especially in emerging markets.
-
Regulatory policies and patent expirations will continue to influence market dynamics, making affordability a defining feature.
FAQs
1. What factors influence the pricing of Glipizide-Metformin?
Pricing is mainly affected by patent status, generic competition, regulatory policies, manufacturing costs, regional price controls, and supply-demand dynamics.
2. How does market penetration vary globally?
While Western countries favor branded formulations with premium pricing, emerging markets heavily rely on generics, resulting in lower prices and higher penetration.
3. Are there new formulations that could affect the market?
Yes, extended-release versions and combinations with newer antidiabetic agents may command higher prices but are currently niche compared to generic staples.
4. What are the main barriers to price reduction?
Limited scope for further cost savings, regulatory constraints, and the entry of slight-value innovations slow down price decline.
5. How will patent expirations impact the market?
Patent expirations will intensify generic competition, further reducing prices and increasing affordability, particularly in markets with strong generic manufacturing sectors.
Sources:
- [1] IQVIA, Global Diabetes Market Report, 2022.
- [2] International Diabetes Federation, IDF Diabetes Atlas, 2022.
More… ↓
