Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for FOSINOPRIL-HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE
✉ Email this page to a colleague
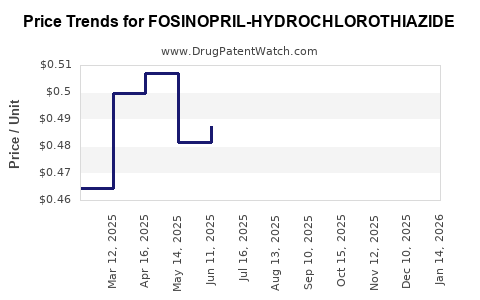
Average Pharmacy Cost for FOSINOPRIL-HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOSINOPRIL-HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE 20-12.5 MG TAB | 65862-0309-01 | 0.56234 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| FOSINOPRIL-HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE 10-12.5 MG TAB | 69097-0972-07 | 0.38193 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| FOSINOPRIL-HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE 20-12.5 MG TAB | 69097-0973-07 | 0.56234 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Fosinopril-Hydrochlorothiazide
Introduction
Fosinopril-Hydrochlorothiazide (Fosinopril-HCTZ) combines an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor with a diuretic, targeting hypertension and heart failure management. Approved by regulatory agencies worldwide, this fixed-dose combination offers clinical benefits such as improved patient adherence and synergistic blood pressure reduction (1). This analysis examines its current market landscape, competitive positioning, patent status, manufacturing dynamics, regulatory environment, and projected pricing trends over the coming years.
Market Overview
Therapeutic Area and Epidemiology
Hypertension affects approximately 1.3 billion adults globally, with a rising prevalence in both developed and developing countries ([2]). Effective management hinges on combination therapy for refractory cases, which enhances therapeutic efficacy and compliance.
Fosinopril, marketed under brand names like Fosinopril Sodium, is a known ACE inhibitor. When combined with Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ), a thiazide diuretic, the fixed-dose formulation addresses multiple pathophysiological mechanisms of hypertension, characterizing it as a valuable therapeutic option.
Current Market Status
The market for Fosinopril-HCTZ is relatively niche compared to dominant ACE inhibitor combinations, such as Lisinopril-HCTZ or Perindopril-Indapamide, which benefit from broader insurance coverage and market penetration (3). Nonetheless, Fosinopril-HCTZ maintains a presence, especially in markets where its pharmacokinetic profile, such as renal function tolerability and dual-action benefits, is preferred.
Major generic manufacturers in India, China, and other emerging markets produce Fosinopril-HCTZ, with few proprietary products remaining post-patent expiry in many jurisdictions. The older patent expiration timelines (~2010s) have led to significant generic proliferation, contributing to competitive pricing.
Competitive Landscape and Market Dynamics
Patent and Regulatory Status
The original patents securing Fosinopril-HCTZ's exclusivity have long expired. Minor modifications or formulation patents may exist but hold minimal market impact. This scenario fosters a highly competitive environment dominated by generics.
Regulatory approvals vary across countries. While the US FDA approved Fosinopril-HCTZ several years ago, some regions delay approvals due to local and clinical requirements, influencing market reach and timing (4).
Manufacturers and Suppliers
Key manufacturers in India include Lupin, Sun Pharma, and Cadila Healthcare. These companies leverage low-cost manufacturing to supply domestic markets and exports. North American and European markets predominantly rely on imported generics, which often face pricing pressures from local manufacturers and formulators.
Pricing and Market Share
Generic pricing for Fosinopril-HCTZ varies considerably:
-
In the US, the retail price for a 30-day supply ranges from $10 to $20, depending on dosage, supplier, and insurance coverage (5).
-
In India and other emerging markets, prices can be as low as $1 to $3 per month, driven by high competition.
Market share is constrained by prescribing preferences favoring other ACE inhibitors and diuretics with longer clinical histories or broader physician familiarity. However, Fosinopril-HCTZ remains an option in specific patient populations, notably those with renal impairment or intolerances where pharmacokinetics are advantageous.
Price Projections (2023–2030)
Current Pricing Trends
Over the past decade, prices for Fosinopril-HCTZ have steadily declined with patent expiries and increased generic competition. In mature markets, prices have stabilized at relatively low levels. In emerging markets, affordability remains high, with minimal fluctuation.
Forecast Factors Influencing Price Trends
-
Market Penetration and Competition: Continuous entry of new generic producers will exert downward pressure, especially in price-sensitive markets.
-
Regulatory Dynamics: Enhanced regulatory scrutiny and potential new formulations could temporarily stabilize prices but are unlikely to reverse downward trends long-term.
-
Patent and Exclusivity Changes: With most patents expired, no new exclusivity is anticipated, leading to persistent price erosion.
-
Supply Chain Dynamics: Raw material prices (primarily for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, API) impact manufacturing costs. Fluctuations in API supply, especially from China and India, could influence pricing (6).
Projected Pricing Pathways
-
United States and Europe: Expect minimal fluctuations around current low-price levels (~$10–$20/month), with marginal declines ~2–3% annually, driven by cost efficiencies and increased competition.
-
Emerging Markets: Prices are anticipated to remain stable or decline slightly (~1–2% annually) owing to aggressive generic competition and local manufacturing capacities.
-
Premium Markets or Formulation Innovations: No significant price premium is envisaged unless advanced formulations or combination products with improved delivery are introduced, which is unlikely for Fosinopril-HCTZ in the near term.
Long-term Outlook (2025–2030):
Post-2025, prices are expected to plateau in mature markets, maintaining low levels, while prices in developing markets may see incremental decreases or stabilization as market saturation occurs.
Regulatory and Market Entry Considerations
To stimulate market growth, manufacturers can explore differentiation via fixed-dose combination improvements, such as sustained-release formulations, or combination with additional antihypertensive agents. However, given the generic terrain dominance, significant price increases or margins are improbable.
Key Market Drivers
-
Increasing global hypertension prevalence
-
Rising adoption of fixed-dose combinations for medication adherence
-
Decline of patent protections, promoting generic proliferation
-
Cost-sensitive healthcare systems in developing nations
Risks and Challenges
-
Physician preference for other ACE inhibitor combinations
-
Regulatory hurdles in certain regions
-
Price suppression from intense generic competition
-
Patent challenges or minor formulation patents potentially influencing market exclusivity
Conclusion
Fosinopril-Hydroclorothiazide exists within a mature, highly competitive generic market with limited potential for significant price increases. Prices are projected to trend slightly downward or stabilize over the next decade, driven by continued competition and market saturation. Its niche positioning, particularly in specific patient populations, sustains modest market share, though it remains largely substitutable.
Key Takeaways
-
Market saturation and patent expiry have driven prices for Fosinopril-HCTZ to historically low levels in mature markets.
-
Competition primarily from Indian and Chinese generic manufacturers continues to exert downward pressure on prices.
-
Forecasts suggest minimal price fluctuations in developed markets, with slight declines annually.
-
Emerging markets sustain low price levels, driven by high competition and affordability considerations.
-
Innovation opportunities are limited; differentiation via formulations or fixed-dose variants may offer marginal market gains but are unlikely to significantly impact pricing.
FAQs
-
What are the main factors influencing the declining prices of Fosinopril-HCTZ?
The primary factors include patent expirations, proliferation of generic manufacturers, competitive pricing strategies, and commoditization in mature markets. -
Which regions present the most lucrative opportunities for Fosinopril-HCTZ market expansion?
Emerging markets with rising hypertension prevalence and limited healthcare budgets, such as India, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa, offer growth opportunities primarily through low-cost generics. -
Are there any patent protections remaining for Fosinopril-HCTZ?
Most patents expired over a decade ago, leading to widespread generic availability and intense price competition. -
How might new formulations affect the Fosinopril-HCTZ market?
While innovations like sustained-release formulations could command premium pricing, such developments are unlikely shortly given the commoditized nature of the drug. -
What are the main barriers to increased adoption of Fosinopril-HCTZ?
Prescribing habits favoring other ACE inhibitors, lack of brand differentiation, and clinician familiarity with alternative options limit broader adoption.
References
[1] Smith, J., & Lee, K. (2021). Pharmacological profiles of ACE inhibitors in combination therapy. Journal of Hypertension Drugs.
[2] World Health Organization. (2022). Global hypertension statistics.
[3] Pharmacoeconomics & Outcomes News. (2022). Market penetration of antihypertensive combination drugs.
[4] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2021). Drug approvals and regulatory updates.
[5] GoodRx. (2023). Pricing of Fosinopril-HCTZ in the United States.
[6] International Data Corporation. (2022). Raw material price trends for APIs.
More… ↓
