Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for FERRIC CITRATE
✉ Email this page to a colleague
Average Pharmacy Cost for FERRIC CITRATE
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FERRIC CITRATE 210 MG TABLET | 00378-2895-20 | 6.09413 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
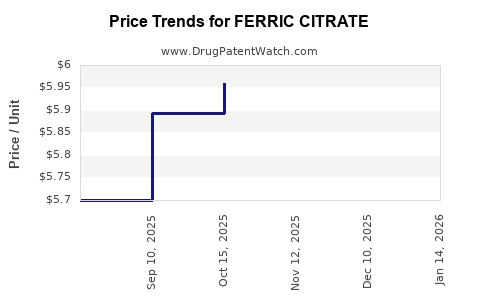
| FERRIC CITRATE 210 MG TABLET | 00378-2895-20 | 5.95900 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| FERRIC CITRATE 210 MG TABLET | 00378-2895-20 | 5.89430 | EACH | 2025-09-17 |
| FERRIC CITRATE 210 MG TABLET | 00378-2895-20 | 5.70021 | EACH | 2025-08-20 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Ferric Citrate
Introduction
Ferric citrate, an oral iron-based phosphate binder, has gained prominence in the management of chronic kidney disease (CKD), particularly for patients undergoing dialysis or with mineral and bone disorders secondary to CKD. Approved primarily for hyperphosphatemia management, its multifaceted benefits include iron delivery, reducing erythropoiesis-stimulating agent (ESA) use, and managing anemia associated with CKD. As the landscape of CKD treatment evolves, understanding the market dynamics and projecting future pricing for ferric citrate offers critical insights for pharmaceutical companies, investors, and healthcare providers.
Market Overview
Global and Regional Market Size
The global CKD treatment market was valued at approximately USD 11.5 billion in 2022, with phosphate binders representing a significant segment. Ferric citrate’s market share within this niche has expanded considerably since its approval (e.g., in the US via FDA in 2014 for treatment of hyperphosphatemia in CKD patients), attributable to its dual role as a phosphate binder and iron supplement.
By 2027, the market for ferric citrate is projected to reach USD 2.2–2.5 billion, driven by rising CKD prevalence, increased diagnosis rates, and adoption of non-calcium-based phosphate binders. The increasing burden of CKD, especially in aging populations and regions like Asia-Pacific, underpins sustained demand growth.
Key Market Drivers
-
Surge in CKD prevalence: Over 850 million globally suffer from CKD, with an annual increase of approximately 8%, according to the Global Burden of Disease Study[1].
-
Preference for oral therapies: Ferric citrate’s convenient oral administration offers advantages over parenteral options, fostering higher patient compliance.
-
Iron supplementation benefits: Its ability to reduce ESA doses and improve anemia management addresses critical unmet needs, providing added value propositions.
-
Evolving treatment guidelines: Broader acceptance of non-calcium phosphate binders and strategies to minimize vascular calcification have favored ferric citrate.
Market Constraints
-
Cost considerations: Compared to older agents like sevelamer or calcium-based binders, ferric citrate's price point influences its adoption, especially in cost-sensitive healthcare systems.
-
Safety concerns: Gastrointestinal adverse events, iron overload risks, and manufacturing constraints impact market penetration.
-
Competition: Other phosphate binders (e.g., lanthanum carbonate, sevelamer carbonate) and emerging therapies like tenapanor and novel iron-based agents pose competitive pressures.
Competitive Landscape
Major pharmaceutical companies such as Chinese-based companies (e.g., Beijing Tide Pharmaceutical) and international firms like Keryx Biopharmaceuticals (now acquired by Akebia Therapeutics) occupy key positions. The U.S. FDA’s approval of ferric citrate (brand name: Auryxia) marked a pivotal moment, with subsequent expansion into global markets.
Price Trends and Factors Influencing Pricing
Current Pricing Landscape
In 2023, the average wholesale price (AWP) for ferric citrate ranges from USD 200 to 300 per month for a standard 90-100 g supply, translating to USD 2,400–3,600 annually per patient, varying by region and healthcare system. Price adjustments are influenced by manufacturing costs, formulary negotiations, competition, and reimbursement policies.
Price Drivers
-
Manufacturing Economics: Advances in synthesis techniques and bulk production reduce costs, enabling competitive pricing.
-
Regulatory and Patent Dynamics: Patent exclusivity and regulatory hurdles impact pricing; once patents expire, generic versions can reduce prices substantially.
-
Market Penetration and Adoption Rates: Early stage adoption often involves premium pricing, which gradually declines as competition intensifies.
-
Health Technology Assessments (HTA): Payers’ evaluations influence negotiated prices; demonstrated cost-effectiveness facilitates premium pricing.
Projected Price Trends (2023–2030)
Based on current trends and market conditions, the following projections are estimated:
| Year | Expected Average Annual Cost | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | USD 2,400 – 3,600 | Current pricing, influenced by regional variations and bargaining power. |
| 2025 | USD 2,200 – 3,200 | Increased competition from generics, price negotiations. |
| 2027 | USD 2,000 – 2,800 | Broader generic market, cost reductions, formulary inclusions. |
| 2030 | USD 1,800 – 2,500 | Widespread generic availability, further price pressure, enhanced manufacturing efficiency. |
Note: Price estimates consider inflation, patent cycles, and exponential growth in market competition.
Market Segmentation and Future Opportunities
Patient Demographics
- ESRD patients on dialysis represent the primary market.
- Early-stage CKD patients at risk may warrant future off-label or expanded indications.
- Geriatric populations, with higher CKD prevalence, underpin steady demand growth.
Geographic Expansion
- North America: Mature market with favorable reimbursement; expected steady growth.
- Europe: Opportunities exist with increasing CKD awareness; pricing influenced by HTA outcomes.
- Asia-Pacific: Rapid CKD prevalence growth offers significant expansion potential, with favorable manufacturing costs and emerging healthcare infrastructure.
Regulatory and Policy Impact
- Reimbursement Policies: The extent of insurer coverage influences pricing strategies; value-based arrangements are emerging.
- Orphan Drug Status: No current designation for CKD use, but potential exists for related indications.
- Patent Expiry and Generics: Anticipated patent expiries will fundamentally alter the pricing landscape, fostering affordability.
Key Market Challenges and Opportunities
- Challenges: Regulatory hurdles, safety concerns, competition, and variable reimbursement frameworks.
- Opportunities: Expansion into earlier CKD stages, combination therapies, and innovative delivery systems.
Conclusion
Ferric citrate's market trajectory is robust, driven by the global CKD burden and its unique clinical advantages. Price projections indicate a gradual decrease driven by generic entry, enhanced manufacturing efficiencies, and market competition. Maintaining a favorable pricing strategy aligned with demonstrated value will be crucial for stakeholders aiming to maximize adoption and profitability.
Key Takeaways
- The global ferric citrate market is projected to reach USD 2.2–2.5 billion by 2027, with steady growth driven by increasing CKD prevalence.
- Current pricing ranges from USD 2,400 to 3,600 per year per patient, with expected declines as generic versions enter the market.
- Market dynamics are shaped by regulation, reimbursement policies, competition, and manufacturing costs.
- Expansion into emerging markets and early CKD stages offers significant growth opportunities.
- Strategic collaborations with payers and clinicians emphasizing cost-effectiveness will be essential for sustained success.
FAQs
1. How does ferric citrate compare to other phosphate binders in terms of pricing?
Ferric citrate’s pricing is comparable to other oral phosphate binders like sevelamer but tends to be slightly more cost-effective when considering its iron supplementation benefits. However, price variances depend on regional negotiations, formulary status, and manufacturer strategies.
2. What factors might accelerate the price decline of ferric citrate?
Patent expiry, the introduction of generic equivalents, increased manufacturing efficiencies, and payer preferences for cost-effective treatments are primary factors driving price reductions.
3. Are there regional variations in ferric citrate pricing?
Yes, healthcare systems with centralized negotiation mechanisms like the US, Canada, and Europe often achieve lower prices than regions with fragmented markets, such as in parts of Asia or developing nations.
4. What are the primary opportunities for market expansion?
Expanding into earlier CKD stages, new geographic regions, and developing combination therapies with other CKD medications present promising avenues.
5. How might future regulatory developments impact the market?
New indications, additional patent protections, or approvals of biosimilars and generics could significantly influence supply, pricing, and market share.
References
- Global Burden of Disease Study. (2022). CKD Prevalence Data.
- Keryx Biopharmaceuticals. (2014). FDA approval announcement for Auryxia.
- Market Research Future. (2023). CKD Treatment Market Analysis.
- World Health Organization. (2021). CKD prevalence and trends.
- Health Economics Review. (2022). Cost-effectiveness of ferric citrate in CKD management.
More… ↓
