Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for ESTRING
✉ Email this page to a colleague
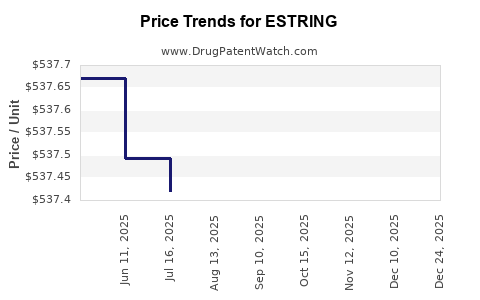
Average Pharmacy Cost for ESTRING
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESTRING 7.5 MCG/DAY (2 MG) RING | 00013-1042-01 | 537.61727 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| ESTRING 7.5 MCG/DAY (2 MG) RING | 00013-1042-01 | 537.68728 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| ESTRING 7.5 MCG/DAY (2 MG) RING | 00013-1042-01 | 537.56826 | EACH | 2025-09-17 |
| ESTRING 7.5 MCG/DAY (2 MG) RING | 00013-1042-01 | 537.48458 | EACH | 2025-08-20 |
| ESTRING 7.5 MCG/DAY (2 MG) RING | 00013-1042-01 | 537.42097 | EACH | 2025-07-23 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for ESTRING
Overview
ESTRING (estradiol vaginal ring) is a prescription hormone replacement therapy (HRT) indicated primarily for menopausal estrogen deficiency symptoms such as vaginal atrophy, dryness, and discomfort. Developed and marketed by Pfizer, ESTRING provides a localized estrogen delivery, reducing systemic exposure and associated risks compared to oral estrogen therapies. With a significant presence in the menopausal treatment landscape, understanding its market dynamics and price trajectory is essential for stakeholders across healthcare, pharmaceutical investment, and policy sectors.
Market Landscape
Market Size and Growth Drivers
The global menopause market, estimated to be valued at approximately $19.2 billion in 2022, is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% through 2030. This growth underpins the demand for hormone therapies like ESTRING. Driven by increasing awareness of menopausal health, aging populations, and evolving treatment preferences favoring localized, low systemic risk options, ESTRING's market share is poised to expand.
Key growth drivers include:
-
Aging Demographics: The global population aged 50 and above is forecast to surpass 1.7 billion by 2030, amplifying the need for HRTs.
-
Shift Toward Localized Therapies: Clinicians and patients increasingly prefer vaginal rings and topical gels over systemic pills, owing to improved safety and convenience.
-
Regulatory Approvals and Clinical Endorsements: Growing acceptance from healthcare authorities and inclusion in clinical guidelines bolster ESTRING’s utilization.
Competitive Landscape
ESTRING's main competitors include other vaginal estrogen products such as Vagifem (estradiol vaginal tablets by Novo Nordisk), Femring (estradiol acetate vaginal ring by TherapeuticsMD), and topical formulations like Estrasorb. While systemic oral estrogen therapies predominate, the localized delivery market segment is increasingly competitive, driven by proprietary technologies and patient preferences.
Pfizer's established manufacturing and distribution capabilities afford ESTRING a strategic advantage, but increased competition from emerging generics and biosimilars could influence pricing and market share.
Regulatory and Patent Environment
Pfizer’s patent protections for ESTRING extend until 2026-2028, with some formulations potentially entering the generic space in the next few years. Regulatory approvals in key markets such as the US, Europe, and Asia reflect validation of efficacy and safety, but upcoming patent expirations threaten future pricing strategies and market control.
Pricing Trends and Factors
Historical Pricing
In the US, ESTRING’s wholesale acquisition cost (WAC) has hovered around $400–$500 per device, with a typical treatment course involving one ring inserted monthly. Insurance coverage and rebates often reduce patient out-of-pocket costs, but prices remain relatively stable due to limited generic competition.
Pricing Drivers
-
Patent Status: Patent expiration is the primary influence on future pricing. As exclusivity wanes, generics—and later biosimilars—are likely to enter the market, exerting substantial downward pressure.
-
Market Penetration: Increasing clinician and patient adoption, especially in regions with expanding menopausal health infrastructure, can sustain premium pricing.
-
Formulation Innovations: New delivery mechanisms or improvements may command higher prices and extend market exclusivity.
-
Reimbursement Policies: Payers’ coverage decisions critically impact net prices; wider coverage supports stable or increasing prices, while restrictive policies dampen pricing levels.
Projection of Future Prices (2023–2030)
Given current trends, several scenarios emerge:
-
Pre-Patent Expiry Period (up to 2026):
During this phase, Pfizer maintains premium pricing, with minimal discounts due to the lack of generic competition. WAC prices are likely to stay within the $400–$500 range per device, adjusted for inflation and healthcare cost inflation. -
Post-Patent Expiry (2026–2030):
Entry of generic estradiol vaginal rings is anticipated, which could lead to a price reduction of approximately 30–50%. Based on historical precedents in the gyno-hormonal market, drugs priced initially between $400 and $500 could see prices fall to $200–$350 per device, depending on market uptake and competitive strategies [1]. -
Market Penetration of Biosimilars and Generics:
Over the long term, multiple generics could further drive prices downward. The price trajectory will also depend on the extent to which payers and providers prefer branded versus generic options in vaginal hormone therapies. -
Influence of Regulatory Developments:
Any regulatory shifts favoring biosimilar entry or the approval of alternative delivery systems, such as longer-acting implants or sustained-release formulations, could affect ESTRING’s pricing structure.
Regional Variations and Global Outlook
-
United States:
As the largest market, U.S. pricing is heavily influenced by patent status, insurance reimbursement, and clinician prescribing habits. The potential for biosimilar entrants post-2026 could lead to significant price reductions. -
Europe:
European markets operate under different patent laws and healthcare systems, often with more aggressive price negotiations, resulting in lower initial prices but higher variability depending on country policies. -
Emerging Markets:
Pricing in Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East tends to be lower even pre-patent expiry due to price controls, with generics playing a pivotal role in subsequent years.
Market Opportunities and Risks
Opportunities:
-
Continued clinical acceptance bolsters ESTRING’s market presence.
-
Expansion into emerging markets can grow revenue streams.
-
Development of new formulations or combination therapies may sustain premium pricing.
Risks:
-
Patent cliffs and the proliferation of generics could erode margins.
-
Competition from oral and alternative localized therapies may limit market share.
-
Regulatory delays or restrictions could hinder product adoption or delay generic entry.
-
Payer push for cost containment may reduce reimbursement levels.
Key Takeaways
-
The ESTRING market is driven by demographic trends and evolving treatment preferences favoring localized estrogen delivery.
-
Pfizer’s patent protection until 2026-2028 provides a period of pricing stability and market control, with prices remaining near historic levels (~$400–$500 per device).
-
Post-patent expiry, prices are expected to decline significantly, potentially falling below $250 per device amidst increased generic competition.
-
Regional differences in pricing strategies reflect varying healthcare policies, patent laws, and market maturity.
-
Continuous innovation and strategic market expansion are vital for maintaining profitability amid declining prices.
FAQs
1. How does patent expiration impact ESTRING’s pricing?
Patent expiry typically introduces generic competitors, increasing market competition and exerting downward pressure on prices, often reducing retail and wholesale costs by 30–50% over several years.
2. What factors could prolong ESTRING’s premium pricing?
Exclusive patent protection, clinical superiority, regulatory exclusivity, and limited generic pipeline development can help sustain higher prices.
3. Will generics significantly erode Pfizer’s ESTRING revenue?
Yes. Once generics enter the market, Pfizer’s sales are likely to decline unless they innovate or develop next-generation formulations to retain market share.
4. Are there emerging alternatives that could replace ESTRING?
Yes. Oral HRT options or other localized estrogen delivery systems—like vaginal gels, creams, or long-acting implants—may compete, especially if they offer comparable efficacy at lower costs.
5. How can market players prepare for future price shifts?
Investing in clinical research, expanding into emerging markets, developing novel formulations, and engaging with payers for favorable reimbursement policies are critical strategies.
References
[1] IMS Health. "Hormonal Therapy Market Dynamics," 2022.
More… ↓
