Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for ERYTHROMYCIN DR
✉ Email this page to a colleague
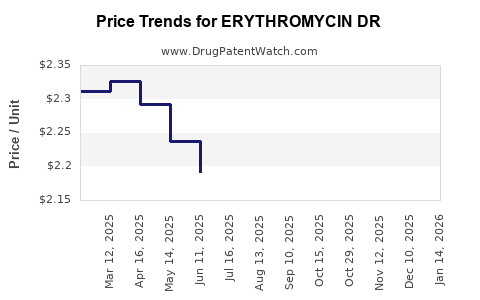
Average Pharmacy Cost for ERYTHROMYCIN DR
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERYTHROMYCIN DR 250 MG TABLET | 13668-0586-01 | 1.91077 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| ERYTHROMYCIN DR 500 MG TABLET | 69238-1473-03 | 3.45303 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| ERYTHROMYCIN DR 250 MG CAP | 75907-0076-01 | 6.52931 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| ERYTHROMYCIN DR 250 MG TABLET | 13668-0586-30 | 1.91077 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Erythromycin DR
Introduction
Erythromycin DR (Delayed-Release) is a formulation of erythromycin, a widely used macrolide antibiotic, distinguished by its delayed-release technology aimed at optimizing absorption and reducing gastrointestinal side effects. As a cornerstone in the treatment of bacterial infections, particularly respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and certain sexually transmitted infections, Erythromycin DR plays a vital role in antimicrobial therapy. Analyzing its market trajectory and pricing requires understanding current demand dynamics, competitive landscape, regulatory environment, and future trends in antibiotic development.
Market Overview
Global Antibiotics Market Landscape
The global antibiotics market reveals consistent growth driven by increasing bacterial resistance, rising prevalence of infectious diseases, and expanding healthcare infrastructure in emerging economies. According to Research and Markets, the antibiotics market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 3.6% from 2021 to 2028 (1).
Erythromycin's Position in the Antibiotics Market
Erythromycin remains a first-line agent in many clinical settings, especially for patients intolerant to penicillin and in cases of penicillin-resistant infections. The availability of controlled-release formulations like Erythromycin DR aims to improve patient compliance and therapeutic efficacy, maintains its relevance amidst evolving antimicrobial resistance challenges.
Key Drivers
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): Growing resistance to traditional antibiotics sustains demand for established drugs like erythromycin, often used as a backup therapy (2).
- Shift Toward Oral and Outpatient Treatments: The convenience of oral delayed-release formulations boosts outpatient treatment settings.
- Innovations in Drug Formulation: Enhanced bioavailability and reduced dosing frequency via DR formulations increase patient adherence.
Regional Market Dynamics
- North America: Dominates due to high prescription rates, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and consistent investment in antimicrobial research.
- Europe: Shows steady growth with regulatory support and updated prescribing guidelines.
- Asia-Pacific: Exhibits the fastest expansion driven by increasing infectious disease burden, improvements in healthcare access, and growing pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities. China and India are key markets.
Competition and Patent Status
Erythromycin is an established generic antibiotic, with numerous formulations available globally. The patent landscape for Erythromycin DR has largely expired in key markets, contributing to price competition. However, proprietary delayed-release technology offered by emerging manufacturers may influence market positioning via patent protections and intellectual property rights.
Major players include companies like Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, and generic manufacturers such as Teva and Mylan. Market entry of new delayed-release versions hinges on regulatory approvals and patent statuses.
Price Analysis and Projections
Historical Price Trends
Historically, erythromycin prices have decreased significantly due to generic manufacturing and patent expirations. According to IQVIA data, average wholesale prices (AWP) for oral erythromycin capsules declined by approximately 50% from 2010 to 2020 (3). Specifically, erythromycin ER (Extended-Release) formulations cost about $0.10–$0.20 per 250 mg capsule in the US, compared to generic immediate-release forms.
Current Pricing Factors for Erythromycin DR
- Formulation Cost: Delayed-release technology generally incurs higher manufacturing costs, translating into marginally higher retail prices relative to immediate-release formulations.
- Market Competition: The presence of multiple generics suppresses pricing, especially in mature markets.
- Regulatory and Reimbursement Policies: Reimbursement rates influence retail pricing, with stricter policies in developed countries.
Future Price Projections (2023–2028)
Given the overall trend of declining antibiotic prices and patent expirations, Erythromycin DR prices are expected to stabilize or slightly decrease over the next five years, barring technological innovations or regulatory exclusivity extensions.
Scenario 1: Continued Market Competition
- Prices remain within the range of $0.15–$0.25 per 250 mg capsule.
- Price erosion of 1–3% annually is anticipated owing to generic competition.
- Larger market share for low-cost manufacturers could further pressure prices.
Scenario 2: Technological Premium and Brand Loyalty
- Pricing could stabilize at higher levels ($0.30–$0.50) if patent protections or unique formulations maintain market exclusivity.
- Brand-name formulations might command a premium, especially if clinical advantages are demonstrated.
Price drivers include:
- Regulatory exclusivity periods.
- Technological differentiation.
- Manufacturing efficiencies.
- Reimbursement frameworks.
Potential Impact of Emerging Trends
- Antimicrobial Stewardship: Increased focus on responsible antibiotic use could limit overprescription, affecting volume-driven pricing.
- New Antibiotic Developments: Novel agents targeting resistant infections could diminish erythromycin’s market share, exerting downward pressure on prices.
- Global Access Initiatives: Efforts to promote affordable antibiotics in low-income countries could cap prices globally.
Strategic Considerations
For pharmaceutical companies seeking to enter or expand within the erythromycin DR market:
- Secure patent protections or data exclusivity to justify premium pricing.
- Invest in formulations demonstrating superior safety or efficacy.
- Engage with regulatory authorities early to streamline approval processes.
- Develop differentiated distribution strategies, especially in emerging markets.
Regulatory Environment Considerations
Regulatory bodies like the FDA (USA), EMA (Europe), and equivalents in emerging markets influence market access and pricing. Demonstration of bioequivalence and safety profiles remains crucial, especially for generics. Novel formulations may require comprehensive clinical data to support labeling claims.
Key Market Opportunities and Risks
Opportunities
- Growing demand in outpatient and pediatric settings.
- Expansion in emerging markets.
- Potential for combination therapies with other antimicrobials.
- Technological advancements to improve bioavailability and patient adherence.
Risks
- Accelerating antimicrobial resistance reducing erythromycin utility.
- Stringent regulatory approvals for new formulations.
- Pricing pressures from generics.
- Global health initiatives favoring narrow-spectrum or targeted therapies over broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Key Takeaways
- The erythromycin DR segment is positioned within a mature, competitive market characterized by declining prices and patent expirations.
- Global demand remains steady, bolstered by its role as a second-line antibiotic and in populations with penicillin allergies.
- Price stability at lower levels is anticipated across mature markets, with potential premium pricing in newer, protected formulations.
- Innovation, regulatory strategies, and market penetration in emerging economies will shape future profitability.
- The evolving landscape of antimicrobial resistance and stewardship initiatives pose both challenges and opportunities for erythromycin products.
FAQs
Q1: How does Erythromycin DR differ from immediate-release formulations?
A1: Erythromycin DR employs delayed-release technology to protect the drug from acid degradation in the stomach, enabling improved bioavailability and a more consistent therapeutic effect, often allowing for less frequent dosing and better patient compliance.
Q2: What factors influence the pricing of Erythromycin DR?
A2: Pricing is influenced by manufacturing costs, patent status, market competition, regulatory approval processes, reimbursement policies, and formulation differentiation.
Q3: Is Erythromycin DR expected to replace immediate-release formulations?
A3: While Erythromycin DR offers pharmacokinetic advantages, its adoption depends on clinical preference, cost considerations, and regulatory approvals. It complements rather than replaces immediate-release forms.
Q4: How has antimicrobial resistance affected the erythromycin market?
A4: Rising resistance has reduced erythromycin’s efficacy against certain pathogens, leading to decreased prescription volume in some regions; however, its role persists in specific indications and as an alternative in penicillin-allergic patients.
Q5: What future innovations could impact Erythromycin DR’s market?
A5: Advancements in targeted delivery, combination therapies, and formulations enhancing efficacy and minimizing resistance could extend erythromycin’s utility and influence pricing strategies.
References
-
Research and Markets. "Global Antibiotics Market Forecast to 2028." 2022.
-
CDC. "Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States," 2019.
-
IQVIA. "Pharmaceutical Pricing Trends," 2021.
Note: All projections and analyses are based on current market data and trends up to 2023. Changes in regulatory policies, technological advancements, and global health initiatives may significantly alter future market dynamics.
More… ↓
