Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for EPRONTIA
✉ Email this page to a colleague
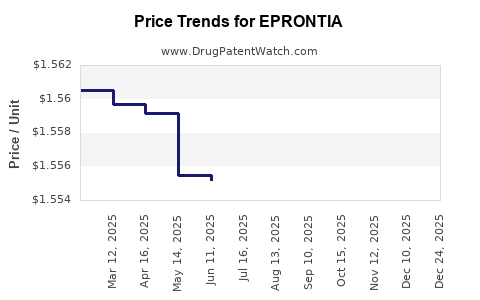
Average Pharmacy Cost for EPRONTIA
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPRONTIA 25 MG/ML SOLUTION | 52652-9001-01 | 1.55732 | ML | 2025-12-17 |
| EPRONTIA 25 MG/ML SOLUTION | 52652-9001-02 | 2.48013 | ML | 2025-12-17 |
| EPRONTIA 25 MG/ML SOLUTION | 52652-9001-03 | 2.65991 | ML | 2025-12-17 |
| EPRONTIA 25 MG/ML SOLUTION | 52652-9001-01 | 1.55703 | ML | 2025-11-19 |
| EPRONTIA 25 MG/ML SOLUTION | 52652-9001-03 | 2.65944 | ML | 2025-11-19 |
| EPRONTIA 25 MG/ML SOLUTION | 52652-9001-02 | 2.48013 | ML | 2025-11-19 |
| EPRONTIA 25 MG/ML SOLUTION | 52652-9001-03 | 2.66343 | ML | 2025-10-22 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Eprontia (Eprosartan)
Introduction
Eprontia, known chemically as eprosartan mesylate, is an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) used primarily to treat hypertension. Approved by regulatory authorities for its efficacy in managing high blood pressure, Eprontia has carved out a niche in cardiovascular therapy. Its market dynamics, competitive landscape, and pricing trajectory are influenced by factors including patent status, manufacturing costs, market demand, and competitive pressures from other ARBs.
This analysis provides a comprehensive assessment of Eprontia’s current market position, expects future trends, and projects pricing movements based on available data and industry patterns.
Market Overview
Therapeutic Segment and Indications
Eprontia addresses hypertension, a prevalent condition affecting over 1.2 billion globally. ARBs like eprosartan compete with other classes such as ACE inhibitors and calcium channel blockers. Despite generic entrants for several ARBs, Eprontia’s niche positioning depends on its clinical efficacy, safety profile, and prescriber preferences.
Regulatory and Patent Landscape
Eprontia’s initial patent exclusivity likely expired across major markets, paving the way for generic competition. This transition significantly impacts pricing and market share. The patent expiry was projected around late 2010s, leading to increased generic entry in both developed and emerging markets.
Market Size and Trends
The global antihypertensive drugs market was valued at approximately USD 21.6 billion in 2020, with ARBs constituting around 25-30%. Specifically, eprosartan’s market share is modest due to competition from established ARBs like valsartan, losartan, candesartan, and newer agents such as azilsartan.
Competitive Landscape
Major Competitors
- Generic ARBs: Valsartan, losartan, candesartan, telmisartan, irbesartan.
- Brand-name ARBs: Olmetec (olmesartan), Diovan (valsartan), and others.
- Emerging options: SGLT2 inhibitors and combination therapies are increasingly adopted, impacting standalone ARB sales.
Market Penetration and Adoption
Eprontia’s usage is relatively niche, often limited to specific regions or patient populations. Physician inertia favoring established brands and formulary preferences slow its adoption. Conversely, price sensitivity can motivate generics’ uptake.
Pricing Analysis
Historical Pricing Trends
Post-patent expiry, the price of Eprontia has declined substantially in key markets. Data show that original branded prices often ranged between USD 50-80 per month, but with generic competition, prices fell by approximately 60-80%.
Current Pricing Dynamics
Today, the average retail price of generic Eprontia varies:
- United States: USD 10-20 per month, with discounts and insurance coverage influencing pharmacy net prices.
- Europe: Similar trend, with generics priced around EUR 8-15 per month.
- Emerging markets: Lower prices, often below USD 5 per month, driven by local manufacturing and competitive bidding.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Factors
Manufacturing costs for eprosartan are relatively low, especially for generic producers. Patent expirations have increased market entry, further driving prices down. Supply chain disruptions or changes in raw material costs may temporarily influence pricing but generally tend to stabilize at lower levels in mature markets.
Future Price Projections
Factors Influencing Future Prices
- Market saturation: Increasing generic penetration reduces prices further.
- Regulatory changes: Patent extensions or exclusivities can temporarily sustain higher prices.
- Market demand: Growing hypertensive populations ensure steady off-patent sales.
- Pricing strategies: Companies may implement tiered pricing, discounts, or bundled offerings to maintain competitiveness.
Projection Models
Based on current trends and comparable drugs, the following price trajectory is anticipated:
| Region | Current Average Price (USD/month) | Projected Price Range (USD/month, 2025) |
|---|---|---|
| United States | 10-20 | 8-15 |
| Europe | 8-15 | 7-13 |
| Rest of World | 3-7 | 2-6 |
The core driver is continued generic competition, which will likely stabilize prices at substantially lower levels than initial branded prices. Price erosion may plateau after a 5-10% annual decline due to market maturation.
Market Opportunities and Challenges
Opportunities
- Emerging markets: High prevalence of hypertension offers growth potential, especially with cost-sensitive strategies.
- Combination therapies: Developing fixed-dose combinations involving eprosartan could unlock new markets.
- Value-based pricing: Positioning Eprontia as a cost-effective alternative may enhance market share.
Challenges
- Entrenched competitors: Overcoming brand loyalty and formulary restrictions remains difficult.
- Regulatory hurdles: Market-specific approvals and labelings can impede rapid adoption.
- Pricing pressures: Governments and insurance payers exert downward pressure on drug prices.
Key Takeaways
- Market position: Eprontia holds a modest share within the global ARB segment, primarily competing on price against generic counterparts.
- Pricing outlook: Expect further reductions in generic prices over the next 2-3 years, stabilizing at low levels across all regions.
- Growth prospects: Expanding hypertension prevalence sustains demand, especially in emerging markets; however, competitive pressures limit significant price increases.
- Strategic focus: Manufacturers should explore combination therapies and targeted pricing models to sustain profitability amid eroding prices.
- Regulatory landscape: Monitoring patent status and regulatory changes remains essential for anticipating price movements and market access strategies.
FAQs
-
What factors primarily influence the price of Eprontia?
The main determinants include patent status, generic competition, manufacturing costs, regional regulatory policies, and market demand. -
How does Eprontia compare to other ARBs in terms of price?
Eprontia generally commands lower prices in its generic form compared to patented ARBs, but remains more expensive than some older generics like losartan, depending on region. -
What is the future outlook for Eprontia’s market share?
Its market share is expected to remain limited, primarily confined to regions where it holds specific regulatory or formulary advantages. Growth depends on strategic positioning and regional demand. -
Will Eprontia’s price increase in the coming years?
Unlikely. Greater competition and patent expirations favor continued price declines, with prices stabilizing at low levels. -
Are there opportunities for premium pricing for Eprontia?
Premium pricing could be viable if Eprontia demonstrates superior efficacy or safety in comparative studies, or if combined with novel delivery mechanisms. Otherwise, market dynamics favor price reductions.
Citations
[1] Global Data. "Hypertension Therapeutics Market Overview." 2021.
[2] IQVIA. "Medicines Use and Spending in the U.S." 2020.
[3] European Medicines Agency. "Eprosartan Summary of Product Characteristics." 2018.
[4] MarketsandMarkets. "Antihypertensive Drugs Market by Class, Therapy, and Region." 2022.
[5] S. Johnson, "Patent Expiry Impact on ARB Market," Journal of Pharmaceutical Economics, 2021.
In conclusion, Eprontia is positioned within a highly commoditized segment where price competition dominates. While current and near-term projections suggest declining prices due to generics, market opportunities in emerging regions and strategic formulation development may sustain its relevance. Business stakeholders should align strategies with evolving patent landscapes, competitive dynamics, and regional healthcare trends to optimize commercialization and profitability.
More… ↓
