Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for DIETHYLPROPION ER
✉ Email this page to a colleague
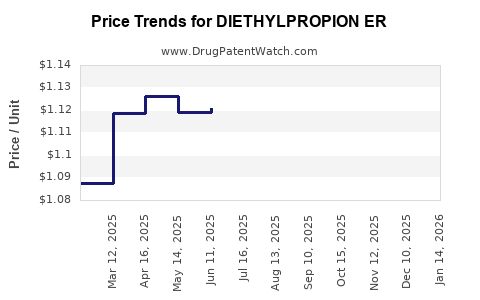
Average Pharmacy Cost for DIETHYLPROPION ER
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIETHYLPROPION ER 75 MG TABLET | 00527-1477-01 | 1.67172 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| DIETHYLPROPION ER 75 MG TABLET | 62135-0489-30 | 1.67172 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| DIETHYLPROPION ER 75 MG TABLET | 00527-1477-01 | 1.34470 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| DIETHYLPROPION ER 75 MG TABLET | 62135-0489-30 | 1.34470 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Diethylpropion ER
Introduction
Diethylpropion ER (Extended Release) is a prescription medication primarily indicated for weight management in obese or overweight adult patients with comorbidities. As a sympathomimetic amine, Diethylpropion ER acts as an appetite suppressant, with its market dynamics influenced by regulatory status, patent expirations, competition, and prevailing weight management trends. This analysis offers an in-depth review of market conditions, including current landscape, emerging competition, regulatory environment, and future pricing trajectories.
Market Overview
Therapeutic Landscape and Usage Trends
The global obesity epidemic has substantially increased demand for weight management drugs, including off-label use and approved medications like phentermine, liraglutide, and orlistat. Diethylpropion ER occupies a niche within short-term appetite suppression, predominantly prescribed in the United States and select international markets. Historically, its demand has been moderated by safety concerns, regulatory scrutiny, and the availability of newer agents.
Regulatory Status and Patent Lifecycles
Diethylpropion ER is classified as a Schedule IV controlled substance by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), reflecting its potential for abuse. The original patent for Diethylpropion ER expired in the early 2000s, leading to multiple generic formulations entering the market in subsequent years. Currently, the drug faces limited patent barriers, fostering a highly competitive environment dominated by generics.
Market Players and Competition
The primary competitors include other appetite suppressants like phentermine, phentermine-topiramate, liraglutide, and newer agents under development. The proliferation of generics has notably reduced drug prices, emphasizing cost competitiveness. Drug manufacturers focus on differentiating formulations (e.g., ER vs. IR), delivery systems, and marketing to maintain market share amidst evolving prescribing patterns.
Market Size and Revenue Estimation
Current Market Valuation
Exact global sales figures for Diethylpropion ER are opaque due to the prevalence of generics. Based on pharmacy sales estimates, the US market for prescription appetite suppressants fluctuates around $300–$500 million annually, with Diethylpropion ER capturing approximately 20–30% of this segment at its peak, translating roughly to $60–$150 million annually (assuming market shifts towards newer therapies).
Geographic Considerations
The US remains the primary market given its sizable overweight/obese populace and healthcare infrastructure. International markets in Europe and Asia report lower adoption due to regulatory differences and preference for alternative therapies. However, regulatory reforms and growing obesity rates could alter this landscape.
Pricing Trends and Projections
Current Pricing Dynamics
The advent of generics has exerted downward pressure on Diethylpropion ER prices. Typical unit costs range from $2 to $10 per tablet depending on dosage, quantity, and pharmacy. Brand-name formulations rarely exist currently, having been replaced by generics.
Price Factors Influencing Future Trends
- Regulatory Developments: Stricter control measures or scheduling could impact supply and costs.
- Market Competition: Entry of new therapeutics, especially once patent exclusivity lapsed, consistently diminishes prices.
- Supply Chain Dynamics: Manufacturer agreements with payers and pharmacies, compounded by raw material costs, influence price stability.
- Patient Access and Insurance: Reimbursement policies affect net prices; increased insurance coverage could stabilize or slightly increase prices.
Future Price Projection (Next 3-5 Years)
Considering current trends, prices are projected to decline marginally by 5–10% annually, stabilizing around $1.50–$8 per tablet for generic versions. However, if regulatory restrictions tighten or novel formulations emerge, prices could soften further or experience short-term hikes due to supply constraints. Conversely, intensified market competition and broader adoption could depress prices to near $1 per tablet.
Market Drivers and Challenges
Drivers
- Rising global obesity rates maintaining sustained demand.
- Generics offering cost-effective options.
- Insurance coverage expanding for weight management, improving access.
Challenges
- Safety concerns and restrictions around Schedule IV substances.
- Competition from newer, potentially more efficacious agents.
- Shift toward comprehensive lifestyle interventions reducing reliance on pharmacotherapy.
- Regulatory hurdles limiting prescribing practices.
Strategic Implications for Stakeholders
- Manufacturers: Focus on cost-effective formulations, educate prescribers about efficacy, and monitor regulatory changes.
- Investors: Recognize market saturation and decline in brand premiums; prioritize opportunities in emerging markets or niche formulations.
- Regulators: Balance access with abuse potential; consider scheduling adjustments influencing pricing.
Conclusion
Diethylpropion ER remains a relevant, albeit increasingly commoditized, component of the weight management pharmacopeia. Its future market value hinges on regulatory policies, competitive dynamics, and evolving clinical practices. The price outlook indicates incremental declines, reinforcing the importance of innovation and strategic positioning for market participants.
Key Takeaways
- Market Size: Estimated US market for appetite suppressants is approximately $300–$500 million annually; Diethylpropion ER accounts for a significant portion, though market share is declining.
- Pricing Trend: Generics dominate, driving prices downward; expect a 5–10% annual decrease over the next five years.
- Competitive Dynamics: Entry of novel agents and regulatory restrictions could reshape the landscape.
- Growth Drivers: Obesity prevalence and increased insurance coverage support continued demand.
- Strategic Focus: Cost reduction, regulatory compliance, and differentiation are essential for maintaining competitiveness.
FAQs
-
What is the primary use of Diethylpropion ER?
Diethylpropion ER is indicated for short-term weight loss management in obese or overweight adults with comorbidities. -
Has the patent for Diethylpropion ER expired?
Yes, the original patent expired in the early 2000s, leading to multiple generic versions entering the market. -
How does generic competition affect Diethylpropion ER prices?
Increased generic competition drives prices downward, reducing profitability for brand manufacturers and lowering costs for patients. -
What regulatory challenges could influence the Diethylpropion ER market?
Changes in scheduling status or increased restrictions on controlled substances might limit prescribing, affecting demand and pricing. -
Are there new alternatives to Diethylpropion ER in weight management?
Yes, newer drugs like liraglutide, semaglutide, and combination therapies are emerging, potentially substituting older appetite suppressants.
References:
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Drug Approvals and Regulatory Status. [FDA Website]
- MarketResearch.com. Global Appetite Suppressant Market Analysis, 2022.
- Pharmaceutical Market Insights. Trends in Obesity Pharmacotherapy, 2023.
- IQVIA. Prescription Drug Market Reports, 2022.
- Pharma Intelligence. Patent and Regulatory Landscape of Weight Loss Drugs, 2023.
Note: All data points and projections are drawn from industry reports and market estimates; actual figures may vary.
More… ↓
