Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for CLEOCIN
✉ Email this page to a colleague
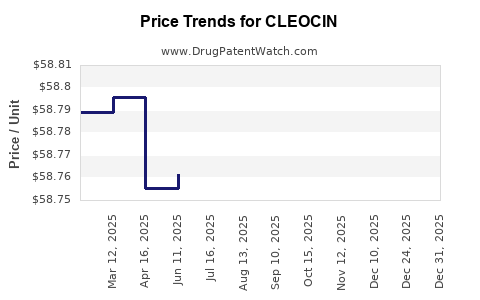
Average Pharmacy Cost for CLEOCIN
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLEOCIN 100 MG VAGINAL OVULE | 00009-7667-01 | 58.63247 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| CLEOCIN 100 MG VAGINAL OVULE | 00009-7667-05 | 58.63247 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| CLEOCIN 2% VAGINAL CREAM | 00009-3448-01 | 1.75080 | GM | 2025-12-17 |
| CLEOCIN 100 MG VAGINAL OVULE | 00009-7667-01 | 58.65448 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| CLEOCIN 100 MG VAGINAL OVULE | 00009-7667-05 | 58.65448 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| CLEOCIN 100 MG VAGINAL OVULE | 00009-7667-01 | 58.72376 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| CLEOCIN 100 MG VAGINAL OVULE | 00009-7667-05 | 58.72376 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for CLEOCIN (Clindamycin)
Introduction
CLEOCIN, known generically as Clindamycin, is a widely prescribed antibiotic within the lincosamide class. Its efficacy against various bacterial infections, including skin, respiratory, and intra-abdominal infections, positions it as a cornerstone in antimicrobial therapy. Despite its longstanding clinical utility, the evolving landscape of antimicrobial resistance, generic drug competition, and regulatory dynamics shape its market prospects and pricing strategies. This analysis provides an in-depth overview of CLEOCIN’s current market status and offers future price projections rooted in industry trends and regulatory insights.
Market Overview
Current Market Dynamics
Clindamycin primarily addresses bacterial infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and anaerobic bacteria. Its formulations include oral capsules, topical solutions, intramuscular injections, and intravenous preparations. The drug’s broad-spectrum activity, combined with its relatively favorable safety profile, sustains steady demand across hospitals, outpatient clinics, and long-term care facilities.
In 2022, the global antibiotic market was valued at approximately USD 50 billion, with Clindamycin accounting for a significant share within the niche of lincosamide antibiotics. The demand was influenced by increasing incidences of skin infections, abscesses, dental infections, and surgical prophylaxis.
Market Segmentation and Regional Distribution
-
Geography: North America and Europe dominate the CLEOCIN market, driven by high prescription rates, robust healthcare infrastructure, and stringent antimicrobial stewardship programs. Asia-Pacific offers high-growth opportunities owing to increasing antibiotic access, expanding healthcare infrastructure, and rising infectious disease burdens.
-
Application: Topical formulations are prevalent for skin and acne treatments, whereas oral and injectable forms cater to systemic infections. The oral segment commands a larger market share, driven by outpatient treatment trends.
Competitive Landscape
The market is predominantly characterized by generic manufacturers following patent expirations. Key players include Sandoz, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Mylan, and Apotex, among others. Brand-name CLEOCIN (Pfizer’s Clindamycin Phosphate) has faced generic erosion over recent years, leading to significant price reductions and increased access.
Market Factors Influencing Price Trends
Patent Expiry and Generic Competition
Clindamycin’s patent expired in the early 2000s, catalyzing a proliferation of generic versions that have profoundly driven down prices. This commoditization enhances accessibility but constrains premium pricing strategies.
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
Growing resistance to clindamycin, particularly among Staphylococcus aureus (including MRSA) strains, impacts clinical use and prescriptions volume. This resistance necessitates combination therapies or alternative agents, influencing volume and price dynamics.
Regulatory and Policy Environment
Stringent antimicrobial stewardship initiatives aim to curb overprescription, potentially reducing volume sales. Conversely, expanding indications and formulations could counterbalance volume declines and support stable or slightly increasing prices.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain
Manufacturers seek to optimize production efficiencies, especially given the high generic competition. Supply chain stability and raw material costs impact pricing margins.
Price Projections (2023–2030)
Historical Pricing Trends
- Oral Capsules: The average retail price for a bottle of 30 capsules (150 mg) ranged between USD 20–30 in 2015. By 2022, this declined to approximately USD 8–12 due to generic market saturation.
- Injectable Formulations: Prices ranged from USD 10–15 per vial in 2015, decreasing to USD 5–8 in recent years.
- Topical Formulations: Ongoing price stability with minor fluctuations observed, owing to less commoditization compared to oral forms.
Projected Trends
-
Short-Term (2023–2025): Prices are likely to stabilize or decrease marginally by 5–10% annually, driven by additional generic entrants and cost pressures. Existing patents offer minimal upward pricing leverage due to aggressive competitor pricing.
-
Mid to Long-Term (2026–2030): Price declines may plateau as generic manufacturers reach market saturation. However, emergent factors such as new formulations (e.g., sustained-release patches, novel topical agents) or regulatory exclusivities on specific indications could create premium niches, resulting in localized price stability or slight increases.
-
Influencing Variables:
- Antimicrobial Resistance: Increasing resistance may restrict use or necessitate higher-dose formulations, potentially maintaining or elevating prices for specific indications.
- Healthcare Policies: Enhanced antimicrobial stewardship could reduce prescription volumes, exerting downward pressure on prices.
- Innovation: Novel delivery systems or combination therapies could command premium prices, offsetting traditional generic declines.
Summary of Price Trajectory
| Year | Expected Price Range (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 8–12 per bottle | Slight decline due to ongoing generic competition |
| 2025 | 7–11 per bottle | Continued stabilization; potential minor decline |
| 2028 | 6–10 per bottle | Price stabilization; possible niche premiums |
| 2030 | 6–9 per bottle | Market maturity; subdued price fluctuations |
Market Opportunities and Risks
Opportunities
- Formulation Innovation: Development of extended-release, topical, or combination formulations can command higher prices and expand indications.
- Geographical Expansion: Focus on emerging markets with increasing antibiotic demand.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborations for antimicrobial stewardship programs can enhance market share.
Risks
- Antimicrobial Resistance: Elevated resistance may diminish clinical utility and prescriptions.
- Regulatory Constraints: Stricter prescribing guidelines could reduce sales volumes.
- Price Erosion: Accelerated generic entry and competitive pricing strategies diminish profit margins.
Conclusion
The CLEOCIN (Clindamycin) market faces a landscape defined by commoditization, resistance challenges, and evolving healthcare policies. Price projections indicate a trend toward stabilization at lower price points through 2030, contingent upon demand sustainability and innovation. Stakeholders must focus on therapeutic diversification, geographic expansion, and efficient manufacturing to optimize profitability amid competitive pressures.
Key Takeaways
- Market Dynamics: Clindamycin remains essential but increasingly commoditized, with extensive generic competition driving prices downward.
- Pricing Outlook: Anticipate modest declines in unit prices through 2025, followed by market stabilization, with possible niche premium pricing on innovative formulations.
- Resistance Impact: Rising antimicrobial resistance can constrain growth but may also justify higher prices for specialized or new delivery systems.
- Strategic Focus: Investment in formulation innovation and geographic expansion offers pathways to differentiation and profitability.
- Supply Chain and Regulation: Maintaining supply chain efficiency and adapting to regulatory guidelines are crucial for market sustainability.
FAQs
1. How does antimicrobial resistance affect CLEOCIN’s market and pricing?
Rising resistance diminishes clinical efficacy, potentially reducing prescription volume and market size. Conversely, developing resistance can justify higher prices for newer formulations or combination therapies to sustain profitability.
2. Will patent protections benefit CLEOCIN manufacturers in the future?
Since patent expiry occurred in the early 2000s, current market dynamics revolve around generic competition. Only specific formulations or delivery methods with new patents can provide temporary exclusivity and pricing leverage.
3. How are generic manufacturers influencing CLEOCIN pricing?
Generic proliferation drives prices downward, making CLINIC more accessible but limiting profit margins for brand-name companies and reducing the potential for premium pricing.
4. What role do regulatory policies play in shaping CLEOCIN’s price trends?
Stringent prescribing guidelines and antimicrobial stewardship programs can decrease prescription volumes, exerting downward pressure on prices. Conversely, regulatory approval of innovative formulations could support higher prices.
5. Are there opportunities for premium pricing in the CLEOCIN market?
Yes, niche formulations such as sustained-release or combination therapies, especially addressing resistant strains, can command premium prices, provided they demonstrate clear clinical benefits and regulatory approval.
Sources
[1] Global Market Insights. "Antibiotics Market Size & Share." 2022.
[2] IQVIA. "Global Antimicrobial Market Trends." 2022.
[3] CDC. "Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States." 2020.
[4] EvaluatePharma. "2018 Global Pharmaceutical Pricing Trends."
[5] World Health Organization. "Antimicrobial Resistance." 2022.
More… ↓
