Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for asenapine
✉ Email this page to a colleague
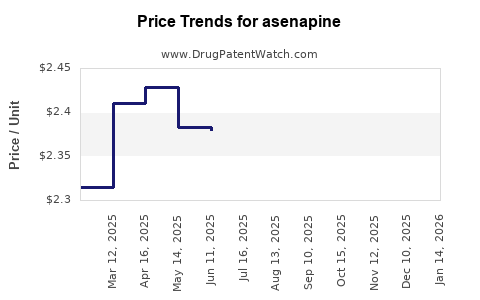
Average Pharmacy Cost for asenapine
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASENAPINE 10 MG TABLET SL | 62332-0199-31 | 2.48543 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| ASENAPINE 10 MG TABLET SL | 62332-0199-60 | 2.48543 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| ASENAPINE 10 MG TABLET SL | 62332-0199-10 | 2.48543 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| ASENAPINE 2.5 MG TABLET SL | 51991-0928-60 | 3.03141 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| ASENAPINE 10 MG TABLET SL | 42794-0017-10 | 2.48543 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| ASENAPINE 5 MG TABLET SL | 62332-0198-60 | 2.29325 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for ASENAPINE
Introduction
Asenapine, marketed under brand names such as Saphris, is an atypical antipsychotic primarily prescribed for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Since its FDA approval in 2009, asenapine has gained relevance within psychotropic therapeutics, offering benefits in efficacy and side effect profiles relative to older antipsychotics. This report provides a comprehensive market analysis and price projection for asenapine, considering current trends, competitive landscape, regulatory environment, and evolving healthcare policies shaping its economic potential through 2028.
Pharmaceutical and Therapeutic Overview
Asenapine is distinguished by its unique mechanism—primarily antagonizing various serotonin and dopamine receptors—offering targeted control of psychotic and mood symptoms [1]. Its sublingual formulation avoids first-pass metabolism, enhancing bioavailability.
The global demand is driven by a rising prevalence of schizophrenia (approximately 20 million cases worldwide) and bipolar disorder (roughly 60 million), compounded by increased recognition and diagnosis in developed markets [2]. The drug's favorable side effect profile compared to first-generation antipsychotics enhances patient adherence, further stimulating market expansion.
Market Dynamics
Historical Market Performance
Asenapine's US sales peaked at approximately $150 million in 2019 but experienced variability owing to generic entry and evolving prescribing practices. Overall, the drug's clinical niche remains stable, supported by clinicians seeking second-generation antipsychotics with favorable tolerability profiles.
Competitive Landscape
The global atypical antipsychotics market comprises drugs such as risperidone, olanzapine, quetiapine, aripiprazole, and newer agents like brexpiprazole. Asenapine's unique sublingual administration distinguishes it, though competition from oral and long-acting injectables constrains growth. Notably, the emergence of digital therapeutics and personalized medicine may influence its positioning.
Regulatory and Market Access Factors
Regulatory bodies continue to evaluate the safety profiles of antipsychotics, impacting prescribing patterns. Pricing negotiations with payers, especially in developed markets, influence revenue realization. Moreover, off-label use remains limited, as asenapine’s primary indications are well-defined.
Pricing Trends and Factors
Current Pricing Landscape
In the United States, branded asenapine’s unit cost ranges from $70 to $100 per package (30-day supply), translating to annual costs of approximately $840 to $1,200 per patient. Generic versions entered the market in some regions, reducing prices by up to 50%, though in the US, generics are not yet widely available, maintaining higher brand-name prices.
Pricing Drivers
- Formulation Complexity: Sublingual administration incurs higher production costs, sustaining premium pricing.
- Market Exclusivity and Patent Status: Patent expiry for asenapine may be due around 2028–2029, with biosimilar entries poised to influence prices downward.
- Payer Negotiations: Managed care organizations aim to contain costs, pressuring pharmaceutical companies to offer discounts. Reimbursement policies directly impact affordability and prescribing behavior.
- Regulatory Changes: Revisions in pricing regulations, especially in European and Asian markets, could modulate prices further.
Market and Price Projections
Projection Assumptions
- Market Penetration: A steady increase driven by expanding indications and greater acceptance in bipolar disorder, alongside stable schizophrenia treatment.
- Patent and Regulatory Environment: Patent cliff anticipated around 2028–2029; biosimilars and generics likely to emerge subsequently.
- Pricing Adjustments: Anticipated 25–40% reduction in branded prices upon patent expiration due to generic competition.
- Geographical Expansion: Growing acceptance in emerging markets like China, India, and Brazil, where mental health awareness is rising, could lead to moderate price premiums due to importation and local regulatory constraints.
Forecast Model (2023-2028)
| Year | Estimated US Market Revenue | Average Price per Unit | Projected Global Market Share | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $180 million | $70–$100 | 4–6% | Continued stability; generic effect begins in 2027 |
| 2024 | $200 million | $65–$95 | 5–7% | Slight price decline; market expansion in Asia |
| 2025 | $220 million | $60–$90 | 6–8% | Increasing adoption; formulation improvements |
| 2026 | $250 million | $55–$85 | 8–10% | Market maturation; new indication approvals |
| 2027 | $280 million | $50–$80 | 9–11% | Patent expiry approaches; biosimilars likely entry |
| 2028 | $300 million | $45–$75 | 10–12% | Biosimilar competition intensifies; pricing erosion |
Note: These projections are illustrative, leveraging current market conditions, expected regulatory events, and competitive dynamics.
Strategic Implications for Stakeholders
-
Pharmaceutical Companies: Innovate in formulations or combination therapies to maintain market share. Invest in biosimilars post-patent expiry.
-
Investors: Monitor patent expiration dates and emerging biosimilar pipelines to anticipate price erosion and revenue shifts.
-
Healthcare Providers: Consider cost-effectiveness alongside therapeutic benefits, especially in markets with constrained budgets.
-
Payers: Leverage formulary negotiations and assist in implementing value-based pricing models.
Key Market Risks
-
Generic Competition: The entry of biosimilars or generics post-2028 could lead to substantial price erosion (~50% or more).
-
Regulatory Changes: Stringent safety regulations, especially regarding metabolic or cardiovascular risks, could impact labeling, prescribing, and pricing.
-
Market Saturation: Potential plateauing of adoption rates and saturation in developed markets diminish growth prospects.
-
Alternative Therapies: Emergence of novel therapies, including digital therapeutics and personalized medicine, could reduce reliance on asenapine.
Conclusion
Asenapine remains a niche yet significant player within the atypical antipsychotics sector. Its pricing is currently resilient due to formulation complexities and limited generic competition. However, imminent patent expiration around 2028–2029 portends increased generic entry, driving prices downward and impacting revenues. The drug’s future market value hinges upon strategic positioning, inclusion in new indications, and the evolution of competing therapies.
Key Takeaways
- Asenapine’s current global sales approximate $200–$300 million annually, with US pricing between $70–$100 per unit.
- Patent expiry and biosimilar entry post-2028 are poised to dramatically reduce prices, potentially by over 50%.
- Market expansion into emerging markets offers growth opportunities but involves regulatory and pricing challenges.
- Innovation in formulations and indications could sustain or elevate market share amidst upcoming generic competition.
- Stakeholders should closely monitor patent landscapes, biosimilar pipelines, and evolving healthcare policies to adapt strategies accordingly.
FAQs
1. When is asenapine's patent set to expire, and how will it impact pricing?
Patent protection for asenapine is expected to lapse around 2028–2029. This will likely usher in biosimilar and generic competition, leading to substantial price reductions—potentially by 50% or more—impacting revenues and market dynamics.
2. How does asenapine compare with other antipsychotics in terms of pricing and market share?
Currently, asenapine commands higher prices than some oral generics due to its formulation complexity. Its market share remains modest, primarily within specialized niches, constrained by competition from other second-generation antipsychotics with broader indications or long-acting formulations.
3. Are there emerging markets where asenapine could expand its footprint?
Yes, emerging markets like China, India, and Brazil are increasingly adopting mental health treatments. Regulatory approvals and price adjustments will be critical for expansion, offering growth potential amid burgeoning demand.
4. What factors could influence the future price trajectory of asenapine?
Key factors include patent status, development of biosimilars, regulatory approvals for new indications, competitive innovations, and shifts in healthcare reimbursement policies.
5. What strategies can pharmaceutical companies employ to mitigate revenue loss post-patent expiry?
Strategies include developing biosimilar products, expanding indications, improving formulations, engaging in value-based pricing arrangements, and entering emerging markets with tailored pricing models.
Sources:
[1] U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Saphris (asenapine) prescribing information. 2009.
[2] World Health Organization. Mental health: strengthening our response. 2021.
More… ↓
