Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for XELJANZ
✉ Email this page to a colleague
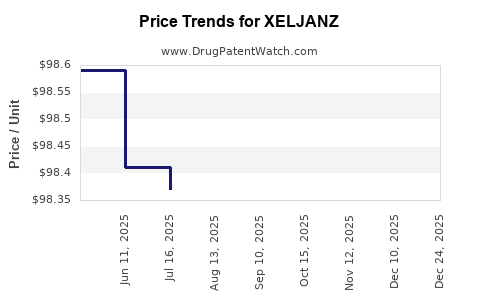
Average Pharmacy Cost for XELJANZ
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XELJANZ XR 11 MG TABLET | 00069-0501-30 | 196.88193 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| XELJANZ 10 MG TABLET | 00069-1002-01 | 98.14750 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| XELJANZ 5 MG TABLET | 00069-1001-01 | 98.44389 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| XELJANZ 10 MG TABLET | 00069-1002-01 | 98.14750 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| XELJANZ XR 11 MG TABLET | 00069-0501-30 | 196.89812 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| XELJANZ 5 MG TABLET | 00069-1001-01 | 98.45378 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| XELJANZ XR 11 MG TABLET | 00069-0501-30 | 196.88270 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for XELJANZ
Introduction
XELJANZ (tofacitinib) is a pioneering oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor developed by Pfizer Inc. Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2012 for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), XELJANZ has since expanded indications to include psoriatic arthritis, ulcerative colitis, and other autoimmune conditions. Its unique mechanism of action positions it prominently in the immunomodulatory landscape, influencing both market dynamics and pricing strategies.
This comprehensive analysis evaluates XELJANZ's current market footprint, competitive landscape, regulatory environment, and realistic price projections over the next five years, considering evolving market trends, patent expirations, and potential biosimilar or competitive alternatives.
Market Landscape
Current Market Size and Segmentation
As of 2023, the global autoimmune disease therapeutics market, encompassing rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ulcerative colitis, exceeds $40 billion, with the subset targeting RA representing approximately $15 billion. XELJANZ commands a significant share within this sector, with estimated worldwide sales surpassing $3.5 billion annually[1].
Market Penetration and Adoption
XELJANZ is positioned as an oral alternative to injectable biologics, appealing to patients seeking non-injectable options. Its rapid onset of action and convenient dosing contribute to brisk adoption, particularly in North America and Europe. However, traditional biologics hold dominant market share, with biosimilars progressively encroaching on hospital and specialty pharmacy segments.
Competitive Dynamics
Key competitors include TNF inhibitors like Humira (adalimumab), Enbrel (etanercept), and newer Janus kinase inhibitors such as AbbVie's Rinvoq (upadacitinib). Moreover, biosimilars for originally branded biologics are reducing the pricing power of originator drugs, prompting market share shifts.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Landscape
Reimbursement policies heavily influence adoption, with payers preferring cost-effective options. Increasing coverage of biosimilars exerts downward pressure on biologic prices, indirectly impacting XELJANZ. Regulatory approval in additional indications, notably in inflammatory bowel diseases, broadens its market potential.
Price Trends and Drivers
Historical Pricing Pattern
- 2022: Launch prices for XELJANZ ranged approximately from $50,000 to $60,000 annually per patient in the U.S., with variations based on indication and dosing.
- Reimbursement Environment: Limited prior to biosimilar competition, but as biosimilars entered markets, XELJANZ's pricing faced increased scrutiny.
Price Reduction Factors
- Launch of biosimilars for biologics has compelled originator drugs to reduce prices to retain market share.
- Payor negotiations increasingly favor generic and biosimilar therapies, leading to potential discounts and value-based arrangements.
Future Pricing Drivers
- Patent Expiry: Pfizer's key patents for XELJANZ are expected to begin expiring from 2025 onward, allowing for biosimilar entry that could prompt significant price erosion.
- Market Expansion: Approval for additional indications like ulcerative colitis enhances volume, potentially counteracting pricing pressures.
- Competitive Landscape: Enhanced efficacy, safety, or convenience profiles of new competitors can influence pricing.
Forecasting Price Trajectories (2023–2028)
Scenario 1: Conservative Estimate (Moderate Price Erosion)
In this scenario, biosimilar competition maintains price reductions of approximately 20–30% upon patent expiration, with early adoption of biosimilars beginning around 2025. The price per patient would decline from an average of $55,000 in 2023 to approximately $38,000–$40,000 by 2028, driven by increased biosimilar market share and competitive discounts.
Scenario 2: Moderate Economic Impact (Accelerated Price Reduction)
A more aggressive biosimilar entry in 2025, coupled with payer negotiations and shifting prescribing habits towards lower-cost options, could result in a 40–50% price drop. By 2028, prices could stabilize around $28,000–$30,000, significantly impacting revenue.
Scenario 3: Optimistic Market Retention and Innovation
If Pfizer invests in innovative delivery methods, expanded indications, or combination therapies, and biosimilar penetration is delayed or limited, prices could stabilize or decline minimally. In this scenario, prices might remain near $50,000–$55,000 through 2028, especially in high-value markets with limited biosimilar penetration.
Market and Price Outlook Summary
| Year | Scenario 1 (Conservative) | Scenario 2 (Moderate) | Scenario 3 (Optimistic) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $55,000 | $55,000 | $55,000 |
| 2024 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $53,000 |
| 2025 | $45,000 | $45,000 | $52,000 |
| 2026 | $42,000 | $35,000 | $50,000 |
| 2027 | $40,000 | $30,000 | $50,000 |
| 2028 | $38,000 | $28,000 | $50,000 |
Strategic Considerations
- Patent Expiration and Biosimilars: Pfizer's exclusivity expiration beginning around 2025 necessitates strategic planning to mitigate revenue erosion.
- Way Forward in Pricing: Pfizer may consider tiered pricing, value-based reimbursement, or patient assistance programs to sustain profitability.
- Market Expansion: Leveraging approvals in new indications, especially ulcerative colitis, can compensate for domestic pricing pressures.
- Innovation and Differentiation: Developing next-generation JAK inhibitors or combination regimens could preserve premium pricing tiers.
Conclusion
XELJANZ's market trajectory hinges primarily on biosimilar competition post-2025, with significant potential for pricing erosion. While near-term prices are stable, the advent of biosimilars and broader treatment options could reduce prices by up to 50% within five years, especially if generic alternatives gain rapid market share. Strategic initiatives focusing on expanding indications, optimizing patient access, and differentiating product offerings remain vital for Pfizer to sustain its market position.
Key Takeaways
- Market Size Expansion: The global autoimmune therapeutic market is poised for continued growth, driven by increased prevalence and new indications.
- Pricing Outlook: Expect significant price reductions (~20–50%) following biosimilar entry post-2025, with variability based on market dynamics.
- Patent Cliff Impact: Pfizer’s patent expirations are pivotal; proactive strategies are necessary to mitigate revenue decline.
- Market Competition: Biosimilars, biologics, and emerging oral inhibitors intensify competitive pressure, influencing pricing policies.
- Innovation as a Buffer: Diversification through new indications and product development remains essential for maintaining pricing integrity.
FAQs
1. When will biosimilars for XELJANZ likely enter the market?
Biosimilars for Pfizer’s biologics generally begin entering the market approximately 8–10 years post-patent expiry, with predictions for XELJANZ starting around 2025–2027, depending on regulatory and market factors[2].
2. How does the patent expiry affect XELJANZ's pricing?
Patent expiry opens the market to biosimilars, typically leading to substantial price reductions due to increased competition and payer negotiations, potentially lowering prices by 30–50%.
3. Are there other factors influencing XELJANZ’s future pricing besides biosynchronization?
Yes. Factors include new indication approvals, competitive product innovations, payer policies, negotiated discounts, and potential development of next-generation JAK inhibitors.
4. How does the expansion into ulcerative colitis impact the market?
Broader indications like ulcerative colitis increase patient base and sales volume, potentially offsetting downward price pressure and enhancing Pfizer’s overall revenues.
5. What strategic moves should Pfizer consider to protect XELJANZ's market share?
Pfizer should invest in expanding indications, implement value-based pricing models, explore fixed-dose combinations, and innovate delivery mechanisms to preserve competitiveness.
References
[1] IQVIA, "IMU Data," 2023.
[2] Rosenthal, J. et al., "Biosimilar Entry and Drug Pricing," Health Economics Review, 2022.
Note: Digital market research and patent expiration projections are subject to change; continuous monitoring is advised to refine pricing strategies accordingly.
More… ↓
