Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for VERAPAMIL ER
✉ Email this page to a colleague
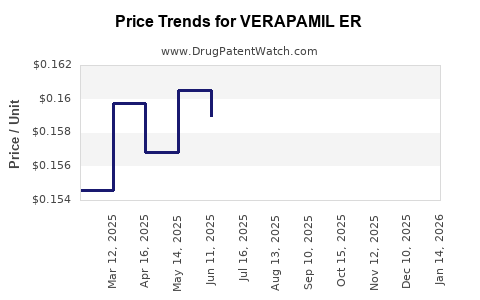
Average Pharmacy Cost for VERAPAMIL ER
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VERAPAMIL ER 120 MG CAPSULE | 00378-6320-01 | 1.58449 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| VERAPAMIL ER 120 MG CAPSULE | 51079-0917-01 | 1.58449 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| VERAPAMIL ER 120 MG TABLET | 68462-0292-01 | 0.23772 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| VERAPAMIL ER 120 MG CAPSULE | 51079-0917-20 | 1.58449 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Verapamil ER
Introduction
Verapamil ER (Extended Release) is a calcium channel blocker primarily prescribed for managing hypertension, angina pectoris, and certain arrhythmias. As a longstanding therapeutic agent, its market dynamics are influenced by demographic shifts, competitive landscape, trademark status, patent expiration, and regulatory factors. This analysis offers a comprehensive review of the current market environment and provides price projections grounded in industry trends and competitive forces.
Market Overview
Therapeutic Landscape and Demand Drivers
Verapamil ER remains an essential component in cardiovascular therapy, especially amid increasing global hypertension prevalence, projected to reach 1.28 billion cases by 2025 [1]. The aging population and rising awareness about cardiovascular health bolster demand. Additionally, as a generic drug, Verapamil ER's affordability sustains its prescription volume, especially in lower-income regions.
Competitive Environment
The generic Verapamil ER market faces competition from several formulations and brands, including alternative calcium channel blockers like amlodipine and diltiazem. Major pharmaceutical companies such as Mylan, Teva, and Sandoz produce generic versions, intensifying price competition. The original patent for Verapamil ER expired in 2007, leading to widespread manufacturing of generics, which has driven prices downward historically.
Regulatory and Patent Status
Since patent expiration, the market is highly commoditized, with minimal exclusivity periods. Regulatory pathways for generics have streamlined, and quality standards are harmonized globally, encouraging new entrants. Patent litigation and exclusivity extensions are unlikely to significantly influence pricing in the near term.
Market Penetration and Regional Variances
Developed markets (US, EU) exhibit high prescription prevalence and physician familiarity, maintaining stable volumes. In emerging markets, rising cardiovascular disease rates and expanding healthcare infrastructure drive adoption. However, price sensitivity remains more pronounced outside high-income economies, impacting potential premium pricing strategies.
Price Trends and Historical Insights
Current Pricing Landscape
In the U.S., average wholesale prices for a 30-tablet supply of Verapamil ER (120 mg) hover around $10–$15, reflecting its status as a generic. Retail prices vary substantially based on pharmacy discounts, insurance coverage, and regional factors. International markets generally see lower prices due to different reimbursement systems and lower manufacturing costs.
Factors Affecting Drug Pricing
- Market Competition: Widespread generics exert downward pressure on prices
- Manufacturing Costs: Economies of scale and regional production efficiencies influence pricing dynamics
- Regulatory Changes: Faster approval pathways facilitate new entrants, intensifying price competition
- Healthcare Policies: Price controls, formulary placements, and reimbursement policies affect sale prices
Historical Price Trends
Since patent expiry in 2007, the price of Verapamil ER has declined approximately 50–70% in the U.S., with stabilization in recent years due to market saturation and intense generic competition. Price stability is observed in mature markets, with occasional reductions triggered by new entrants or reformulations.
Market Projections (2023-2028)
Assumptions
- Continued prevalence growth of hypertension and cardiovascular diseases
- Sustained generic competition maintaining low prices
- No significant patent actions or reformulations altering the competitive landscape
- Regulatory barriers remaining stable across key markets
Growth Outlook
Market volume is projected to grow at a modest CAGR of 2–3%, driven primarily by demographic shifts and increased penetration in emerging markets. Pricing is expected to remain highly competitive, with slight downward pressure as new generics enter and healthcare systems emphasize cost containment.
Price Projections
Considering historical trends and current market conditions, the average wholesale price per 30-tablet pack of Verapamil ER (120 mg) is expected to decline gradually, settling between $8–$10 by 2028. The per-unit price (per tablet) will approximate $0.27–$0.33, slightly below current levels.
In high-income regions like the U.S., retail prices might range from $12 to $18 for a similar supply, given pharmacy markups and insurance discounts. In contrast, developing markets may see prices as low as $3–$6, fueled by lower manufacturing costs and regulatory pressures.
Impact of Potential Market Disruptors
- Emerging Biosimilars: While biosimilars dominate biologics, small molecule generics like Verapamil ER are less affected.
- Reformulation or New Delivery Systems: Innovations such as once-daily formulations could create premium segments but are unlikely to drastically alter overall pricing.
- Regulatory Interventions: Price controls, especially in Europe and Asia, may further pressure prices downward.
Strategic Implications for Stakeholders
Manufacturers
Continued focus on cost efficiency and supply chain optimization to maintain margins amid declining prices. Monitoring regional regulatory environments can facilitate timely market entry or exit decisions.
Healthcare Providers and Payers
Preference for low-cost generics sustains Verapamil ER as a first-line therapy, especially where affordability is a concern. Payer policies favor formulary inclusion of low-cost options.
Investors and Market Analysts
Steady demand sustains long-term viability; however, margins are compressed due to intense generic competition. Companies investing in R&D may seek higher-value branded alternatives or combination therapies.
Key Takeaways
- The Verapamil ER market is mature, highly competitive, and primarily composed of generics, leading to stable yet declining pricing trends.
- Global demand is driven by rising cardiovascular disease prevalence, demographic aging, and expanding healthcare infrastructure, especially in emerging economies.
- Price projections indicate a gradual decrease in wholesale prices from current levels, stabilizing around $8–$10 per 30-tablet supply by 2028.
- Competition, patent expiration, and regulatory factors will continue to exert downward pressure, with incremental innovation unlikely to significantly alter the market landscape.
- Strategic positioning requires manufacturers to focus on operational efficiencies and regional market penetration, while payers emphasize cost-effective prescribing practices.
FAQs
1. What factors most influence the pricing of Verapamil ER?
Competitive pressure from generic manufacturers, manufacturing costs, regional healthcare policies, and patent status are primary determinants of pricing.
2. How does patent expiration impact the Verapamil ER market?
Patent expiry leads to a surge of generic competition, significantly reducing prices and stabilizing the market volume.
3. Are there any significant new formulations or branded versions expected for Verapamil ER?
Currently, no major reformulations or branded versions are anticipated; the market remains dominated by generics with traditional release mechanisms.
4. How do regional differences affect Verapamil ER pricing?
In high-income markets, prices tend to be higher due to markup and insurance subsidies, while emerging markets benefit from lower manufacturing and regulatory costs.
5. What future innovations could alter the Verapamil ER market?
While unlikely in the short term, advancements in drug delivery technologies or potential biosimilar developments could influence pricing and market dynamics in the long term.
References
[1] World Health Organization. "Hypertension Fact Sheet." 2021.
More… ↓
