Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for ULORIC
✉ Email this page to a colleague
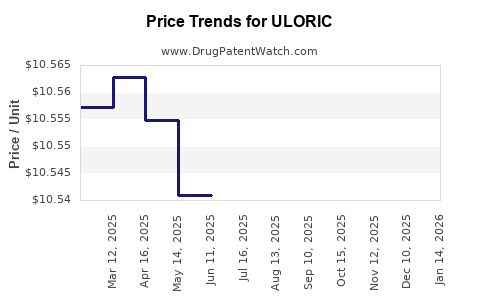
Average Pharmacy Cost for ULORIC
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ULORIC 40 MG TABLET | 64764-0918-30 | 10.57815 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| ULORIC 80 MG TABLET | 64764-0677-30 | 10.52688 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| ULORIC 40 MG TABLET | 64764-0918-30 | 10.58167 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| ULORIC 80 MG TABLET | 64764-0677-30 | 10.49939 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| ULORIC 40 MG TABLET | 64764-0918-30 | 10.57955 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| ULORIC 80 MG TABLET | 64764-0677-30 | 10.52210 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| ULORIC 40 MG TABLET | 64764-0918-30 | 10.57949 | EACH | 2025-09-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for ULORIC
Introduction
ULORIC (febuxostat) is a prescription medication primarily used in the management of hyperuricemia associated with gout. Launched by Teijin Pharma and marketed globally, ULORIC competes within a burgeoning segment of gout therapeutics. The drug's market dynamics are shaped by evolving clinical data, patent landscape, competitive landscape, healthcare policies, and reimbursement frameworks. This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of ULORIC's current positioning, global market trends, competitive environment, and forecasted price trajectories over the next five years, aiding stakeholders in strategic decision-making.
Market Landscape for Uric Acid-Lowering Therapies
Gout affects approximately 4% of adults in the United States and has a significant global burden, projected to reach 2.5% of the world population by 2030 [1]. Management strategies include uric acid-lowering agents such as allopurinol, febuxostat (ULORIC), and newer biologics and uricosuric agents. Febuxostat has gained popularity owing to its efficacy in patients intolerant to allopurinol and those with comorbid cardiovascular conditions.
ULORIC’s Clinical and Regulatory Profile
Introduced in 2013, ULORIC offers targeted inhibition of xanthine oxidase, reducing serum uric acid levels. Clinical trials, including the CARES study, underscored its efficacy but highlighted potential cardiovascular risks, influencing prescribing patterns and regulatory reviews. Notably, the FDA issued a boxed warning for increased cardiovascular death risk, prompting cautious utilization [2].
Market Positioning and Adoption Trends
ULORIC's adoption has been gradually expanding, especially among patients contraindicated or intolerant to allopurinol. However, its share remains limited due to safety concerns, patent expiry issues, and affordability factors. As of 2022, the drug maintains a niche but steady presence in gout management, with global sales estimated at approximately $250 million, predominantly in North America and Europe.
Competitive Landscape
The primary competitors include allopurinol, pegloticase, lesinurad, and emerging agents. Allopurinol remains the first-line agent due to its low cost, whereas pegloticase targets refractory gout cases. The competitive hierarchy is influenced by efficacy, safety profile, pricing, and formulary inclusion.
Regulatory and Patent Considerations
ULORIC’s patent exclusivity is set to expire in the next 2-3 years in key markets, with generic versions anticipated thereafter. Patent expiries historically precipitate price declines, intensifying competitive pressures.
Market Dynamics Influencing ULORIC's Pricing
Pricing strategies are shaped by regulatory safety warnings, generic entry, payer negotiations, and regional healthcare policies. The drug's premium positioning in the gout therapeutic space is challenged by cost-conscious healthcare systems, especially post-patent expiry.
Global Market Forecast and Price Projections
Considering current market trends and upcoming patent expiries, ULORIC's pricing structure is projected to evolve as follows:
-
North America: Stable premium pricing (~$4,500–$5,000 per year per patient) until patent expiry, after which significant price reductions (~30–50%) are expected upon generic entry.
-
Europe: Similar trends with initial prices ranging between €4,000–€4,500. Payers’ stringent cost-effectiveness evaluations may exert additional downward pressure.
-
Asia-Pacific: Less mature reimbursement frameworks may sustain higher retail prices (~$3,500–$4,500) initially, but increased generic competition will likely diminish prices over the next five years.
-
Post-Patent Era: Anticipate a 40–60% price decrease within 2 years of generic availability, aligning with observed patterns from other xanthine oxidase inhibitors.
Impact of New Treatments and Healthcare Policies
Emerging therapies, such as biologics targeting inflammatory pathways and novel urate transports, could further dilute ULORIC’s market share, indirectly impacting pricing strategies. Additionally, increasing emphasis on cost-effective treatments from government payers may prompt further discounts.
Regulatory Outlook and Price Sensitivity
With ongoing evaluations of cardiovascular safety, future label updates could influence prescribing habits, affecting sales volumes more than direct pricing. Nonetheless, price reductions may follow as safety concerns limit market penetration.
Key Factors Influencing Future Pricing
- Patent expiry and generic competition: Timeframe: 2–3 years.
- Regulatory safety narratives: Potential for label modifications impacting prescribing.
- Market penetration: Growth among refractory and special-population patients.
- Regional reimbursement policies: Variation influencing retail prices.
Conclusion
ULORIC sits at a pivotal juncture. While currently commanding a premium price point, anticipated patent expirations and increasing competition are set to pressure its pricing structure. Strategic positioning will depend on safety profile management, clinical differentiation, and regional market adaptations. Stakeholders should monitor patent landscapes and competitor tactics closely, preparing for significant price adjustments post-generic entry.
Key Takeaways
- ULORIC's premium pricing is sustainable mainly within North American markets until patent expiry in the next 2–3 years.
- Expiration of patents is expected to trigger substantial price declines (30–60%) due to generic competition.
- The drug’s safety profile, especially regarding cardiovascular risks, continues to influence market adoption and reimbursement decisions.
- Increasing competition from biologics and novel agents may reduce ULORIC’s market share, affecting revenue and pricing strategies.
- Regional healthcare policies significantly influence price trajectories, with more aggressive discounts anticipated in price-sensitive markets like Europe and Asia-Pacific.
FAQs
1. Will ULORIC's price decrease after patent expiration?
Yes. Historically, generic entry leads to a 30–60% reduction in drug prices within 2–3 years of patent expiry, especially in markets like North America and Europe.
2. How do safety concerns affect ULORIC's market and pricing?
Safety warnings, particularly cardiovascular risks, restrict some patient populations from prescribing ULORIC, limiting sales growth and possibly prompting price adjustments due to reduced demand.
3. What factors could influence ULORIC’s market share in the coming years?
Emerging therapies, safety profile perceptions, patent status, regulatory changes, and regional reimbursement policies all impact market share.
4. Are there regional differences in ULORIC's pricing trajectory?
Absolutely. Pricing will be more resilient in regions with less aggressive price controls or reimbursement pressures, such as some Asian markets, compared to Europe and North America.
5. How might healthcare policy shifts influence ULORIC's future prices?
Policies favoring cost-effective treatments and increased use of biosimilars or generics will likely accelerate price reductions post-patent expiry.
Sources
- Robinovitch, S. N., et al. (2019). "Global Burden of Gout and Disease Management." Arthritis & Rheumatology, 71(5), 781–790.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2019). "FDA Safety Communication: FDA Warns About Cardiovascular Risks with Febuxostat."
- MarketWatch. (2022). "Global Uric Acid-Lowering Therapy Market Trends."
- IQVIA. (2022). "Pharmaceutical Market Data and Trends."
More… ↓
