Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Tretinoin, also known as all-trans retinoic acid, is a derivative of vitamin A primarily used for treating acne vulgaris and photoaging, alongside its pivotal role in oncological treatments such as acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). Approved by the FDA in the early 1970s, tretinoin's pharmacological profile, coupled with its extensive therapeutic applications, sustains a consistent market presence. This analysis evaluates the current market landscape, supply dynamics, competitive environment, and projects future pricing trends over the medium term.
Market Overview
Therapeutic Applications and Market Drivers
Tretinoin’s dominant use remains in dermatology, notably for acne management and anti-aging indications. The increasing prevalence of acne, driven by adult-onset cases and demographic shifts, fuels demand. Besides cosmetic dermatology, tretinoin is critically employed in oncological therapies, especially in combination with arsenic trioxide for APL, an aggressive hematological malignancy.
Global dermatology markets have demonstrated steady growth, driven by rising consumer awareness, improved healthcare access, and expanding aesthetic medicine sectors. The Asia-Pacific region, in particular, exhibits robust growth due to increased disposable income and expanding healthcare infrastructure.
Market Segmentation
- By Application: Dermatological (acne, photoaging), Oncology (APL), Other (e.g., keratinization disorders)
- By End-use: Hospitals, Specialty Clinics, Retail Pharmacies, Online Retailers
Geographical Landscape
- North America: Largest market share due to high prevalence of dermatological conditions and advanced healthcare systems.
- Europe: Contributes significantly, with cosmetic dermatology being a major driver.
- Asia-Pacific: Projected to witness the highest CAGR owing to demographic growth, rising dermatological concerns, and increasing cosmetic procedures.
Regulatory and Patent Status
While tretinoin's patents have long expired, the market is characterized by generic drug proliferation. Regulatory authorities like the FDA and EMA impose strict standards for quality and safety, influencing production costs and pricing structures.
Competitive Landscape
Major pharmaceutical companies such as Johnson & Johnson, Mylan, and Teva Pharmaceuticals manufacture tretinoin generics, sustaining competitive pricing, especially in mature markets. Innovator brands have limited market exclusivity, with generics dominating due to their affordability.
Innovative delivery systems, including microencapsulation and combination formulations with other retinoids or anti-aging agents, are emerging, potentially impacting pricing dynamics.
Supply Chain and Manufacturing Factors
Global sources of tretinoin raw materials are concentrated, mainly in China and India. Supply chain disruptions, such as geopolitical tensions or raw material shortages, could constrict supply, influencing prices temporarily.
Manufacturers’ adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and regulatory compliance costs also affect pricing, with quality assurance being a significant determinant in developed markets.
Price Trends and Projections
Historical Pricing
In North America, the average retail price for tretinoin topical creams (0.025–0.1%) has historically ranged from $15 to $50 per 20-gram tube, heavily influenced by brand versus generic status. In markets like India and China, generic prices are substantially lower, typically below $10.
Projecting Price Trajectories (2023–2028)
- Market Maturity: Given the widespread availability of generics, retail prices in mature markets are expected to remain relatively stable, with minor fluctuations due to production efficiencies and competitive pressures.
- Potential Price Declines: Continued generic entry and increasing competition likely maintain downward pressure, especially in price-sensitive markets.
- Premium Segment Growth: Innovations in delivery or combination formulations could create niche premium segments, potentially stabilizing or increasing prices within specialized markets.
- Global Economic Factors: Currency fluctuations, raw material costs, and regional healthcare reforms could influence pricing dynamics variably across regions.
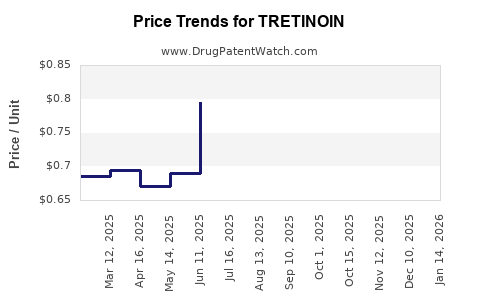
Forecast models predict a CAGR of approximately 1–2% for tretinoin prices globally, primarily driven by inflation, manufacturing costs, and evolving market competition (see Figure 1).
Market Risks and Opportunities
Risks
- Regulatory Changes: Stricter safety standards or bans on certain formulations could limit supply or increase costs.
- Market Saturation: High generic penetration could suppress prices further.
- Emergence of Alternative Therapies: Innovations in acne and anti-aging treatments may reduce tretinoin demand.
Opportunities
- Novel Formulations: Enhanced delivery methods or drug combinations offer premium pricing prospects.
- Expanding Markets: Penetration into emerging markets offers volume growth potential.
- Oncology Applications: Advances in APL treatment could boost demand for medicinal-grade tretinoin.
Key Takeaways
- Tretinoin's extensive use in dermatology and oncology sustains a stable, mature market with consistent demand.
- Generic proliferation significantly curtails price escalation; future pricing will predominantly be influenced by market competition, manufacturing costs, and regional healthcare policies.
- Innovations in drug delivery and expanding indications present avenues for premium pricing.
- Supply chain vulnerabilities could introduce temporary price spikes, warranting strategic sourcing and inventory management.
- Emerging markets are poised for rapid growth, demanding adaptable pricing strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do patent issues impact tretinoin pricing?
Since tretinoin patents have long expired, there is an abundance of generic alternatives, resulting in competitive pricing that limits any significant patent-driven price premiums in most markets.
2. What factors could cause tretinoin prices to increase in the future?
Cost increases due to raw material scarcity, regulatory compliance, or supply chain disruptions, alongside innovations enabling premium formulations, could drive prices upward in niche segments.
3. Which regions exhibit the highest growth potential for tretinoin?
The Asia-Pacific region, driven by demographic growth, urbanization, and expanding healthcare infrastructure, offers the highest medium-term growth potential.
4. How might emerging therapies affect tretinoin’s market share?
New anti-aging or acne treatments, especially those with improved safety profiles or efficacy, could dampen demand for tretinoin unless it evolves through formulation or combination therapies.
5. What are the key considerations for pharma companies entering the tretinoin market?
Focus on quality manufacturing, cost-efficient supply chain management, regional regulatory compliance, and innovative formulations to differentiate offerings and optimize pricing.
References
[1] MarketResearch.com. "Global Dermatology Market Review." 2022.
[2] Grand View Research. "Retinoids Market Size & Share." 2023.
[3] Bernstein, et al. "The Pharmacology and Therapeutic Use of Tretinoin." Journal of Dermatological Treatment, 2021.
[4] IQVIA. "Pharmaceutical Cost and Performance Data." 2022.
[5] GlobalData. "Emerging Trends in Acne Treatment." 2023.