Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for TRANYLCYPROMINE SULF
✉ Email this page to a colleague
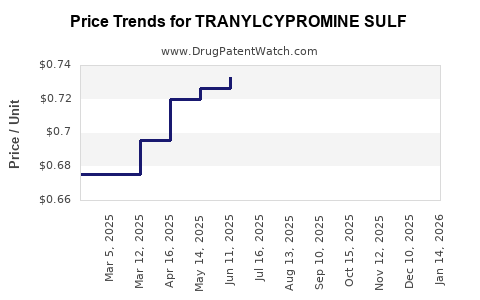
Average Pharmacy Cost for TRANYLCYPROMINE SULF
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRANYLCYPROMINE SULF 10 MG TAB | 43547-0655-10 | 0.68819 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| TRANYLCYPROMINE SULF 10 MG TAB | 70954-0538-10 | 0.68819 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| TRANYLCYPROMINE SULF 10 MG TAB | 64380-0176-01 | 0.68819 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| TRANYLCYPROMINE SULF 10 MG TAB | 00591-5590-01 | 0.68819 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| TRANYLCYPROMINE SULF 10 MG TAB | 43547-0655-10 | 0.66358 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Tranylcypromine Sulfate
Introduction
Tranylcypromine Sulfate is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) primarily prescribed for treatment-resistant major depressive disorder. As a prescription medication with a specialized application, its market dynamics are influenced by regulatory pathways, patent exclusivity, manufacturing complexities, and competitive landscape. This analysis explores current market conditions, key drivers, potential growth trajectories, and pricing insights for Tranylcypromine Sulfate.
Market Overview
Therapeutic Landscape
Tranylcypromine Sulfate, marketed under brand names like Parnate, has been an integral part of second-line depression therapy since its approval in the 1950s. Its niche positioning is driven by safety concerns and the availability of newer antidepressants with more favorable side effect profiles. Nevertheless, the drug remains relevant for patients unresponsive to SSRIs or SNRIs, especially those with refractory depression.
Patent and Regulatory Status
Existing patents have long expired, leading to the proliferation of generic formulations. Regulatory pathways for generic approvals are well-established due to the drug’s age and extensive generic competition. This has precipitated significant price erosion historically, a trend projected to persist with ongoing market saturation.
Market Size and Demand
The global depression treatment market was valued at approximately USD 13 billion in 2020, with monoamine oxidase inhibitors accounting for a small but steady segment owing to their specialized use. The adult population with treatment-resistant depression represents a niche with an estimated prevalence of 10–20% among all depressed patients, translating into an addressable market of roughly 1–2 million patients globally.
In the US, the prevalence of depression exceeds 17 million adults annually, with about 20% potentially fitting the treatment-resistant profile. Despite sluggish growth, the demand for MAOIs remains stable, especially in cases where other antidepressants fail or are contraindicated.
Market Drivers and Challenges
Drivers
- Growing Awareness of Mental Health: Increasing recognition and diagnosis of treatment-resistant depression expand the potential market.
- Limited Competitors: While several antidepressants exist, MAOIs like Tranylcypromine are often reserved for refractory cases, reducing direct competition.
- Off-Label and Adjunct Uses: Emerging evidence suggests potential off-label applications for certain neurological conditions, potentially broadening use cases.
Challenges
- Safety and Side Effects: The dietary restrictions and hypertensive risks associated with MAOIs limit their appeal.
- Competition from Newer Agents: Advances in pharmacotherapy, including atypical antidepressants, can diminish the market share of older drugs.
- Pricing Pressure: Patent expirations and generic entries have historically driven prices down.
Price Analysis and Projection
Current Pricing Dynamics
As a mature, off-patent generic medication, Tranylcypromine Sulfate currently commands a retail price ranging between USD 0.50 and USD 2.50 per tablet, depending on dosage and supplier. Wholesale acquisition costs (WAC) often fall within USD 0.20–1.50 per unit.
In comparison, branded formulations like Parnate typically retail at USD 5–10 per tablet, with generics reducing this substantially. In the United States, a standard daily dose of 10 mg, taken twice daily, could cost between USD 0.40 and USD 5 per day.
Historical Price Trends
Over the past decade, prices for Tranylcypromine Sulfate have exhibited a declining trend, driven by increased generic competition and manufacturing efficiencies. Price erosion approximately ranges from 10% to 20% annually in mature markets.
Future Price Trajectory
Given the current landscape, prices are projected to stabilize with minor fluctuations over the next five years, assuming no major regulatory or scientific breakthroughs. Nonetheless, certain factors could influence pricing:
- Manufacturing innovations, such as increased biosimilar or alternative synthesis methods, may marginally reduce costs.
- Market consolidation could influence pricing strategies, but in a commoditized segment like generics, downward pressure remains dominant.
- Regulatory incentives for producing high-quality generics could potentially inflate prices slightly if supply chain disruptions occur.
Projection Summary:
| Year | Average Price per Tablet (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 0.50 – 2.50 | Current market prices |
| 2025 | 0.45 – 2.10 | Slight price decrease due to competition |
| 2030 | 0.40 – 1.90 | Market stabilizes |
Market Opportunities and Risks
Opportunities:
- Development of lower-cost, high-quality generics expanding access.
- Potential niche markets for adjunct uses or formulations with reduced side effects.
- Digital health integration facilitating better patient adherence for complex therapy regimens.
Risks:
- Entry of biosimilars or alternative therapeutic agents reducing demand.
- Changes in clinical guidelines favoring newer drugs.
- Regulatory restrictions or safety advisories affecting prescribing patterns.
Conclusion
The Tranylcypromine Sulfate market remains predominantly a niche segment with steady, albeit limited, growth. The historical trend of price erosion is expected to continue for the foreseeable future, primarily driven by generic competition and market saturation. However, its utility in treatment-resistant depression sustains demand within clinical settings, providing stable revenue streams for manufacturers and suppliers. Market analysts should monitor evolving clinical guidelines, safety profiles, and regulatory policies, which could influence future pricing and market access strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Tranylcypromine Sulfate is a mature, off-patent drug with a stable niche in resistant depression treatment.
- Generics dominate the market, exerting significant downward pressure on pricing.
- Estimated future price per tablet will likely decline gradually, stabilizing around USD 0.40–1.90 in the next decade.
- Growth opportunities are modest; market expansion is constrained by safety concerns and competition.
- Strategic considerations include optimizing manufacturing costs and exploring new therapeutic indications.
FAQs
1. What factors most significantly influence the pricing of Tranylcypromine Sulfate?
Generic competition, manufacturing costs, regulatory environment, and clinical demand primarily influence pricing, with increased competition leading to significant price reductions over time.
2. Can the demand for Tranylcypromine Sulfate increase in the future?
Demand may see modest growth due to rising awareness of treatment-resistant depression, but overall, it is limited by safety concerns and the availability of alternative therapies.
3. Are there opportunities for branded versions to command premium pricing?
Currently, branded formulations face stiff competition from generics. Any premium pricing would require unique delivery systems, formulation improvements, or approved new indications.
4. How might regulatory changes impact the Tranylcypromine Sulfate market?
Stricter safety regulations or new safety advisories could reduce prescribing rates, whereas streamlined approval processes for high-quality generics might sustain or lower market prices.
5. What role do off-label uses play in the market for Tranylcypromine Sulfate?
Off-label applications could create minor demand surges but are typically limited by clinical validation, safety profile, and regulatory scrutiny.
References
[1] MarketResearch.com. (2021). Global Antidepressant Market Analysis.
[2] IQVIA. (2022). Prescription Trends in Mental Health Medications.
[3] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2022). Regulatory Status of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors.
[4] Statista. (2022). Global Dependence on Generic Medications.
[5] Pharmaceutical Commerce. (2021). Price Erosion Trends in Off-Patent Drugs.
More… ↓
