Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for THYROID
✉ Email this page to a colleague
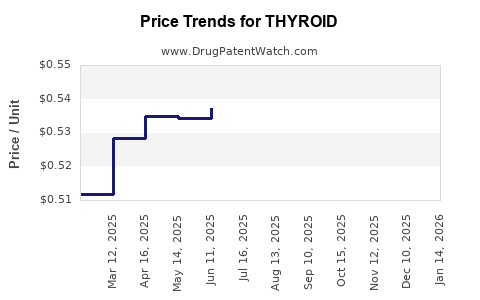
Average Pharmacy Cost for THYROID
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| THYROID 15 MG TABLET | 62559-0740-01 | 0.52851 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| THYROID 120 MG TABLET | 69680-0169-00 | 1.21847 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| THYROID 90 MG TABLET | 69680-0168-00 | 1.04971 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Thyroid Medications
Introduction
Thyroid disorders, including hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, affect millions globally and represent a substantial portion of endocrine drug markets. Medications such as levothyroxine, liothyronine, and antithyroid drugs dominate this sector. As the global prevalence of thyroid disease rises, driven by aging populations and health awareness, understanding market dynamics and pricing trajectories becomes essential for pharmaceutical companies, investors, and healthcare policymakers.
This analysis provides a comprehensive evaluation of the current market landscape for thyroid medications, assessing key drivers, competitive landscape, regulatory environment, and projecting future price trends.
Market Overview
Global Prevalence and Demand
Thyroid disorders impact approximately 200 million individuals worldwide, with hypothyroidism being more prevalent than hyperthyroidism. According to the World Health Organization, iodine deficiency remains a leading cause, although autoimmune thyroid diseases such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease are also primary contributors [1]. The rise in screening programs and diagnostic capabilities has led to increased detection, driving demand for thyroid therapies.
Major Drug Classes and Market Share
- Levothyroxine (T4): The mainstay treatment for hypothyroidism, accounting for over 80% of prescriptions in this segment.
- Liothyronine (T3): Used in specific cases, often in combination therapy.
- Antithyroid drugs: Such as methimazole and propylthiouracil, primarily for hyperthyroidism management.
The levothyroxine market dominates, with an estimated global valuation exceeding $3 billion as of 2022, growing annually at approximately 4-6% [2].
Key Players
Major pharmaceutical companies, including Merck, Abbott (now AbbVie), and pharmaceutical generics manufacturers, hold significant market share. The dominance of generic versions has contributed to price variability, with brand-name drugs often priced substantially higher.
Regulatory Environment and Patent Landscape
Patent Expirations and Generic Entry
Patent protections for original formulations of levothyroxine expired in many jurisdictions between 2012 and 2020, facilitating increased generic competition. This influx has exerted downward pressure on prices but also introduced variability due to formulation standards, bioequivalence concerns, and manufacturing quality.
Regulatory Approvals and Quality Standards
Regulatory authorities such as the FDA and EMA enforce strict bioequivalence standards, influencing formulation quality and pricing. The availability of different formulations (liquid, gel capsules) impacts market segmentation and pricing strategies.
Price Trends and Influencing Factors
Historical Price Dynamics
After generic entry, average prices for levothyroxine saw a decline ranging from 30% to 50% in developed markets. However, recent shortages and quality concerns, notably in 2019-2020, led to price surges and increased demand for specific formulations [3].
Factors Affecting Future Pricing
- Generic Competition: Continued entry of biosimilar and generic versions may sustain downward pressure but can be offset by manufacturing complexities.
- Supply Chain Stability: Disruptions, exemplified by COVID-19, have caused shortages, temporarily increasing prices.
- Regulatory Approvals of Novel Formulations: Innovative delivery systems and formulations (e.g., liquid levothyroxine) are entering the market, potentially commanding premium prices.
- Market Consolidation: Mergers and acquisitions among manufacturers can influence pricing strategies and market power dynamics.
Emerging Market Trends
In developing countries, increasing access and healthcare coverage are expanding the market, often characterized by lower price points but higher volume sales. Local manufacturing, price controls, and generic proliferation influence regional pricing structures.
Price Projection: 2023-2028
Short-term Outlook (2023-2025)
- Stabilization of Prices: Post-pandemic supply chain stabilization and increased manufacturing capacity are expected to dampen previous volatility.
- Moderate Price Decline: Competition among generic manufacturers is likely to sustain a steady decline in unit prices, especially in mature markets.
- Premium Formulations: Innovative formulations priced at 20-30% above generics may gain market share, offsetting declines elsewhere.
Mid to Long-term Outlook (2026-2028)
- Price Plateauing or Slight Increase: With the potential for supply constraints or regulatory interventions targeting drug quality, prices for select formulations could stabilize or marginally increase.
- Impact of Biosimilars and Biobetters: Although currently less prominent in thyroid therapy, biosimilar development could influence price dynamics if approved for synthetic hormone formulations.
- Market Expansion in Asia and Africa: Growing demand in emerging markets will provide volume growth opportunities, albeit with lower price points.
Quantitative Projection:
Analysts forecast an average annual price decline of 2-3% in developed markets over the next five years for standard levothyroxine formulations, with premium formulations maintaining or slightly increasing their price premium. Regional variations are expected, with Asian markets experiencing slower declines due to different regulatory and competitive landscapes.
Strategic Insights
- For Manufacturers: Focus on high-quality formulations and expanding into emerging markets remains vital. Investment in bioequivalent formulations and alternative delivery systems may create premium pricing opportunities.
- For Policymakers: Ensuring drug quality amid affordable pricing requires stringent regulation and monitoring of generic manufacturing standards.
- For Investors: Monitoring patent expirations, regulatory developments, and supply chain trends can identify pricing opportunities and risks.
Key Takeaways
- The global thyroid medication market is mature, with levothyroxine dominating due to established efficacy, safety, and patent expirations.
- Price reductions post-generic entry have been significant but are now stabilizing. Short-term fluctuations stem from supply chain issues and quality concerns.
- Innovative formulations and emerging market growth present new premium pricing avenues.
- Regulatory oversight and manufacturing standards will continue to influence market pricing dynamics.
- Overall, steady moderate price declines are projected, with regional disparities driven by economic and regulatory factors.
FAQs
Q1: How has the patent expiry of levothyroxine influenced market prices?
A1: Patent expiry led to a surge of generic manufacturers, increasing competition and reducing prices by up to 50%. However, recent shortages and formulation quality issues have caused price variability and occasional increases in specific formulations.
Q2: Are biosimilars expected to impact thyroid medication pricing?
A2: Currently, biosimilars are less prominent in this segment due to the synthetic nature of levothyroxine. However, future development could introduce biosimilar or biobetter versions, potentially lowering prices and increasing competition.
Q3: Which regions are anticipated to see the fastest market growth?
A3: Emerging markets in Asia, Africa, and Latin America are projected to experience rapid growth driven by increased diagnosis, expanding healthcare infrastructure, and greater market access.
Q4: What factors could lead to significant price increases in the future?
A4: Supply disruptions, stringent regulatory interventions, or quality crises could reduce supply or force manufacturers to upgrade formulations, resulting in higher prices.
Q5: How do regulatory standards affect thyroid medication pricing?
A5: Strict bioequivalence and manufacturing standards ensure drug quality but can increase production costs, influencing pricing strategies. Conversely, regulatory barriers can limit generic entry, affecting competition and prices.
References
- WHO. Iodine deficiency. World Health Organization. 2020.
- MarketWatch. Thyroid Drugs Market Size, Trends & Forecasts. 2022.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Levothyroxine Shortage Update. 2020.
More… ↓
