Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for TETRACYCLINE
✉ Email this page to a colleague
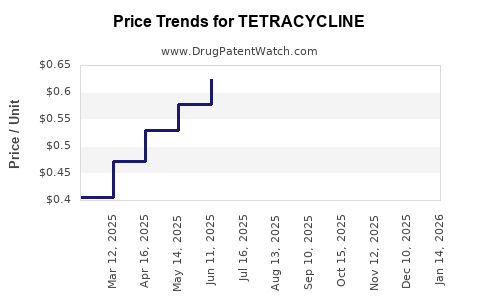
Average Pharmacy Cost for TETRACYCLINE
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TETRACYCLINE 250 MG CAPSULE | 51991-0906-01 | 0.58203 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| TETRACYCLINE 250 MG CAPSULE | 23155-0766-01 | 0.58203 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| TETRACYCLINE 500 MG CAPSULE | 69238-1523-01 | 0.66356 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Tetracycline
Introduction
Tetracycline, a broad-spectrum antibiotic discovered in the 1940s, remains a cornerstone in antimicrobial therapy. Despite advances in antimicrobial agents, tetracycline continues to hold clinical relevance, especially in resource-limited settings and specific niche applications. Analyzing its market landscape, value chain, regulatory environment, and future price projections reveals insightful trends essential for healthcare stakeholders, manufacturers, and investors aiming to navigate this enduring yet evolving drug market.
Global Market Overview
Historical Market Dynamics
Initially, tetracycline achieved widespread global adoption, driven by its efficacy against a variety of bacterial infections such as respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, and sexually transmitted diseases. Over the decades, its volume peaked in the 1970s and 1980s, aligning with high prescription rates. However, subsequent challenges—antibiotic resistance, side effect profiles, and the emergence of newer agents—diminished its dominance.
Current Market Landscape
Today, tetracycline's market size is substantially smaller, estimated at approximately $200–$250 million annually globally (MarketWatch, 2022). The primary markets include India, China, and some African nations, where cost-effective antibiotics retain prominence. The United States and Europe observe limited tetracycline sales, mainly confined to specialized or compounded formulations due to antibiotic resistance concerns.
Key Market Drivers
- Antimicrobial Stewardship and Resistance: Rising resistance has affected tetracycline’s utility, reducing its prescription in many developed countries. Nonetheless, ongoing research suggests renewed interest in tetracyclines, particularly for resistant bacteria and specific indications.
- Generic Availability: The drug's patent expiry in the late 20th century led to widespread generic manufacturing, significantly lowering prices and enhancing accessibility.
- Resource-Limited Settings: Tetracycline remains crucial in developing regions where affordable antibiotics are vital for public health.
Market Challenges
- Antibiotic Resistance: Increasing resistance limits efficacy, resulting in decreased usage.
- Regulatory Restrictions: Stricter regulations and limited indications curb production growth.
- Competition from Newer Agents: Advanced antibiotics (e.g., doxycycline) with improved pharmacokinetics have supplanted tetracycline in many indications.
Supply Chain and Manufacturing Trends
Manufacturing Landscape
Major producers include Indian pharmaceutical companies (e.g., Aurobindo, Cipla) and Chinese manufacturers. These firms benefit from low-cost production, leveraging the global demand for generics. The supply chain’s robustness ensures consistent availability, although quality control and regulatory compliance remain crucial factors.
Regulatory Environment
The FDA (U.S.), EMA (European Union), and WHO maintain strict standards for antibiotics. Tetracycline formulations require adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), especially amid the ongoing antimicrobial resistance threat, which influences production and market accessibility.
Pricing Dynamics
- Historical Prices: In the 1980s, tetracycline’s API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient) traded around $50–$100 per kilogram.
- Current Prices: Today, prices for generic tetracycline API hover around $10–$25 per kilogram, reflecting increased manufacturing efficiency and market saturation.
Market Segmentation
| Segment | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Formulations | Capsules, tablets, oral solutions, topical formulations. |
| Applications | Human medicine, veterinary applications, compounded preparations. |
| Geography | Developing countries dominate in volume, while developed markets are restricted to niche uses. |
Price Projections for the Next 5-10 Years
Factors Influencing Price Trends
- Antibiotic Resistance Trends: As resistance shifts, tetracycline demand may decline in traditional markets but could increase in specific niches.
- Regulatory Changes: Stricter quality standards could elevate manufacturing costs, impacting prices.
- Innovation and Reformulation: Newer tetracycline derivatives (e.g., doxycycline, minocycline) may reduce demand for tetracycline, causing price suppression.
- Manufacturing Costs: Continued efficiency gains and economies of scale could stabilize or lower API costs.
- Market Demand in Low-Income Countries: Increased healthcare access and public health initiatives may sustain or boost demand for affordable tetracycline formulations.
Projected Price Range (API & Finished Formulation)
| Year | API Price Projections | Finished Formulation Price | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $10–$25/kg | $0.05–$0.15 per pill | Stable, highly competitive market with consistent supply. |
| 2025 | $8–$20/kg | $0.04–$0.12 per pill | Slight downward trend driven by manufacturing efficiencies and generic competition. |
| 2030 | $7–$18/kg | $0.03–$0.10 per pill | Potential further decline; market saturation in key regions; resistance-driven demand decline in developed countries. |
Note: These projections assume no significant shifts in resistance patterns, regulatory frameworks, or technological breakthroughs.
Emerging Trends and Future Outlook
Resurgence in Specific Indications
Recent research suggests tetracyclines’ role in treating resistant bacterial infections and certain chronic inflammatory conditions. If clinical data supports expanded indications, market demand might stabilize or grow modestly, influencing pricing.
Industry Innovation
The development of novel formulations—such as controlled-release or combination products—could command premium pricing. However, the generic nature of tetracycline APIs implies cost-driven competition will likely prevail.
Regulatory and Quality Standards
Enhanced quality and safety standards, particularly from WHO and national agencies, could marginally increase manufacturing costs, slightly elevating end-user prices.
Market Entry Barriers
Limited due to generic manufacturing, but regulatory hurdles—especially for export into highly regulated markets—may influence supply and pricing landscapes.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
While tetracycline remains affordable and accessible in many regions, overuse raises concerns about antimicrobial resistance, necessitating responsible prescribing and regulatory oversight. Future policies may restrict or encourage standardized usage, impacting consumption patterns and demand.
Key Takeaways
- Market Shrinkage but Enduring Relevance: Tetracycline’s global market has decreased markedly but persists in resource-limited settings and niche indications.
- Price Stability and Slight Decline: API and finished product prices are expected to decline modestly over the next decade, driven by generics and manufacturing efficiencies.
- Resistance Concerns and Regulatory Impact: Growing resistance and regulatory scrutiny will influence demand dynamics and pricing strategies.
- Innovation and Niches: Potential for new formulations and targeted applications could create pockets of price resilience or growth.
- Supply Chain Dynamics: Asia remains dominant in manufacturing, with ongoing quality and regulatory compliance critical to market stability.
Conclusion
Despite decades of competition from newer antibiotics, tetracycline maintains a vital position within specific healthcare contexts. Manufacturers and investors should monitor antimicrobial resistance trends, regulatory developments, and regional demand shifts to anticipate pricing and market opportunities. Strategic focus on quality, compliance, and niche applications will be essential for profitability in this mature yet resilient market.
FAQs
-
What factors most significantly influence tetracycline’s market price?
The primary influences include manufacturing costs, regulatory compliance, antimicrobial resistance trends, and regional demand, especially in low-income markets where affordability drives sales. -
Will the demand for tetracycline increase in the future?
Potentially in regions battling resistant bacterial strains or where newer antibiotics are inaccessible. However, in developed markets, demand is expected to decline due to resistance and competition. -
How does antibiotic resistance impact tetracycline’s market?
Rising resistance reduces clinical efficacy, limiting prescribing and consequently decreasing potential revenues, though specific niches may still sustain demand. -
Are there opportunities for innovation in tetracycline formulations?
Yes. Controlled-release formulations, combination therapies, or derivatives with improved pharmacokinetics could command premium prices and open new markets. -
What are the key risks for investors in the tetracycline market?
Resistance-driven demand decline, regulatory hurdles, competition from newer antibiotics, and potential shifts in global health policies pose significant risks.
References
More… ↓
