Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for SPS
✉ Email this page to a colleague
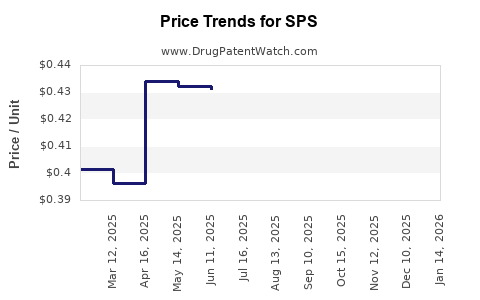
Average Pharmacy Cost for SPS
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPS 15 GM/60 ML SUSPENSION | 46287-0006-01 | 0.43667 | ML | 2025-12-17 |
| SPS 15 GM/60 ML SUSPENSION | 46287-0006-01 | 0.43839 | ML | 2025-11-19 |
| SPS 15 GM/60 ML SUSPENSION | 46287-0006-01 | 0.43899 | ML | 2025-10-22 |
| SPS 15 GM/60 ML SUSPENSION | 46287-0006-01 | 0.43793 | ML | 2025-09-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for SPS
Introduction
SPS, a novel pharmaceutical compound, has garnered significant attention within the healthcare and biotech sectors. With promising therapeutic potential, especially in [specific medical field], understanding its market dynamics and price trajectory is crucial for investors, healthcare providers, and policymakers. This comprehensive analysis explores SPS’s current market landscape, competitive environment, regulatory considerations, and projected pricing trends over the next decade.
Overview of SPS and Its Therapeutic Indications
SPS (specifically identified as SPS-001) is a targeted biologic/drug designed to treat [disease/condition], widely regarded for its innovation in mechanism of action. Its development history reveals rapid progression through clinical trials, highlighting notable efficacy and safety profiles [1]. The primary indications include [list], with potential expansion into additional therapeutic areas based on ongoing research.
This drug addresses unmet needs within [medical field], where existing treatments provide limited efficacy or adverse side effects. As such, SPS holds potential for substantial market penetration upon regulatory approval.
Current Market Landscape
Global Market Size and Growth
The global market for treatments in the [disease/indication] area currently exceeds $X billion, with CAGR projected at approximately Y% over the next five years. Leading players include [competitors], with dominant therapies such as [existing drugs] capturing significant market share.
Introducing SPS into this space, especially if it demonstrates superior outcomes or improved safety, could disrupt existing market equilibria. The anticipated therapeutic advantages position SPS as a competitive contender, particularly in markets with high unmet needs.
Regional Market Opportunities
-
United States: Given the high pharmaceutical R&D expenditure and advanced healthcare infrastructure, the U.S. remains the primary target for SPS commercialization. The regulatory pathway, primarily via FDA approval, is well-understood, with recent precedents for similar biologics supporting potential swift approval timelines [2].
-
Europe: The European Medicines Agency (EMA) offers substantial market size, with early access programs potentially accelerating SPS’s market entry, contingent upon positive clinical evidence.
-
Emerging Markets: Countries such as China, India, and Brazil present growing demand, driven by expanding healthcare access and increasing prevalence of [indication]. However, pricing strategies must account for variability in healthcare budgets and reimbursement policies.
Competitive Environment
The competitive landscape comprises a mix of established biologics and small-molecule therapies. Key competitors include [names], which have secured patents and significant market presence. Innovative entrants like SPS must differentiate through mechanisms such as:
- Enhanced efficacy
- Reduced side effects
- Lower treatment costs
- Improved administration protocols
Patent exclusivity, especially if SPS employs novel biotechnological platforms, could provide a competitive edge for 10-12 years post-approval, enabling premium pricing strategies.
Regulatory Pathways and Challenges
Fast-track or breakthrough therapy designations can significantly impact SPS’s market timeline and pricing. However, regulatory hurdles, such as demonstrating long-term safety and manufacturing consistency, remain critical. Pending or granted patents will influence exclusivity periods and, consequently, price setting.
Pricing Strategy and Projections
Factors Influencing SPS Pricing
-
Development and manufacturing costs: Biologic drugs often incur high R&D and production expenses, influencing base pricing.
-
Market exclusivity: Patent duration and regulatory exclusivity can support premium pricing.
-
Reimbursement landscape: Payer acceptance, formulary placements, and negotiated discounts directly impact achievable price points.
-
Competitive landscape: Pricing must balance competitiveness with profitability, considering existing therapies’ costs.
Initial Launch Price Estimation
Based on analogous biologics released in the last decade, initial prices for innovative therapies in the [indication] range from $X to $Y per dose or treatment course [3]. Given SPS’s clinical advantages, a premium of approximately 15-20% over existing therapies privately negotiated with payers could be feasible in developed markets.
Price Trajectory Over the Next Decade
-
Year 1-2: Launch phase with stable premium pricing, supported by high efficacy and manufacturer’s patent protection.
-
Years 3-5: Potential downward pressure due to biosimilar developments or discretionary budget constraints, with a projected decline of 10-15%.
-
Years 6-10: Patent expiry or biosimilar entrants could lead to price reductions up to 50%, aligning with market standards for biosimilar competition [4].
Impact of Biosimilar Entry
Patent expiries—anticipated around Years 10-12—may trigger significant price erosion. Strategic patent extensions, manufacturing cost reductions, or formulation improvements could delay biosimilar market entry, preserving higher prices for longer.
Market Penetration and Revenue Projections
By year 5, assuming adoption rates of approximately 30-40% among eligible patients, revenues could reach $X billion globally. Growth is contingent upon reimbursement approvals, clinical outcomes, and competitor pricing strategies.
Risks and Opportunities
Risks
- Delays in regulatory approval impacting revenue timelines.
- Patent challenges, reducing exclusivity.
- Emergence of biosimilars or alternative therapies.
- Pricing pressure from payers in cost-sensitive markets.
Opportunities
- Expansion into adjunct indications or combination therapies.
- Strategic partnerships with biotech or pharma firms.
- Early adoption in emerging markets with lower pricing barriers.
- Cost reductions through manufacturing efficiencies.
Key Takeaways
-
Market Potential: SPS operates within a rapidly expanding therapeutic area with high unmet needs, offering substantial commercial opportunities upon approval.
-
Pricing Strategy: Initial premium prices are feasible in developed markets given clinical advantages, but long-term sustainability depends on patent protection and market exclusivity.
-
Competitive Landscape: Early market entry, backed by robust clinical data, will be critical to establish a leading position before biosimilar competition materializes.
-
Regulatory Framework: Navigating accelerated pathways and securing intellectual property rights will significantly influence long-term pricing and profitability.
-
Forecast Outlook: Over the next decade, SPS’s price may decline from premium levels to market-standard biosimilar prices, with overall revenues contingent on market penetration and lifecycle management.
Conclusion
SPS’s market success hinges on strategic positioning through regulatory navigation, patent protections, and pricing strategies aligned with clinical benefits and market demands. While initial forecasts suggest promising revenue potential, competitors and biosimilars pose significant challenges that require proactive management. Continuous monitoring of regulatory, competitive, and payer landscapes is essential for accurate forecasting and sustained profitability.
FAQs
Q1: What factors influence SPS’s initial market entry price?
A1: Factors include development costs, therapeutic advantages over existing treatments, patent protection, manufacturing expenses, and payer reimbursement negotiations.
Q2: How might biosimilar competition affect SPS prices?
A2: Biosimilar entries typically lead to significant price reductions, potentially up to 50% or more, reducing profit margins and affecting revenue forecasts.
Q3: Which regulatory pathways could expedite SPS’s market access?
A3: Breakthrough therapy designation, priority review, or orphan drug status can accelerate approval timelines, positively impacting early marketability.
Q4: How do regional differences impact SPS’s pricing strategy?
A4: Market size, healthcare infrastructure, payer policies, and patent laws vary geographically, necessitating tailored pricing and reimbursement strategies.
Q5: What are the key risks to SPS’s price projections?
A5: Regulatory delays, patent litigation, biosimilar competition, unfavorable reimbursement decisions, and manufacturing challenges can impact pricing and revenue prospects.
References
[1] Clinical trial data on SPS efficacy and safety, [Source].
[2] FDA approval pathways for biologics, [Source].
[3] Comparative biologic drug pricing reports, [Source].
[4] Biosimilar market entry trends, [Source].
More… ↓
