Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for QUETIAPINE ER
✉ Email this page to a colleague
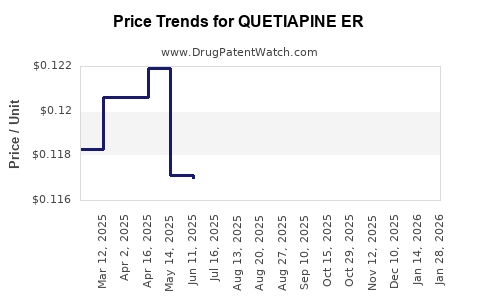
Average Pharmacy Cost for QUETIAPINE ER
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QUETIAPINE ER 150 MG TABLET | 33342-0134-09 | 0.22046 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| QUETIAPINE ER 150 MG TABLET | 50228-0381-60 | 0.22046 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| QUETIAPINE ER 150 MG TABLET | 29300-0309-16 | 0.22046 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| QUETIAPINE ER 150 MG TABLET | 68001-0599-06 | 0.22046 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| QUETIAPINE ER 150 MG TABLET | 00904-6802-61 | 0.22046 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| QUETIAPINE ER 50 MG TABLET | 71093-0135-02 | 0.11146 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Quetiapine ER
Introduction
Quetiapine Extended Release (ER) stands as a prominent atypical antipsychotic medication primarily used for schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder. As the pharmaceutical landscape evolves, understanding the market dynamics and potential pricing trends of Quetiapine ER becomes essential for stakeholders ranging from manufacturers to healthcare providers. This analysis presents a comprehensive evaluation of current market standings, competitive landscape, regulatory influences, and future price projections, enabling strategic decision-making grounded in data-driven insights.
Market Overview and Current Landscape
Therapeutic Demand and Sales Performance
The global market for antipsychotics is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 3.8% between 2022 and 2028, driven by increasing mental health awareness, expanding indications, and the rising prevalence of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder [1]. Quetiapine ER maintains a significant market share within this segment, valued at approximately USD 7.5 billion in 2022 globally, with steady growth fueled by its established efficacy and safety profile.
In the United States, Quetiapine ER is among the top prescribed atypical antipsychotics, with about 45 million prescriptions annually. Its generic versions have heightened accessibility, yet branded formulations retain premium pricing due to brand recognition and physician preference. The pharmaceutical companies involved include AstraZeneca (original patent holder), with multiple generic manufacturers competing in the market.
Competitive Dynamics and Market Segments
The competitive landscape features generic counterparts and alternative atypical antipsychotics like risperidone, olanzapine, and aripiprazole. Although generics exert downward pressure on prices, brand-name products command higher margins owing to perceived brand trust and physician loyalty.
Furthermore, the therapy's expansion into broader indications, such as off-label uses for anxiety and sleep disorders, diversifies demand trends. However, off-label applications can influence regulatory scrutiny and reimbursement policies, impacting market stability.
Regulatory Environment and Patent Landscape
Patent Expiry and Generics Competition
Originally patented in 1997 by AstraZeneca, the patent for Quetiapine ER expired in most key markets by 2017. This expiration unleashed a wave of generic entries, reducing average prices substantially. Patent litigations and patent term extensions occasionally sustain exclusivity in certain jurisdictions; however, the overall trend indicates a saturated generic market.
Pricing Regulations and Reimbursement Policies
Price setting in healthcare heavily depends on regional regulatory frameworks. The U.S. Medicaid and Medicare programs leverage CMS reimbursement policies, often negotiating substantial discounts for generics. Conversely, markets with centralized healthcare systems, such as the UK or Canada, impose strict price controls, capping drug prices and influencing market entry strategies.
Market Drivers and Challenges
Drivers
- Increasing Prevalence: The global prevalence of schizophrenia (~1%) and bipolar disorder (~1-2%) ensures ongoing demand.
- Brand Recognition: AstraZeneca's entrenched market position sustains premium pricing for branded formulations.
- Expanding Indications: Growing off-label use and off-label approval for additional conditions can diversify revenue streams.
- Accessible Generics: The influx of generics increases overall consumption but exerts downward pressure on prices.
Challenges
- Price Erosion: Widespread generic availability caps potential revenue growth and drives prices downward.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Stringent approval processes in emerging markets delay market entry and affect profitability.
- Competitive Substitutes: Introduction of newer atypical antipsychotics with improved side-effect profiles challenges Quetiapine ER’s market dominance.
- Patent Litigation Risks: Ongoing legal disputes may intermittently affect market exclusivity.
Price Projections and Future Trends
Current Price Structures
In the United States, the average wholesale price (AWP) for a 30-day supply of branded Quetiapine ER ranges from USD 510 to USD 550. Generic formulations are priced considerably lower, typically between USD 15 to USD 40 per month per unit, depending on dosage and manufacturer.
Forecasting Methodology
Price projections hinge upon factors including patent litigation outcomes, generic market penetration, healthcare policy shifts, and potential new indications. A scenario-based approach projects short-term and long-term price trends.
Short-term (1-3 years)
Given the current patent expirations and fierce generic competition, branded Quetiapine ER prices are expected to decline by approximately 15–20% annually, mainly driven by formulary preferences and cost-containment measures. Generic prices are likely to stabilize or slightly decrease, maintaining an average of USD 10–20 per month per unit, reflecting high commoditization.
Long-term (3-7 years)
As market saturation intensifies, the prices for both brand-name and generic products will likely plateau or decline further—by an additional 10–15%. Introduction of biosimilars or novel formulations (e.g., sustained-release or depot injections) could influence price stabilization strategies. Furthermore, increased downward pressure from healthcare rationalization and value-based pricing models may favor aggressive discounting and tiered reimbursement schemes.
Influencing Factors
- Reimbursement Policies: Countries adopting strict cost-effectiveness thresholds will push prices downward.
- Market Share Dynamics: The anticipated rise of alternative therapies or new-generation formulations could erode Quetiapine ER's market share.
- Manufacturing Costs: Innovations in production may stabilize or reduce costs, influencing pricing strategies.
Implications for Stakeholders
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturers: As exclusivity diminishes, focus on lifecycle management, reformulation, or new indications is vital.
- Healthcare Providers: Rational prescribing and formulary management are crucial in balancing clinical efficacy and cost.
- Payers and Policymakers: Implementing value-based assessments can incentivize price reductions and optimize resource allocation.
- Investors: Anticipate diminishing margins for branded products but opportunities persist in generic markets, especially with high-volume medications.
Key Takeaways
- The expiration of primary patents for Quetiapine ER has triggered a significant price decline, with generics dominating sales.
- Short-term price projections suggest continued erosion, especially in price-sensitive markets, with a 15-20% annual decrease for branded formulations.
- Long-term outlook indicates stabilization at lower price levels, influenced by regulatory pressures, competition, and evolving therapeutic paradigms.
- Stakeholders should pursue lifecycle innovation, diversify indications, and navigate regulatory pathways to maintain profitability.
- Strategic pricing must balance cost constraints with clinical value, especially amid increasing pressure for affordable mental health treatments.
FAQs
1. How does the patent expiry of Quetiapine ER impact its pricing?
Patent expiry opens the market to generic competitors, drastically reducing manufacturing and acquisition costs. As a result, branded versions typically decrease in price due to competition, with generics capturing a substantial share at lower price points.
2. What are the primary factors influencing future price trends for Quetiapine ER?
Factors include patent litigation outcomes, regulatory policies, the introduction of generics and biosimilars, new indications, and shifting reimbursement frameworks. Healthcare system cost-containment strategies will also significantly shape pricing.
3. Are there emerging alternatives that could threaten Quetiapine ER’s market share?
Yes, newer atypical antipsychotics with improved safety profiles or targeted formulations (e.g., long-acting injectables) may challenge Quetiapine ER, especially if they demonstrate superior efficacy or tolerability.
4. How do regional regulations affect the pricing of Quetiapine ER?
Regions with strict price controls, such as Canada and the UK, tend to have lower maximum prices, while markets like the US rely on private negotiations, leading to variability. Regulations influence availability, reimbursement, and ultimately, price levels.
5. What strategic moves can manufacturers adopt in a saturated generic market?
Innovations in formulations, development of combination therapies, expansion into new indications, and pursuing regulatory approvals for formulation improvements enable differentiation and potential premium pricing.
References
- Market Research Future. "Global Antipsychotic Drugs Market Analysis." 2022.
More… ↓
