Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for OPIUM TINCTURE
✉ Email this page to a colleague
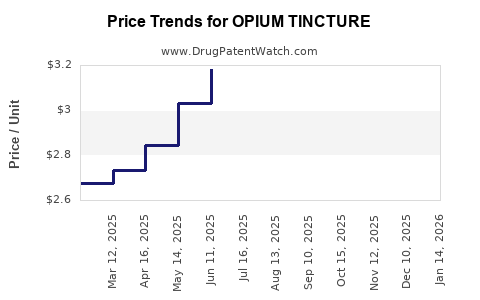
Average Pharmacy Cost for OPIUM TINCTURE
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPIUM TINCTURE 10 MG/ML | 42799-0217-01 | 3.06291 | ML | 2025-12-17 |
| OPIUM TINCTURE 10 MG/ML | 62559-0153-04 | 3.06291 | ML | 2025-12-17 |
| OPIUM TINCTURE 10 MG/ML | 42799-0217-01 | 3.19914 | ML | 2025-11-19 |
| OPIUM TINCTURE 10 MG/ML | 62559-0153-04 | 3.19914 | ML | 2025-11-19 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Opium Tincture
Introduction
Opium tincture, historically utilized in medical settings for pain management and diarrhea treatment, remains a controlled substance under international and national drug regulations due to its high potential for abuse and addiction. Despite declining therapeutic use, the illicit market persists, complicating market analysis and pricing dynamics. This report delineates the current state of the opium tincture market, assesses regulatory influences, evaluates supply and demand factors, and projects future price trends with a focus on legal and illicit channels.
Regulatory Context and Market Landscape
Legal Framework
Globally, opium tincture falls under stringent drug control regulations, notably the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs (1961), which classifies opium and derivatives as Schedule I substances. Countries impose strict licensing, import/export restrictions, and tracking mechanisms to govern production and distribution [1].
Medical and Illicit Use
While approved as a medicinal product in certain jurisdictions—primarily for palliative care in some European nations—the medical market is shrinking due to the advent of synthetic opioids with more predictable pharmacokinetics. Consequently, legitimate markets for opium tincture are limited, prompting a significant segment of its consumption to occur in illicit markets.
Illicit Market Dynamics
In illegal markets, opium tincture often serves as a precursor or intermediate product in the illicit opioid supply chain or as a consumable product for users seeking a cost-effective alternative to heroin. Its clandestine nature results in price volatility driven by law enforcement activities, supply disruptions, and regional demand surges.
Supply Chain Analysis
Cultivation and Production
The primary raw material, opium poppies, are cultivated predominantly in Afghanistan, Myanmar, and Mexico. Political instability, climate variability, and enforcement crackdowns influence raw material availability [2].
Extraction and Manufacturing
Legal pharmaceutical manufacturing is highly regulated, with production limited to licensed facilities, leading to controlled supply chains. However, illicit extraction and clandestine production—particularly in conflict zones—introduce unregulated, unpredictable supplies.
Distribution Networks
Distribution channels are complex; legal channels are minimal, primarily restricted to licensed pharmacies and medical institutions. Illicit channels encompass clandestine laboratories and smuggling routes consistently affected by enforcement efforts.
Demand Factors Influencing the Market
Medical Demand
The legitimate medical demand for opium tincture dwindles amid alternative medications, limiting its role to niche applications.
Illicit Demand
Illicit consumption, driven by heroin users seeking an alternative or lower-priced substitute, sustains a steady demand in certain regions, notably Southeast Asia, North Africa, and parts of Eastern Europe.
Regulatory Impact
Stringent controls restrict supply, often elevating illicit prices. Conversely, relaxed regulations or policy shifts—such as medicinal legalization—could expand legal markets, impacting overall demand and pricing.
Price Analysis and Historical Trends
Historical Pricing Data
Reliable historical data are scarce due to illegal market opacity. However, sources indicate that illicit opium tincture prices vary significantly, often correlating with regional enforcement intensity and raw material costs. Studies estimate street prices ranging from $40 to $100 per milliliter, with higher values in heavily policed markets [3].
Price Drivers
- Supply Constraints: Political instability and eradication campaigns reduce available supply, increasing prices.
- Purity and Potency: Variability in potency affects consumer preferences and prices.
- Law Enforcement and Seizures: Increased seizures lead to short-term price spikes in local markets.
Pricing in Legal Markets
Legal markets for opium tincture are minimal; available products typically command higher prices due to production costs, regulatory compliance, and limited supply.
Future Price Projections
Short-term Outlook (1–3 years)
The illicit opium tincture market is expected to remain volatile. Law enforcement crackdowns and crop reductions in primary cultivation countries are likely to diminish available supply roads temporarily, raising prices. Conversely, clandestine production may adapt, stabilizing supplies over time. Market analysts project a moderate upward trend in illicit prices, with fluctuations influenced by enforcement cycles.
Medium to Long-term Outlook (3–10 years)
Potential legalization for medicinal or scientific purposes in certain jurisdictions could introduce a legal supply stream, exerting downward pressure on illicit prices. Conversely, increased restrictions or disruptions in cultivation zones might sustain or elevate prices. Climate change, geopolitical conflicts, and evolving law enforcement strategies will be pivotal in shaping supply and, consequently, price dynamics.
Projected Price Range
Considering current trends, estimates suggest that illicit opium tincture prices may stabilize around $50–$120 per milliliter over the next five years, with regional variations. Legal market prices are anticipated significantly higher, potentially exceeding $200 per milliliter, reflecting quality control and regulatory compliance costs.
Market Opportunities and Risks
Opportunities
- Medical and Scientific Research: Growing interest in alternative opioids for pain management presents opportunities for legal, regulated production and sale.
- Harm Reduction Programs: Some regions explore substitution therapies that may include opium derivatives, potentially expanding legal markets.
Risks
- Regulatory Intensification: Stricter international controls could further suppress legal markets and inflate illicit prices.
- Enforcement Disruptions: Increased seizures and eradication efforts in primary cultivation zones could constrain supply.
- Market Volatility: The clandestine nature entails exposed risks for producers and consumers, leading to price fluctuations.
Key Takeaways
- The opium tincture market is primarily illicit, with limited legal uses and heavily regulated international trade.
- Supply is heavily impacted by geopolitical stability, law enforcement, and crop yields in major producing regions.
- Prices are highly volatile, generally rising in response to supply disruptions and enforcement actions.
- Short-term price projections indicate a moderate upward trajectory, while long-term prices depend on policy shifts, cultivation patterns, and technological developments.
- Opportunities exist within scientific and medical research sectors, but risks from regulation and enforcement continue to dominate market dynamics.
FAQs
1. What are the main factors influencing opium tincture prices?
Supply disruptions, law enforcement activities, regional demand, potency variability, and regulatory changes are primary factors impacting prices.
2. How does legal regulation affect the market for opium tincture?
Strict legal controls limit legal supply, elevating illicit market prices. Potential legalization for medical uses could introduce regulated competition, potentially reducing illegal prices but increasing legal supply costs.
3. Is the illicit market for opium tincture growing or shrinking?
Currently, the market remains active but is subject to fluctuations based on enforcement and crop yields. Overall, heightened enforcement tends to increase illicit prices temporarily.
4. Are there legitimate medical uses for opium tincture today?
Yes, in certain jurisdictions, it is used for pain management and palliative care, but the overall demand is declining due to synthetic alternatives.
5. What regions are most affected by the opium tincture market?
South and Southeast Asia, North Africa, and parts of Eastern Europe are most impacted, primarily through illicit channels.
Sources
[1] United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC). "The International Drug Control Conventions."
[2] United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). "Opium Production and Cultivation Reports."
[3] UNODC. "World Drug Report 2022."
More… ↓
