Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for NORVIR
✉ Email this page to a colleague
Average Pharmacy Cost for NORVIR
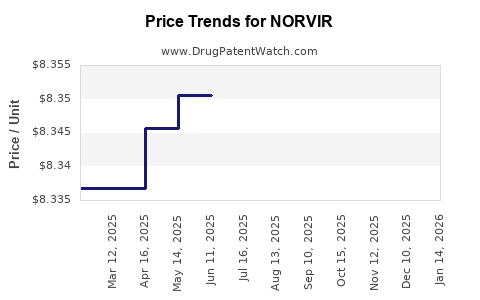
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NORVIR 100 MG TABLET | 00074-2340-30 | 8.34158 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| NORVIR 100 MG TABLET | 00074-2340-30 | 8.34158 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| NORVIR 100 MG TABLET | 00074-2340-30 | 8.34158 | EACH | 2025-09-17 |
| NORVIR 100 MG TABLET | 00074-2340-30 | 8.30007 | EACH | 2025-08-20 |
| NORVIR 100 MG TABLET | 00074-2340-30 | 8.32087 | EACH | 2025-07-23 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for NORVIR (Ritonavir)
Introduction
NORVIR, the trade name for Ritonavir, is an antiretroviral medication used primarily in the management of HIV/AIDS. Since its approval, NORVIR has maintained a significant market position owing to its role as a pharmacokinetic enhancer in combination with other antiretrovirals. Its unique profile as a protease inhibitor and booster has sustained demand amid evolving HIV treatment landscapes. This analysis explores the current market dynamics, competitive landscape, patent and regulatory environment, and provides forward-looking price projections for NORVIR.
Market Overview
Historical Market and Usage Trends
Ritonavir was first approved in 1996 and has since become integral to combination antiretroviral therapy (ART). Initially marketed as a primary protease inhibitor, its role has shifted predominantly to that of a booster for other protease inhibitors, notably in fixed-dose combinations such as Kaletra (Lopinavir/Ritonavir), which remains a revenue driver.
Recent years have seen a plateau in global HIV patient populations on Ritonavir-containing therapies, owing to advances in newer antiretrovirals with improved tolerability and efficacy. Nonetheless, Ritonavir maintains a critical niche, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), where patent status, manufacturing capacity, and pricing influence access.
Market Size and Segmentation
Global HIV/AIDS treatment markets are valued at approximately USD 21 billion (2022), with antiretroviral therapy (ART) comprising the lion’s share. Ritonavir’s role as a booster is embedded within combination regimens, which constitute over 80% of ART prescriptions. The demand in high-income countries (HICs) stabilizes, while LMICs—primarily in Sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia—continue to drive volume growth.
The demand for Ritonavir is driven by factors such as:
- The aging HIV-positive population requiring lifelong ART.
- Continuous procurement through global health initiatives like GAVI and PEPFAR.
- The expansion of HIV treatment programs in emerging markets.
Growth is primarily influenced by the transition to newer, cost-effective antiretrovirals, yet Ritonavir remains indispensable in certain regimens, especially where alternatives are limited.
Competitive Landscape
Key Patent and Regulatory Considerations
Traditionally, Pfizer owned the patent rights for Ritonavir, which expired in numerous jurisdictions, including the U.S. in 2014; however, secondary patents and formulations have delayed generic entry in some markets.
Generic manufacturers, notably in India and China, have been able to produce Ritonavir formulations in recent years, leading to significant price reductions worldwide. The transition from brand-name NORVIR to generic versions has markedly impacted the market share dynamics and pricing structures.
Generic Competition and Market Entry
The entry of generics has led to a substantial decline in Ritonavir prices, with cost reductions between 60-80% depending on jurisdiction and formulation. In low-resource settings, generics dominate procurement pipelines, and tenders favor lower-cost options, pressuring prices downward further.
Despite generics, branded NORVIR retains a presence in certain markets, especially where supply chain stability and regulatory approvals favor patented formulations. However, its market share has diminished substantially relative to generics.
Price Analysis
Historical Pricing Trends
- Brand-name NORVIR initially commanded high prices (~USD 100 per tablet) in early 2000s.
- Post-patent expiration, prices plummeted, with generic Ritonavir formulations now available at approximately USD 2-5 per tablet in high-volume markets.
Current Market Pricing
- In HICs, negotiated prices for branded NORVIR remain relatively high, often USD 50-80 per treatment course, overshadowed by newer agents.
- In LMICs, generic Ritonavir prices are markedly lower, frequently under USD 1-3 per dose, facilitated by bulk procurement, WHO prequalification, and voluntary licensing agreements.
Forecasted Price Trends (2023–2030)
Given the ongoing patent expiries and expanding generic capacity, the following projections are anticipated:
- Short-term (2023-2025): Continued price erosion in LMIC markets; branded NORVIR pricing will stabilize or marginally decline due to market saturation.
- Mid-term (2026-2028): As newer boosters and combination therapies gain prominence, Ritonavir’s standalone demand is expected to decline further in HICs, pressuring prices downward.
- Long-term (2029-2030): Prices in negligible markets may approximate USD 1-2 per tablet; in high-income markets, where patent protections or supply constraints persist, prices may remain elevated but limited in scope.
Major determinants include the rate of generic manufacturing scale-up, patent litigations, and the adoption pace of next-generation therapeutics.
Market Drivers and Constraints
Drivers
- Continued demand for ART in LMICs via global health initiatives.
- The ongoing necessity of Ritonavir as a pharmacokinetic booster in combination therapies.
- Favorable manufacturing and licensing agreements lowering costs in emerging markets.
Constraints
- Patent expiry and widespread availability of generics.
- Competitive pressure from newer, more tolerable agents such as Bictegravir and Dolutegravir.
- Regulatory delays in adopting generic formulations in certain markets.
- The evolving HIV treatment landscape favoring integrase inhibitors over protease inhibitors.
Strategic Implications and Investment Outlook
Investors and pharmaceutical companies analyzing this market should consider the following:
- Patent landscapes: Opportunities emerging from patent litigations or licensing arrangements.
- Manufacturing capacity: Countries with robust generic production can supply lower-cost Ritonavir, influencing global pricing.
- Healthcare policy shifts: Increased adoption of integrase-based regimens could diminish Ritonavir's market share further.
- Pricing strategies: Companies focusing on LMICs should aggressively compete through volume-based pricing and licensing.
While Ritonavir’s standalone market is shrinking, its role as a booster in combination therapies sustains a residual niche. Prices are projected to decline gradually, reaching minimal levels in the next decade, primarily sustained through generic availability.
Key Takeaways
- Market size: Ritonavir’s global market, dominated by generics, has declined significantly but remains vital in HIV therapy, especially in resource-limited settings.
- Pricing trajectory: Expect prices to stabilize or decline slightly in HICs, with more substantial reductions in LMICs, driven by generic competition.
- Competitive pressures: The rise of newer agents and evolving treatment guidelines will reduce Ritonavir’s standalone use, influencing long-term pricing.
- Strategic focus: Stakeholders should monitor patent expirations, licensing agreements, and manufacturing capacity to optimize market positioning.
- Sustainability: The residual demand for Ritonavir as a booster suggests limited but steady revenue streams, primarily in global health-assisted markets.
FAQs
-
What factors primarily influence Ritonavir pricing?
Patent status, generic market entry, manufacturing scale, procurement volume, and regional healthcare policies influence Ritonavir’s pricing landscape. -
How will patent expiries affect the Ritonavir market?
Patent expirations have led to widespread generic manufacturing, significantly lowering prices and reducing profitability for branded formulations. -
What is the outlook for Ritonavir in high-income versus low-income markets?
In HICs, demand is declining due to newer agents, maintaining stable or slightly decreasing prices. In LMICs, prices are expected to remain low due to extensive generic production and global procurement programs. -
Which competitors are emerging as alternatives to Ritonavir?
Newer pharmacokinetic boosters like Cobicistat are replacing Ritonavir in many fixed-dose combinations, further diminishing Ritonavir’s standalone market. -
What are the opportunities for pharmaceutical companies regarding Ritonavir?
Companies can focus on licensing, manufacturing, and distribution in emerging markets, whereas innovation opportunities are limited due to the drug’s age and patent landscape.
References
[1] World Health Organization. HIV/AIDS Treatment Guidelines, 2022.
[2] IQVIA. Global HIV/AIDS Market Data Reports, 2022.
[3] Pfizer. NORVIR (Ritonavir) Product Monograph, 2021.
[4] GlobalData Healthcare. Antiretroviral Market Insights, 2022.
[5] patents.google.com. Ritonavir patents and expiry dates.
More… ↓
