Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for NIFEDIPINE ER
✉ Email this page to a colleague
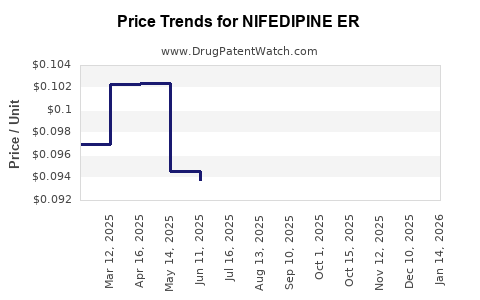
Average Pharmacy Cost for NIFEDIPINE ER
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NIFEDIPINE ER 30 MG TABLET | 00904-7208-06 | 0.11786 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| NIFEDIPINE ER 30 MG TABLET | 00904-7208-61 | 0.11786 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| NIFEDIPINE ER 30 MG TABLET | 24979-0011-12 | 0.11786 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| NIFEDIPINE ER 30 MG TABLET | 24979-0011-01 | 0.11786 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Nifedipine ER
Introduction
Nifedipine Extended Release (ER) is a widely prescribed calcium channel blocker used predominantly for managing hypertension and angina pectoris. Its sustained-release formulation offers a comprehensive therapeutic profile, leading to its high utilization globally. As healthcare systems evolve and generic formulations proliferate, understanding the market landscape and pricing trajectories for Nifedipine ER becomes critical for stakeholders across pharmaceutical manufacturing, distribution, and investment domains.
This analysis explores the current market dynamics of Nifedipine ER, examines key factors influencing its pricing, and projects future price trends based on market drivers, regulatory factors, and patent landscapes.
Market Overview
Global Market Size and Trends
The global calcium channel blocker market was valued at approximately USD 2.4 billion in 2021, with Nifedipine ER constituting a significant segment. The increasing prevalence of hypertension — estimated to affect over 1.3 billion adults worldwide — propels demand for effective antihypertensive agents like Nifedipine ER [1].
Key regional markets include North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Latin America, each with distinct dynamics. North America led the market in 2021, supported by high prescription rates and advanced healthcare infrastructure. Asia-Pacific is projected to register the fastest growth due to rising hypertension prevalence, expanding healthcare access, and generics’ affordability.
Manufacturers and Market Share
Major pharmaceutical firms such as Pfizer, Novartis, and Mylan hold significant market shares; however, the landscape is increasingly fragmented with the growth of generic manufacturers. The patent expiration of branded formulations, notably Pfizer’s Adalat CC, facilitated a surge in generic competition, exerting downward pressure on prices but expanding accessibility.
Regulatory and Patent Landscape
Many formulations of Nifedipine ER have lost patent protections, leading to widespread generic adoption. However, some formulations still enjoy patent protection, impacting pricing and market exclusivity. Regulatory authorities like the FDA and EMA enforce standards that influence manufacturing and pricing strategies.
Factors Influencing Market Dynamics
1. Patent Expirations and Generic Competition
Patent expirations catalyze market entry of generics, drastically reducing drug prices. For Nifedipine ER, the expiration dates primarily occurred between 2010 and 2020, leading to numerous generic entrants. This dynamic significantly compresses profit margins but increases patient access [2].
2. Cost of Raw Materials and Manufacturing
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) costs directly impact pricing. Raw material prices for Nifedipine, traditionally derived from chlorinated compounds, have experienced volatility due to supply chain constraints and geopolitical factors. Efficient manufacturing and supplier competition can mitigate upward pressure on costs.
3. Reimbursement and Pricing Policies
Government policies in major markets influence drug prices. For instance, price negotiations and formulary inclusion in the US via Medicare and private insurers, as well as price control policies in Europe and Asia, determine the final consumer price. Increased emphasis on generic drug use aims to contain costs.
4. Healthcare Infrastructure and Demographics
Growing aging populations and increased prevalence of hypertension boost demand for Nifedipine ER. In emerging markets, expanding healthcare coverage elevates prescription rates, but pricing strategies must adapt to different economic conditions.
5. Patent Litigation and Variants
Some companies develop new formulations or sinlge-dose variants to extend exclusivity, impacting pricing structures. Patent disputes can temporarily restrict generic entry, stabilizing or elevating prices.
Price Trends and Projections
Historical Price Movements
Over the past decade, Nifedipine ER prices have declined substantially. In the United States, retail prices for brand-name formulations initially ranged between USD 100-150 per month but have decreased to USD 10-30 per month post-generic entry [3].
Current Price Landscape
As of 2023, the average wholesale acquisition cost (WAC) for generic Nifedipine ER (30 mg) ranges from USD 5-15 per month, depending on supplier and packaging. Branded formulations retain higher prices, often exceeding USD 100 per month, but they have diminished market share.
Projected Price Trends (2023-2030)
Based on current market forces, the following trends are anticipated:
-
Sustained Low Prices for Generics: With multiple generics available, prices are expected to plateau at USD 3-10 per month in developed markets. Margins will be constrained unless innovative formulations or delivery methods are introduced.
-
Premium Pricing for Patent-Protected Variants: New formulations targeting niche markets (e.g., once-daily dosing, combination therapies) may command higher prices initially, likely USD 50-100 per month, until patent expiry or market saturation.
-
Market Entry in Emerging Economies: Price points will continue to be lower (USD 1-5/month), driven by purchasing power and regulatory policies.
-
Impact of Biosimilars: Although not directly applicable, biosimilar trends imply broader cost reductions across drug classes, including calcium channel blockers.
Future Drivers of Price Shifts
-
Regulatory Environment: Price caps and health technology assessments (HTAs) in European countries, such as Germany’s G-BA, aim to lower costs further.
-
Innovation and Research: Investments in fixed-dose combinations or formulations with improved pharmacokinetics could command higher prices temporarily.
-
Market Consolidation: Larger pharmaceutical firms increasing market share may influence pricing strategies, either moderating or elevating prices depending on their focus.
Strategic Market Implications
Stakeholders should monitor patent landscapes, regulatory policies, and supply chain developments to optimize pricing strategies. For generic manufacturers, economies of scale and efficient sourcing will be key to maintaining competitiveness. For innovator firms, patent protection and formulation patents remain vital to commanding premium pricing.
Investors should consider the potential for price stabilization in mature markets due to generics but remain attentive to regional policy shifts that could create market opportunities or impose pricing constraints.
Conclusion
The Nifedipine ER market is characterized by mature competition and downward pricing trends in developed markets, driven by patent expirations and generic proliferation. While prices have stabilized at low levels in many regions, opportunities exist in specialized formulations and emerging markets where price sensitivity and healthcare access are evolving. Long-term, prices are expected to remain subdued in highly competitive segments, but innovation and regional policy shifts could create pockets of pricing differentials.
Key Takeaways
-
Market Maturity: The Nifedipine ER market is highly mature, with aggressive generic competition leading to significant price reductions, especially in North America and Europe.
-
Pricing Trajectory: Prices are projected to stabilize at low levels (USD 3-10/month) in most developed markets; premium pricing remains possible for novel formulations.
-
Regulatory and Patent Influence: Expiry of key patents has spurred generic entry; emerging patent filings or formulations could temporarily elevate prices.
-
Global Impact: Price reductions are most pronounced in developed economies; emerging markets offer growth opportunities, albeit at lower price points.
-
Strategic Focus: Manufacturers should prioritize supply chain efficiency, innovation, and regional policy navigation to optimize profitability.
FAQs
-
What factors most significantly influence Nifedipine ER pricing?
Patent status, generic competition, manufacturing costs, regulatory policies, and regional pricing regulations are key determinants. -
How has generic entry affected the Nifedipine ER market?
Generic entry has drastically reduced prices, expanding patient access while squeezing profit margins for brand-name manufacturers. -
Are there emerging markets with higher Nifedipine ER prices?
Yes, in regions with less competition or higher healthcare costs, such as parts of Asia and Latin America, prices remain relatively higher compared to developed countries. -
What future innovations could impact Nifedipine ER pricing?
Development of fixed-dose combinations, improved delivery formulations, and patent protections for new variants may temporarily sustain higher prices. -
How do healthcare policies influence Nifedipine ER prices?
Price regulations, reimbursement strategies, and formulary inclusions in different jurisdictions directly impact the final retail and hospital procurement prices.
References
[1] World Health Organization. (2022). Hypertension Fact Sheet. WHO.
[2] U.S. Food & Drug Administration. (2022). Patent Expiration Data for Nifedipine.
[3] SSR Health. (2023). U.S. Retail Price Trends for Nifedipine ER.
More… ↓
