Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for NIACIN ER
✉ Email this page to a colleague
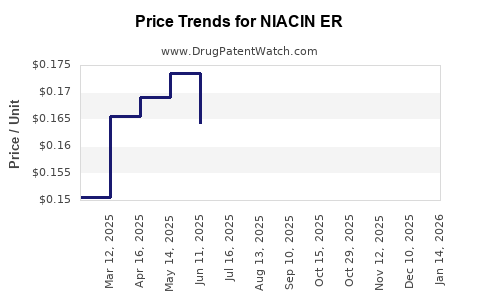
Average Pharmacy Cost for NIACIN ER
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NIACIN ER 1,000 MG TABLET | 47335-0613-81 | 0.27526 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| NIACIN ER 1,000 MG TABLET | 59651-0020-18 | 0.27526 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| NIACIN ER 1,000 MG TABLET | 33342-0189-10 | 0.27526 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| NIACIN ER 1,000 MG TABLET | 59651-0020-90 | 0.27526 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| NIACIN ER 1,000 MG TABLET | 00093-7394-86 | 0.27526 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| NIACIN ER 1,000 MG TABLET | 00093-7394-98 | 0.27526 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Niacin ER (Extended-Release Niacin)
Introduction
Niacin ER (Extended-Release Niacin) is a pharmaceutical compound primarily employed to manage dyslipidemia, including elevated LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, and to increase HDL cholesterol. As a recognized therapeutic agent, Niacin ER presents a unique market positioning: a legacy drug with longstanding clinical applications and opportunities for formulation improvements, alongside facing generic competition.
Understanding its market dynamics and price trajectories requires an in-depth review of current demand, patent landscape, regulatory environment, competitive landscape, and emerging trends, such as biosimilars and value-based healthcare initiatives.
Market Landscape Overview
Historical Market Perspective
Niacin ER has experienced fluctuating demand over recent years. Initially dominant as a cost-effective lipid-modifying agent, its global market has been shaped significantly by clinical guidelines. Notably, its prominence declined with the advent of newer agents offering similar or superior efficacy with fewer side effects, such as PCSK9 inhibitors and ezetimibe. However, Niacin ER retains a niche due to its affordability, tolerability profile, and oral dosing convenience.
Global Market Size & Growth
The global niacin market, predominantly driven by extended-release formulations, was valued at approximately USD 700 million in 2022, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 2-3% through 2030. Key markets include the United States, European Union, and emerging regions like Asia-Pacific, where increasing dyslipidemia prevalence fuels demand.
In the U.S., Niacin ER holds a significant share within the lipid-modifying agents segment, often utilized as an adjunct therapy. According to IQVIA, the prescription volume of Niacin ER remained steady, with slight declines attributable to the shift toward newer therapies (e.g., PCSK9 inhibitors) [1].
Patent and Regulatory Dynamics
Patent Landscape
Most of the original patents for Niacin ER formulations expired by 2015-2017, leading to widespread generic availability. This shift radically altered market pricing, with branded versions facing heightened competition from generics. The expiry of key patents precipitated price erosion, with average prices declining by 50-70% post-patent expiry.
However, formulation patents or new delivery mechanisms could afford limited exclusivity; currently, no significant patent protections limit generic entry for standard Niacin ER formulations, intensifying price competition.
Regulatory Considerations
FDA approval standards categorize Niacin ER as a modified-release formulation with established safety and efficacy. The drug’s over-the-counter (OTC) availability in some regions further complicates patent and market strategies but reduces payor-driven demand in those markets.
Any new formulations or delivery systems seeking approval might be eligible for expedited pathways or orphan status if indicated for rare subgroups, though no such filings are currently prominent.
Competitive Landscape
Generic Dominance
Generic Niacin ER dominates the market, with multiple manufacturers supplying bioequivalent products at substantially lower prices than branded versions. Dosing tends to be standardized at 500 mg, 1000 mg, and 2000 mg tablets, with generic entries offering cost-efficiencies.
Brand vs. Generic Pricing
Brand-name Niacin ER products typically retail at USD 10–$30 per month’s supply, whereas generics often sell for less than USD 5–$10, making them highly attractive to cost-conscious providers and patients.
Emerging Alternatives
Newer lipid-lowering agents, especially PCSK9 inhibitors, provide more potent LDL reduction but at significantly higher costs. Consequently, Niacin ER's market is increasingly confined to niche indications, low-income settings, or patients intolerant to statins or other agents.
Market Dynamics and Price Projections (2023-2030)
Factors Influencing Market and Pricing
- Generic Competition & Price Erosion: The proliferation of generics continues to drive prices downward, with an expected annual decrease of 10-15% in branded prices due to increased competition.
- Reimbursement Policies: Insurance payers favor generics; coverage for branded Niacin ER has become limited, exerting downward pressure on prices.
- Clinical Practice Trends: A decline in Niacin ER prescriptions is observable—driven by guideline adjustments emphasizing statins and newer agents—resulting in reduced volume and potential price stabilization or further decline.
- Regulatory Innovations: No major reformulations or patents are anticipated to influence pricing in the foreseeable future.
- Market Localization: Rapid growth in emerging markets might temporarily stabilize prices due to limited generic penetration and differing reimbursement mechanisms.
Projected Price Trajectory
- Short-Term (2023-2025): Branded Niacin ER prices will continue to decline modestly, averaging 10-15% annually, primarily affected by generic market saturation.
- Mid to Long-Term (2025-2030): As patent protections for original formulations remain absent, prices are expected to plateau at low margins, with generic versions maintaining price points around USD 2-4 per month of therapy.
- Premium Formulations: Any novel delivery system or combination device might command higher costs temporarily but unlikely to significantly alter market-wide pricing.
Key Market Opportunities and Risks
-
Opportunities:
- Developing fixed-dose combinations (FDCs) to improve patient compliance.
- Targeting niche populations such as patients intolerant to other lipid-modifying agents.
- Exploring formulations with improved tolerability or adherence features.
-
Risks:
- A declining prescription trend due to evolving treatment guidelines.
- Competitive bleed from newer, more effective agents.
- Price erosion driven by pervasive generic competition.
Conclusion
The Niacin ER market is characterized by mature status, significant generic penetration, and declining demand, with prices trending downward. While the core product remains affordable and accessible, its future profitability hinges on niche applications, formulation innovations, and strategic positioning within healthcare reimbursement frameworks.
Key Takeaways
- Market saturation and patent expiration have led to robust generic competition, exerting downward pressure on prices.
- Demand for Niacin ER is gradually declining in primary indications due to evolving clinical guidelines favoring newer therapies.
- Price projections indicate a continued decline of 10-15% annually for branded formulations, stabilizing at low-cost generic levels.
- Opportunities exist in niche markets, combining formulations, and targeting intolerant patient groups.
- Emerging market growth in developing economies may temporarily influence prices but will not substantially alter global price trends.
FAQs
1. Will Niacin ER prices increase with new formulation technologies?
Unlikely. Innovations typically command premium prices temporarily, but widespread adoption will be limited by the entrenched presence of low-cost generics.
2. How does patent expiry affect Niacin ER’s market share?
Patent expiry led to significant generic entry, dramatically reducing branded product prices and market share, with generics dominating volume.
3. Are there potential regulatory changes that could revive Niacin ER’s market?
No significant regulatory changes are currently anticipated; however, new formulations or combination therapies could renew interest if supported by clinical benefits.
4. Which regions offer the highest growth potential for Niacin ER?
Emerging markets like Asia-Pacific present growth opportunities driven by increasing dyslipidemia prevalence and limited access to newer therapies.
5. How does Niacin ER compare to newer lipid-lowering agents in cost-effectiveness?
Niacin ER remains a cost-effective option for specific indications, especially where affordability is a priority, but may be less favorable compared to more potent agents in terms of clinical outcomes.
Sources:
[1] IQVIA, Prescription Data Reports, 2022.
More… ↓
