Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for LEVALBUTEROL TAR HFA
✉ Email this page to a colleague
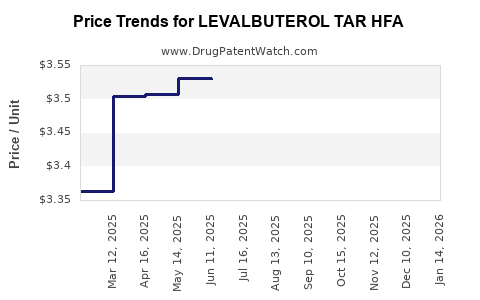
Average Pharmacy Cost for LEVALBUTEROL TAR HFA
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LEVALBUTEROL TAR HFA 45 MCG INH | 00591-2927-54 | 3.41832 | GM | 2025-11-19 |
| LEVALBUTEROL TAR HFA 45 MCG INH | 00591-2927-54 | 3.32817 | GM | 2025-10-22 |
| LEVALBUTEROL TAR HFA 45 MCG INH | 00591-2927-54 | 3.31292 | GM | 2025-09-17 |
| LEVALBUTEROL TAR HFA 45 MCG INH | 00591-2927-54 | 3.42454 | GM | 2025-08-20 |
| LEVALBUTEROL TAR HFA 45 MCG INH | 00591-2927-54 | 3.50395 | GM | 2025-07-23 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Levalbuterol Tar HFA
Introduction
Levalbuterol Tar HFA (hydrofluoroalkane) is a bronchodilator primarily used in the management of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). As a selective β2-adrenergic receptor agonist, it provides rapid relief from bronchospasm without significant cardiovascular side effects, positioning it as a preferred inhaler for quick symptom control. The product's market landscape, competitive positioning, and pricing expectations are influenced by evolving regulatory standards, patent status, strategic mergers, and the growing global respiratory disease burden.
Market Landscape Overview
Global Prevalence and Growth Drivers
The global asthma and COPD populations are expanding, driven by rising pollution levels, smoking prevalence, and aging populations. The Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) estimates over 300 million asthma sufferers worldwide, with COPD affecting approximately 210 million globally [1]. These epidemiological trends foster sustained demand for bronchodilator therapies, including Levalbuterol Tar HFA.
Product Approvals and Market Exclusivity
Levalbuterol Tar HFA is marketed by several pharmaceutical firms, with the most prominent being United Therapeutics and its subsidiaries. In the U.S., it gained FDA approval as a metered-dose inhaler (MDI), expanding options from racemic albuterol, which contains both active isomers. Patent protections for specific formulations often extend until the late 2020s, although the expiration of key patents may catalyze the entry of biosimilars or generics.
Competitive Landscape
The principal competitors include:
- Albuterol Sulfate Inhalers: Racemic formulations widely available; often less expensive.
- Levalbuterol (R-isomer): Occasionally marketed as a standalone product or via generics.
- Other Bronchodilators: Such as formoterol, salmeterol, tiotropium, and combination therapies.
The differentiation of Levalbuterol Tar HFA as a selective, faster-acting agent with superior side-effect profiles sustains its niche in acute management, high-risk patient populations, and specific therapeutic regimens.
Pricing and Market Penetration Dynamics
Historically, inhaler pricing has ranged from $30 to $60 per inhaler in the U.S., influenced by brand exclusivity and negotiated insurance reimbursements. Market penetration hinges on physician prescribing patterns, insurance coverage, patient adherence, and the availability of lower-cost alternatives.
Pricing Analysis and Future Price Projections
Current Pricing Landscape
As of 2023, the retail price of Levalbuterol Tar HFA inhalers averaged approximately $45 per inhaler in the U.S., based on data from IQVIA and consumer reports. Insurance reimbursement rates vary, with commercial carriers often negotiating discounts, thereby lowering out-of-pocket costs.
Market Drivers Affecting Price Trends
- Patent Expirations: The upcoming expiration of core patents, projected around 2025–2027, paves the way for biosimilar and generic entrants, which could reduce prices by 20–50%, similar to trends observed in other inhaler therapies.
- Regulatory Pathways for Biosimilars: The FDA's recent approval pathways facilitate the entry of biosimilars, intensifying competition.
- Manufacturing Costs: Advances in inhaler device technology and supply chain efficiencies can influence production costs, potentially leading to price reductions.
- Healthcare Policy and Pricing Regulations: Increasing focus on drug affordability and value-based pricing may further pressure manufacturers to lower prices.
Projected Price Trajectories (2023–2030)
| Year | Price Range (USD) | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $45 per inhaler | Brand dominance; limited biosimilar competition |
| 2024–2025 | $42–$45 | Pending patent challenges; increasing competition |
| 2026–2027 | $30–$40 | Patent expirations initiate biosimilar market entry |
| 2028–2030 | $25–$35 | Market saturation; price stabilization/settling |
Note: These projections assume steady market growth, no major regulatory shifts, and proportional adoption of biosimilars.
Market Opportunities and Challenges
Opportunities
- Emerging Markets Expansion: Growing healthcare infrastructure in Asia, Latin America, and Africa creates new avenues for inhaler sales.
- Combination Therapies: Developing combination inhalers involving Levalbuterol could foster incremental revenue.
- Digital Health Integration: Incorporation of smart inhalers and adherence monitoring can enhance patient outcomes and justify premium pricing.
Challenges
- Pricing Pressure: Payer negotiations and governmental policies aimed at drug cost containment could suppress prices.
- Generic Competition: Entry of generic or biosimilar products is likely to significantly reduce market margins.
- Formulation Innovations: Tailoring inhaler devices for convenience and adherence remains essential to maintaining market share.
Regulatory and Patent Considerations
Patent landscapes suggest that the primary patents on Levalbuterol Tar HFA are set to expire between 2025 and 2027, with orphan drug exclusivities possibly extending some protections. Regulatory agencies are increasingly scrutinizing inhaler device designs, which may influence future approvals and reformulations.
Conclusion
Levalbuterol Tar HFA occupies a vital position in the respiratory therapeutics market with steady demand driven by the global respiratory disease burden. While current pricing is resilient due to brand loyalty and clinical differentiation, upcoming patent expirations and regulatory trends are poised to catalyze significant price declines over the next five years. Stakeholders should carefully monitor patent cliffs, biosimilar development pipelines, and healthcare policy shifts to navigate the evolving competitive landscape effectively.
Key Takeaways
- The global respiratory disease burden fuels sustained demand for Levalbuterol Tar HFA, maintaining its market relevance.
- Current pricing benchmarks average around $45 per inhaler, with projections indicating potential reductions to $25–$35 following patent expirations.
- Patent expiries around 2025–2027 are critical inflection points, likely ushering in biosimilar competition and significant price erosion.
- Market expansion into emerging markets and integration with digital health solutions present growth opportunities.
- Regulatory, patent, and reimbursement landscapes are key determinants influencing future pricing and market share.
FAQs
1. When are the patents for Levalbuterol Tar HFA expected to expire?
Patent protections are anticipated to expire between 2025 and 2027, opening the market to biosimilars and generics.
2. How will biosimilar entry impact the market price of Levalbuterol Tar HFA?
Biosimilar competition is projected to lower prices by 20–50%, significantly reducing brand market share and increasing price sensitivity.
3. Are there significant regulatory hurdles for biosimilars of Levalbuterol?
Yes, biosimilars must meet FDA standards for safety, efficacy, and interchangeability, which can delay market entry but are facilitated by recent regulatory pathways.
4. What strategies can pharmaceutical companies adopt to maintain market share?
Investing in device innovation, expanding into emerging markets, and integrating digital adherence tools can counteract pricing pressures.
5. Is Levalbuterol Tar HFA used for indications beyond asthma and COPD?
Currently, its primary approved indications are for bronchospasm related to asthma and COPD; off-label uses are minimal and not broadly authorized.
Sources
[1] GINA Report, 2022. Global Initiative for Asthma.
More… ↓
