Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for KARIVA
✉ Email this page to a colleague
Average Pharmacy Cost for KARIVA
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
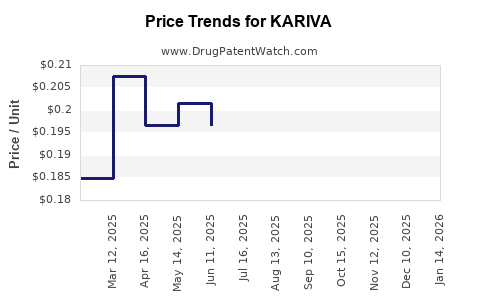
| KARIVA 28 DAY TABLET | 00555-9050-79 | 0.18537 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| KARIVA 28 DAY TABLET | 00555-9050-58 | 0.18537 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| KARIVA 28 DAY TABLET | 00555-9050-79 | 0.20291 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for KARIVA
Introduction
KARIVA, a popular oral contraceptive marketed predominantly in North America, combines ethinyl estradiol and desogestrel to prevent pregnancy. As a leading product in reproductive health, understanding its market landscape and future pricing trends is vital for pharmaceutical stakeholders, healthcare providers, and investors. This analysis delves into the current market positioning of KARIVA, competitive dynamics, regulatory considerations, and offers price projections grounded in market data and industry trends.
Market Overview
Product Profile and Market Positioning
KARIVA is a generically marketed oral contraceptive, initially developed by NDA Group, and later acquired by other manufacturers such as Allergan (now part of AbbVie). Its formulation, involving desogestrel—a progestin with minimal androgenic activity—appeals to women seeking effective contraception with a favorable side-effect profile.
Its differentiation primarily hinges on its pharmacokinetics and safety profile, positioning it as an alternative to other combination oral contraceptives (COCs). Its inclusion in prescription formularies worldwide sustains its market presence despite fierce competition from both branded and generic equivalents.
Market Size and Growth
The global oral contraceptive market was valued at approximately USD 8.2 billion in 2022, with North America accounting for significant share—around 32%—driven by high contraceptive use and healthcare accessibility [[1]]. The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of roughly 4.3% through 2030, propelled by increased awareness, broader insurance coverage, and ongoing demand for safe, reliable birth control options [[2]].
In North America alone, the contraceptive market—including pills, intrauterine devices, and patches—is expected to surpass USD 3 billion by 2027 [[3]]. KARIVA, as a widely prescribed generic, benefits from this expanding market, especially amid growing consumer preference for cost-effective alternatives.
Competitive Landscape
Brand and Generic Competition
KARIVA faces mounting competition from both branded products like Yasmin (also containing desogestrel) and other generics such as Generess Fe and Apri. Since the expiration of key patents or exclusivities, generic manufacturers have increased their market share, exerting downward pressure on prices.
Additionally, long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs), including intrauterine devices (IUDs) and implants, are gaining popularity, potentially limiting growth for oral contraceptives. Nevertheless, oral pills remain the preferred choice for many due to ease of use and lower upfront costs.
Regulatory Factors and Market Access
Regulatory policies influence KARIVA’s market penetration. Recent FDA guidelines emphasizing safety profiles, especially regarding risks of thromboembolism and hormone-related adverse effects, have led to updated prescribing information and potential formulary restrictions [[4]].
Insurance coverage adds another layer. Favorable reimbursement policies, including Medicare and private insurance, bolster accessibility, sustaining market presence for generic formulations like KARIVA.
Pricing Dynamics
Current Pricing Landscape
Modern generic oral contraceptives like KARIVA typically retail for USD 20–USD 50 per pack in the U.S., depending on pharmacy discounts and insurance coverage [[5]]. Out-of-pocket costs hover around USD 30–USD 45 for insured patients, with uninsured women often paying higher prices.
Brand-name equivalents may command a premium, with some branded products costing USD 60–USD 80 per pack, although insurance often mitigates this disparity.
Factors Influencing Price Trends
Multiple factors shape KARIVA's pricing trajectory:
- Patent Expirations and Generic Entry: As patents for desogestrel-containing contraceptives expire, increased generic competition suppresses prices.
- Regulatory Changes: Safety warnings or label updates can influence prescribing patterns and costs.
- Market Penetration: Increasing adoption in emerging markets can lead to price stabilization or slight decreases due to volume growth.
- Healthcare Policy: Reimbursement modifications and formulary placements can either restrict or expand access, impacting prices.
- Manufacturing Costs: Raw material prices for hormones and excipients influence production costs and subsequent pricing.
Price Projections
Short-term (1–3 years):
Given current competition among generics and regulatory factors, the average retail price for KARIVA is expected to stabilize around USD 20–USD 35 per pack. Discounting trends and increased market penetration are likely to exert downward pressure, particularly as more generics enter the market.
Medium to long-term (4–10 years):
As patent protections for many comparable oral contraceptives lapse and biosimilar-like competition intensifies, prices could further decline by approximately 10–20%. Should new formulations or delivery systems (e.g., low-dose or novel progestins) gain prominence, KARIVA's relative market share might diminish, further influencing its pricing.
However, factors such as inflation, raw material costs, and regulatory stringency may moderate this decline. A conservative estimate suggests an average price point of USD 15–USD 25 per pack by 2030, primarily driven by consolidation among generic manufacturers and increased bargaining power of payers.
Implications for Stakeholders
- Manufacturers: Emphasize cost efficiency and differentiation through adherence to safety profiles to sustain margins amid declining prices.
- Healthcare Providers: Focus on cost-conscious prescribing, balancing efficacy with affordability, especially for insured populations.
- Investors: Monitor generic market entry timelines and patent expirations to gauge long-term profitability trends.
- Policy Makers: Consider regulations fostering fair pricing while ensuring access to safe contraceptive options.
Key Takeaways
- KARIVA holds a stable position within North America's expanding contraceptive market, buoyed by general acceptance and insurance coverage.
- Competitive pressures from generics are likely to drive prices downward, with a projected decline to USD 15–25 per pack by 2030.
- Regulatory landscape and healthcare policies significantly influence market access and pricing strategies.
- The rise of alternative contraceptive methods may temper long-term growth, emphasizing the need for differentiation and cost competitiveness.
- Stakeholders should leverage market data and regulatory trends to optimize pricing, marketing, and distribution strategies for KARIVA.
FAQs
1. How does KARIVA compare to other oral contraceptives in terms of efficacy?
KARIVA’s efficacy aligns with standard combination pills, averaging a typical-use failure rate of approximately 9% per year. Its formulation with desogestrel offers a favorable profile regarding androgenic effects, making it a preferred choice for certain users.
2. What factors could significantly impact KARIVA’s future pricing?
Patent expirations, increased generic competition, regulatory safety warnings, and shifts in healthcare reimbursement policies are primary factors influencing future price points.
3. Is KARIVA available outside of North America, and how does its pricing vary internationally?
Availability outside North America is limited. In regions where it is marketed, pricing depends on local regulations, import tariffs, and distribution costs, often resulting in higher or lower retail prices compared to the U.S.
4. Are there any upcoming regulatory changes that could affect KARIVA’s market?
Potential FDA updates regarding hormonal contraceptives’ safety standing could influence prescribing habits and formulary inclusion, indirectly affecting market dynamics and pricing.
5. How might emerging contraceptive technologies affect KARIVA's market share?
Advancements like long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs) and non-hormonal options pose competitive threats, especially if they demonstrate superior efficacy, safety, and patient adherence, potentially reducing the demand for oral pills like KARIVA.
References
- MarketWatch. Global Contraceptive Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report. 2022.
- Grand View Research. Oral Contraceptives Market Forecast & Trends. 2023.
- Allied Market Research. North America Contraceptive Market Outlook. 2022.
- FDA. Updates on Hormonal Contraceptive Safety Guidelines. 2022.
- GoodRx. Oral Contraceptive Prices and Discounts Analysis. 2023.
More… ↓
