Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for ISOSORBIDE MONONIT ER
✉ Email this page to a colleague
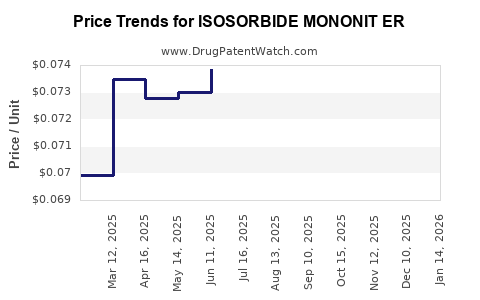
Average Pharmacy Cost for ISOSORBIDE MONONIT ER
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISOSORBIDE MONONIT ER 120 MG | 42799-0960-01 | 0.18334 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| ISOSORBIDE MONONIT ER 120 MG | 23155-0628-01 | 0.18334 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| ISOSORBIDE MONONIT ER 60 MG TB | 62135-0587-90 | 0.09751 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Isosorbide Mononitrate ER
Overview of Isosorbide Mononitrate ER
Isosorbide mononitrate extended-release (ER) is a prescription nitrate primarily prescribed for the management of chronic angina pectoris, a condition caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. As a long-acting nitric oxide donor, it alleviates chest pain by vasodilation, reducing myocardial oxygen demand. Approved by regulatory authorities such as the FDA, it occupies a significant niche within the cardiovascular therapeutics segment. The drug's unique extended-release formulation offers consistent plasma drug levels, improving patient adherence and outcomes.
Market Landscape
Global Market Size and Trends
The global cardiovascular drugs market is projected to reach approximately $97 billion by 2025, driven by increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), aging populations, and expanding healthcare access (GlobalData, 2022). Within this domain, nitrates like isosorbide mononitrate ER constitute a substantial segment owing to their chronic management application.
The demand for once-daily formulations such as ER tablets is rising globally, especially in North America and Europe, where healthcare standards emphasize patient convenience and adherence. Emerging markets—namely China, India, and Latin America—are experiencing accelerated growth due to increased CVD incidence and improving healthcare infrastructure.
Key Market Players
Major pharmaceutical companies, including Mylan (now part of Viatris), Teva, Sun Pharma, and pharmaceutical subsidiaries of Pfizer and Bayer, manufacture generic and branded formulations of isosorbide mononitrate ER. Patent expirations, typically around 2024-2026, have intensified generic competition, leading to price erosion and market commoditization.
Regulatory and Patent Dynamics
The original patent for the branded product expired in key markets, prompting a surge in generic entrants. Regulatory pathways such as the abbreviated new drug application (ANDA) in the U.S. facilitate rapid generic market entry, raising pricing pressures but also expanding access. Biosimilar or alternative nitrate formulations are less relevant given the molecule's chemical nature.
Market Drivers and Constraints
Drivers
- Rising CVD Prevalence: Globally, CVD remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality, with an estimated 523 million people affected worldwide (WHO, 2021). This sustains consistent demand for nitrates.
- Generic Penetration: Post-patent expiry, generics supply over 80% of prescriptions, substantially reducing costs and expanding patient access.
- Improved Formulations: Extended-release formulations improve patient compliance, reinforcing prescription rates.
- Aging Demographics: Elderly populations are more susceptible to angina, further propelling demand.
Constraints
- Pricing Pressures: Generic competition has led to significant price drops, impacting revenue streams for manufacturers.
- Market Saturation: High availability of generic alternatives limits pricing power and profit margins.
- Side-Effect Profile: Adverse effects such as headaches and hypotension may impact market uptake, especially in sensitive patient groups.
- Regulatory Variability: Differing regulatory standards across regions influence market entry timelines and costs.
Price Projections
Historical Pricing Trends
Historically, the price per unit of branded isosorbide mononitrate ER tablets has ranged from $10 to $30 for a 30-day supply, depending on formulation strength and geography. Following patent expiration, generic prices have plummeted by 50–80%, with some markets witnessing prices as low as $2–$5 per month.
Short-Term Future (Next 2-3 Years)
Given the current patent cliff, a significant price reduction is anticipated. Generic competition will intensify, leading to a projected decline of approximately 20–30% annually in prices across North America and Europe. For instance, the average wholesale price (AWP) for 30 tablets of 30 mg ER is expected to stabilize around $3–$4 by 2024.
Medium to Long-Term Outlook (3-7 Years)
As patent exclusivity diminishes further and biosimilars or alternative formulations become available, prices are expected to plateau. Market forecasts suggest stabilization around $2–$3 per 30-day supply, with a potential further decrease as manufacturing efficiencies improve and production scales up.
In emerging markets, less price erosion is expected, owing to regulatory delays and affordability constraints, maintaining prices at approximately $5–$8 for comparable supplies.
Pricing Influencers
- Regulatory Approvals of Generics: Accelerated approvals intensify price competition.
- Market Penetration of Generics: Increased access drives prices down.
- Healthcare Policy and Reimbursement: Reimbursement schemes favor low-cost generics, pressuring list prices.
- Supply Chain Dynamics: Manufacturing capacity and supply chain efficiency impact pricing.
Competitive Dynamics and Market Opportunities
The entry of multiple generics has created a highly competitive environment. While branded formulations face erosion, niche opportunities exist in specialized formulations, combination therapies, and developing or licensing novel delivery systems. Furthermore, partnerships with payers to ensure formulary inclusion can sustain revenues during transitional periods.
Risks and Uncertainties
- Regulatory Delays: Post-patent expiry, regulatory delays or legal challenges can temporarily stabilize prices.
- Market Adoption: Physician and patient acceptance of cheaper generics hinges on perceptions of efficacy and safety.
- Pricing Regulations: Political and regulatory initiatives aiming to control drug prices may suppress future price potential.
Conclusion and Strategic Recommendations
The outlook for isosorbide mononitrate ER aligns with typical patterns of cardiovascular patent expiries: a shift toward commoditization and declining prices. To maximize value, stakeholders should focus on optimizing manufacturing efficiencies, expanding licensing opportunities, and pursuing differentiated formulations or clinical positioning.
Key strategic insights include:
- Preparing for significant price erosion post-patent expiry.
- Focusing on markets with delayed generic entry or limited competition.
- Innovating through alternative delivery mechanisms to extend product lifecycle.
- Engaging with payers for formulary inclusion to maintain market share.
Key Takeaways
- The global demand for isosorbide mononitrate ER remains robust, driven by the rising prevalence of CVD.
- Patent expirations and subsequent generic entries have reduced prices by up to 80% in mature markets.
- Price projections indicate annual declines of 20–30% over the next 2-3 years, stabilizing afterward.
- Competitive pressures emphasize the importance of cost-effective manufacturing and strategic market positioning.
- Emerging markets may sustain higher prices longer due to delayed generics and affordability constraints.
FAQs
1. How will patent expirations affect the market for isosorbide mononitrate ER?
Patent expirations will lead to increased generic competition, sharply reducing prices and squeezing profit margins for branded manufacturers. This transition typically results in a broader customer base adopting more affordable options, expanding access but challenging existing revenue streams.
2. Are there potential growth opportunities despite pricing pressures?
Yes. Developing differentiated formulations, combination therapies, or novel delivery systems can create niche markets. Strategic partnerships and licensing can also facilitate market expansion in emerging regions with less generic competition.
3. How does the patent landscape influence future pricing?
Patent protections delay generic entry, allowing for stable or higher prices. Once patents expire, widespread generic manufacturing drives prices down, with subsequent stabilization at significantly lower levels.
4. What regional differences impact the pricing of isosorbide mononitrate ER?
Healthcare policies, patent enforcement, regulatory approval timelines, and market maturity influence regional pricing. North America and Europe see earlier and steeper price declines due to advanced generic markets, while emerging regions may sustain higher prices longer.
5. What are the main risks facing manufacturers of isosorbide mononitrate ER?
The primary risks include aggressive generic competition, regulatory hurdles, changing reimbursement policies, and perceptions of efficacy or safety affecting market acceptance. External factors like patent litigation or supply chain disruptions also pose threats.
Sources:
[1] GlobalData. (2022). Cardiovascular Drugs Market Forecast.
[2] World Health Organization. (2021). Cardiovascular Disease Factsheet.
[3] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2022). ANDA Approvals.
More… ↓
