Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for ISONIAZID
✉ Email this page to a colleague
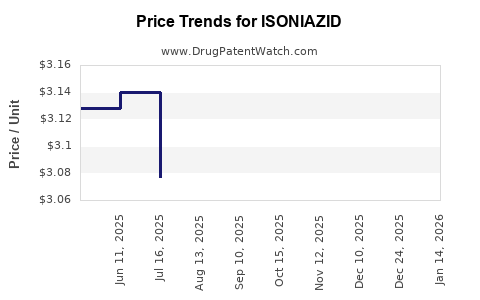
Average Pharmacy Cost for ISONIAZID
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISONIAZID 300 MG TABLET | 00555-0071-01 | 2.71956 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| ISONIAZID 300 MG TABLET | 00555-0071-02 | 2.71956 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| ISONIAZID 100 MG TABLET | 00555-0066-02 | 1.61163 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| ISONIAZID 300 MG TABLET | 51079-0083-01 | 2.71956 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| ISONIAZID 100 MG TABLET | 64950-0216-10 | 1.61163 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| ISONIAZID 300 MG TABLET | 81665-0108-30 | 2.71956 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Isoniazid
Introduction
Isoniazid (INH) remains a cornerstone in tuberculosis (TB) management, especially as part of first-line therapy for active and latent TB infections. Its developmental history dates back over six decades, and despite advances in TB therapeutics, Isoniazid maintains a pivotal position globally, especially in low- and middle-income countries. However, the evolving landscape of TB treatment, rising resistance, and market dynamics necessitate meticulous analysis and forward-looking price projections for stakeholders across pharmaceutical manufacturing, healthcare, and investment domains.
Market Overview
Global Burden of Tuberculosis and Implications for Isoniazid Demand
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), TB caused approximately 1.5 million deaths in 2021, making it one of the top infectious disease killers worldwide [1]. The WHO's End TB Strategy emphasizes widespread use of effective anti-TB medicines, with Isoniazid serving as a key component due to its efficacy, affordability, and availability.
The global TB pipeline indicates persistent demand for Isoniazid, especially in countries with high disease prevalence such as India, Indonesia, China, and parts of Africa. Despite ongoing research for novel therapeutics, Isoniazid's role is unlikely to diminish significantly in the near term, owing to its established efficacy and low cost.
Market Segmentation
The TB drug market can be segmented into:
- First-line regimens: Primarily comprising Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Pyrazinamide, and Ethambutol.
- Second-line treatments: Used in resistant forms, including drugs like fluoroquinolones, bedaquiline, and linezolid.
- Latent TB infection (LTBI) management: Prophylactic regimens where Isoniazid remains a standard choice.
Global demand for Isoniazid is driven predominantly by the published TB treatment guidelines, with 100+ countries relying on government procurement systems and international aid programs such as the Global Fund.
Market Dynamics and Competitive Landscape
Market Players
The Isoniazid supply chain is characterized by a limited number of generic manufacturers, as patent exclusivity largely expired decades ago. Major producers include:
- Ferozsons Laboratories (Pakistan)
- Mylan (India)
- Lupin (India)
- Dr. Reddy's Laboratories (India)
- Glenmark Pharmaceuticals (India)
These firms primarily produce WHO-prequalified generic formulations, ensuring broad global reach.
Regulatory and Quality Standards
Adherence to WHO prequalification and South Asia-focused pharmacopeial standards (e.g., Indian Pharmacopoeia) is essential for market access, especially for procurement agencies in low-income countries.
Impact of Resistance and Emerging Challenges
Rising cases of Isoniazid-resistant TB (estimated at 4.7% among new cases globally) threaten to reduce reliance on monotherapy and necessitate combination regimens that may alter demand patterns temporarily [2].
Furthermore, the development of novel drugs and shorter regimens, such as the BPaL (Bedaquiline, Pretomanid, and Linezolid) regimen, could impact Isoniazid's prominence over extended periods, but current data suggest sustained demand.
Price Analysis
Historical Pricing Trends
Historically, Isoniazid has been available at extremely low prices, driven by the generic market and high-volume procurement. For example:
- India: Average government procurement prices in 2021 ranged between $0.02 to $0.05 per 300 mg tablet [3].
- Global: WHO reports a median price of $0.04 per tablet for quality-assured generics in 2022.
This low-cost structure supports extensive use but leaves minimal room for significant price variation under current therapeutic paradigms.
Price Determinants
- Manufacturing costs: Arbitrarily low, with economies of scale dominating.
- Regulatory compliance: Slightly higher costs for WHO prequalification.
- Market competition: Numerous manufacturers drive prices downward.
- Procurement strategies: Large-volume, government-led bulk purchasing further suppresses unit costs.
Future Price Projections
Given the entrenched generic manufacturing base, future prices are expected to remain stable or decline marginally, driven by:
- Increased competition: Entry of new generic manufacturers, especially in Africa and Southeast Asia.
- Technological advances: Process improvements reducing manufacturing costs.
- Global procurement policies: Continuation of price ceilings and procurement come with tendering mechanisms favoring lowest bids.
Projected future unit prices for quality-assured Isoniazid tablets are likely to hover around $0.02 to $0.03 per 300 mg tablet over the next 5 years.
Market Drivers and Constraints
Drivers
- Global TB burden: Persistent demand sustains market volume.
- International funding: Initiatives such as the WHO's End TB Strategy and Global Fund support procurement.
- Combination regimens: Continued inclusion in standard therapy frameworks maintains essentiality.
- Regulatory adherence: WHO prequalification and national tender systems favor standardized, affordable generics.
Constraints
- Resistance development: Rising resistance could necessitate combination therapies that alter demand.
- Innovation stagnation: Lack of new formulations or improved delivery systems may limit growth.
- Price sensitivity: Governments and NGOs prioritize low-cost medicines, keeping prices under downward pressure.
- Market consolidation: Limited number of manufacturers, with potential for monopolistic practices or supply chain disruptions.
Conclusion and Outlook
Isoniazid's market remains heavily reliant on generic formulations supplied predominantly from Asia, notably India and Pakistan. The product's essential role in TB therapy, combined with a robust manufacturing infrastructure, ensures stable demand and low pricing. Despite challenges such as emerging drug resistance and evolving treatment paradigms, Isoniazid's price trajectory is expected to remain relatively flat or trend downward slightly, driven by competition and procurement efficiencies.
For investors and healthcare policymakers, maintaining access to affordable Isoniazid is vital. Strategic partnerships, ongoing quality assurance, and inclusion in global health initiatives will support market stability. Innovations in drug delivery or resistance management may influence future demand dynamics but are unlikely to significantly impact the core low-price, high-volume market in the near term.
Key Takeaways
- Persistent global demand for Isoniazid ensures its continued relevance as a foundational TB treatment.
- Pricing remains low, averaging around $0.02–$0.03 per 300 mg tablet, driven by fierce generic competition and procurement policies.
- High-quality manufacturing and regulatory compliance (e.g., WHO prequalification) are key to market access.
- Emerging drug resistance and development of combination regimens could influence demand, but impact remains moderate in the short term.
- Market stability is underpinned by international funding, public health priorities, and the entrenched role of Isoniazid in TB management.
References
[1] WHO. Global Tuberculosis Report 2022. World Health Organization.
[2] WHO. Global Tuberculosis Report 2022 – Resistance Data.
[3] Drugs.com. Price Trends for Isoniazid (2021-2022).
More… ↓
