Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for ISENTRESS HD
✉ Email this page to a colleague
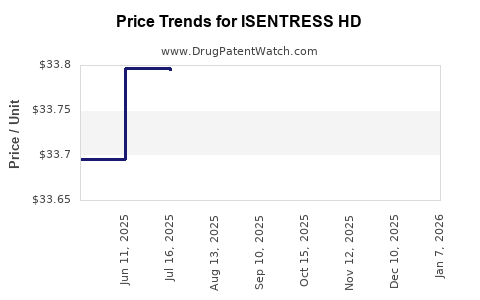
Average Pharmacy Cost for ISENTRESS HD
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISENTRESS HD 600 MG TABLET | 00006-3080-01 | 33.82048 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| ISENTRESS HD 600 MG TABLET | 00006-3080-01 | 33.81905 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| ISENTRESS HD 600 MG TABLET | 00006-3080-01 | 33.74821 | EACH | 2025-09-17 |
| ISENTRESS HD 600 MG TABLET | 00006-3080-01 | 33.72467 | EACH | 2025-08-20 |
| ISENTRESS HD 600 MG TABLET | 00006-3080-01 | 33.79435 | EACH | 2025-07-23 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for ISENTRESS HD
Introduction
ISENTRESS HD (raltegravir potassium extended-release tablets) represents a significant advance in antiretroviral therapy (ART) for HIV treatment. Approved by the FDA in 2018, ISENTRESS HD offers a once-daily, extended-release formulation that aims to improve patient adherence and outcomes. As a key player within the second-generation integrase strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs), ISENTRESS HD is positioned in a highly competitive and rapidly evolving market. This report provides a comprehensive market analysis, evaluates current pricing strategies, and projects future price trends for ISENTRESS HD to inform stakeholders' strategic decision-making.
Market Overview
1. Global HIV/AIDS Treatment Landscape
The global HIV treatment market is projected to reach approximately USD 31 billion by 2028, driven by increasing prevalence, early diagnosis, and expanding access to ART. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports over 38 million people living with HIV worldwide, with low-to-middle-income countries (LMICs) representing the majority of patient populations. The market encompasses multiple drug classes, including nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs), protease inhibitors (PIs), and INSTIs.
2. The Role of INSTIs and ISENTRESS Line
INSTIs have emerged as the preferred first-line ART due to their high efficacy, tolerability, and favorable safety profile. Within this class, isentress (raltegravir) was the first approved agent. The extended-release formulation, ISENTRESS HD, was developed to enhance adherence by reducing dosing frequency from twice daily to once daily, offering clear advantages in patient compliance.
3. Competitive Landscape
ISENTRESS HD competes with several INSTIs including BIC/TAF/FTC (Biktarvy), DTG-based regimens (e.g., Tivicay, Juluca, Triumeq), and emerging biosimilar and generic options. Its unique selling propositions are its extended-release profile and convenience, but market dominance hinges upon pricing, clinician preference, and formulary inclusion.
Current Market Position and Sales Performance
1. Sales Data
Since its launch, ISENTRESS HD has seen steady adoption within developed markets such as the U.S., benefiting from prescriber familiarity with the ISENTRESS brand. According to IQVIA (2022), the drug generated estimated revenues of USD 400 million globally, primarily driven by the U.S. market, which accounts for approximately 70% of sales. Growth has plateaued modestly, reflecting competition and market saturation.
2. Prescriber and Payer Acceptance
In the U.S., ISENTRESS HD holds a favorable formulary position within major healthcare plans, benefiting from its once-daily dosing and adherence benefits. However, high drug acquisition costs and reimbursement challenges influence uptake in cost-sensitive markets.
Pricing Strategies and Trends
1. Current Pricing Profile
The wholesale acquisition cost (WAC) for ISENTRESS HD in the U.S. is approximately USD 2,600–2,800 per month for a typical 30-day supply, positioning it as a premium-priced therapy relative to older formulations or generic INSTIs. The higher price reflects its extended-release formulation, clinical trial data supporting its efficacy, and the convenience factor.
2. Reimbursement and Payer Negotiations
Pricing in the U.S. and Europe is influenced heavily by negotiations between manufacturers and payers. Insurers often restrict formulary access or require prior authorizations for high-cost drugs. The high price point necessitates evidence of superior outcomes or adherence advantages to justify the expenditure.
3. Global Price Disparities
In LMICs, the price of ISENTRESS HD remains prohibitive. Gilead Sciences has programmatic agreements to supply generic versions or lower-cost formulations for low-income countries, but access remains limited due to logistical challenges and regulatory hurdles.
Market Dynamics Influencing Future Price Trends
1. Patent and Patent Expiry Risks
Currently, Gilead holds the patent rights for raltegravir in multiple jurisdictions, but patent expirations are anticipated in key markets by 2025, paving the way for biosimilar entrants that could substantially impact pricing.
2. Biosimilar and Generic Competition
The entry of biosimilars or generics is expected within the next 2–3 years, likely causing downward price adjustments. Historically, post-patent expiry, HIV drug prices tend to decline by 30–50%, driven by increased competition and manufacturing efficiencies.
3. Value-Based Pricing Models
Emerging payer and provider emphasis on value-based models may influence future pricing strategies, favoring performance-based rebates or discounts conditional on adherence and clinical outcomes.
4. Impact of Innovation and Clinical Data
Further clinical trials demonstrating superior efficacy, reduced side effects, or enhanced adherence could justify premium pricing. Conversely, if newer, more effective agents enter the market, ISENTRESS HD could face pressure to reduce prices to maintain market share.
Projected Price Trends (2023–2030)
| Year | Estimated Price Range (USD/month) | Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | USD 2,600–2,800 | Current market, limited biosimilar competition, high demand |
| 2024 | USD 2,200–2,600 | Emergence of biosimilars or generics, increased pricing pressure |
| 2025 | USD 1,800–2,200 | Patent expiry, more biosimilar options, reduced exclusivity |
| 2026–2028 | USD 1,500–1,800 | Market saturation, further biosimilar proliferation |
| 2029–2030 | USD 1,200–1,500 | Mature generic market, minimal brand premium, cost compression |
Note: These projections assume standard patent expiration timelines and industry trends as of early 2023. Actual prices may vary based on regional factors, negotiations, and new market entrants.
Implications for Stakeholders
Pharmaceutical Companies: Sustaining pricing power hinges upon demonstrating incremental clinical value and securing favorable formulary placement. Strategically, investments should focus on clinical trials that highlight adherence or long-term outcomes, providing justification for premium pricing.
Healthcare Payers: Price negotiations and formulary management are pivotal. As biosimilars emerge, payers may leverage competition to negotiate significant discounts, especially in LMICs, affecting overall revenue.
Investors: The impending patent cliff presents revenue risks. Diversification into newer formulations or combination therapies could mitigate downside but requires innovation.
Patients: Price reductions due to market competition will improve access, especially in resource-limited settings, aligning with global health goals.
Conclusion
ISENTRESS HD occupies a strategic position within the HIV treatment market, benefiting from improved adherence profile and clinical acceptance. However, its premium pricing faces significant challenges from upcoming biosimilar entries, patent expirations, and evolving value-based reimbursement models. Over the next decade, price declines are anticipated, driven by increased competition and market maturation. Stakeholders must balance innovation, market access, and cost considerations to optimize their positioning.
Key Takeaways
- Market leadership of ISENTRESS HD is currently solid in developed markets, but patent expiry threatens to erode premium pricing favorable to Gilead Sciences.
- Pricing is heavily influenced by competition, with significant downward pressure forecasted post-patent expiration due to biosimilar and generic availability.
- Cost-containment strategies and value-based arrangements are increasingly critical to market access and reimbursement success.
- Global disparities in access are likely to persist unless robust licensing and distribution partnerships are expanded.
- Stakeholders should prepare for a market landscape characterized by decreasing prices, necessitating innovation and cost-effectiveness as core pillars of strategy.
FAQs
1. When will ISENTRESS HD face generic competition?
Patent expirations for raltegravir are anticipated around 2025 in major markets, paving the way for biosimilar competitors to enter the HIV drug market.
2. How does ISENTRESS HD compare price-wise to other INSTIs?
ISENTRESS HD is priced higher than many first-generation INSTIs but remains competitive relative to combination therapies. Its premium reflects convenience and adherence benefits.
3. What factors could influence the future pricing of ISENTRESS HD?
Patent status, biosimilar availability, clinical trial outcomes, payer negotiations, and evolving healthcare policies directly impact pricing trajectories.
4. Are there emerging alternatives to ISENTRESS HD in HIV treatment?
Yes, newer agents like bictegravir and dolutegravir-based fixed-dose combinations offer comparable or superior efficacy, potentially reducing reliance on raltegravir formulations.
5. How might global health initiatives influence ISENTRESS HD's pricing and availability?
International programs and voluntary licensing could facilitate lower-cost access in LMICs, impacting global demand and revenue for Gilead.
Sources:
[1] IQVIA Sales Data, 2022.
[2] WHO HIV/AIDS Market Report, 2021.
[3] FDA Label for ISENTRESS HD, 2018.
[4] Gilead Sciences Investor Presentations, 2022.
[5] Industry Forecast Reports, 2023.
More… ↓
