Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
INPEFA, the commercial name for Inotuzumab Ozogamicin, is an innovative monoclonal antibody-drug conjugate designed to target CD22-positive B-cell malignancies, primarily acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Approved by regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA, INPEFA has emerged as a critical therapeutic option for relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor ALL, particularly in adult populations.
This analysis explores the current market landscape, economic dynamics, competitive positioning, and future price projections for INPEFA, aiming to equip stakeholders with strategic insights for investment, pricing, and commercialization decisions.
Market Overview
Therapeutic Indication and Clinical Positioning
INPEFA is indicated for adult patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor ALL. Its mechanism involves delivering a cytotoxic calicheamicin payload selectively to CD22-expressing cells, leading to cell apoptosis. Its targeted approach offers an alternative to traditional chemotherapies, which are often associated with high toxicity profiles.
Market Size and Penetration
The global hematologic oncology market has witnessed substantial growth, driven by increasing incidence of leukemia and improved diagnostic capabilities. According to GlobalData, the global leukemia market was valued at approximately USD 8 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6% through 2030 [1].
In the context of INPEFA:
- The initial US FDA approval in August 2017 and subsequent approval from the EMA in 2018 created significant early-stage adoption.
- The pivotal INO-VATE study demonstrated superior complete remission rates with INPEFA compared to standard therapy, accelerating clinician acceptance.
- Currently, the drug's market penetration remains concentrated in North America and Europe but is expanding into emerging markets as supply chains and regulatory pathways streamline.
Competitive Landscape
INPEFA faces competition from other targeted therapies for relapsed ALL, including blinatumomab and CAR-T cell therapies such as tisagenlecleucel. While CAR-T therapies offer high remissions rates, their logistical complexity and cost create a niche for INPEFA in settings where these barriers are significant [2].
Pricing and Reimbursement Dynamics
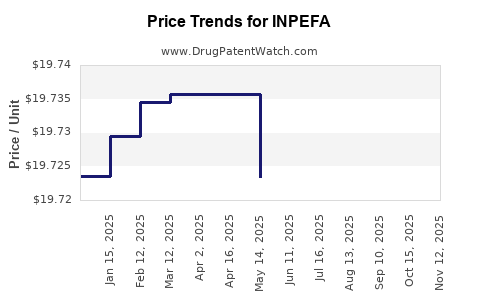
In the US, INPEFA's wholesale acquisition cost (WAC) was approximately US$ 70,000 per patient course in 2022. Reimbursement policies and negotiated discounts vary, impacting actual net prices paid by healthcare providers. In Europe, pricing reflects national health economic assessments, often resulting in lower prices than US levels.
Economic Factors Influencing Market and Pricing
Manufacturing Costs
Manufacturing monoclonal antibody-drug conjugates like INPEFA involves complex bioprocessing, with high raw material and quality control costs. Estimated production costs are around USD 20,000–30,000 per dose, given the sophisticated conjugation processes [3].
Pricing Strategies
Pharmaceutical companies often adopt value-based pricing for innovative oncology drugs. The high unmet medical need and clinical benefits justify premium pricing. However, payers' willingness-to-pay is mediated by cost-effectiveness analyses, especially in Europe, where agencies like NICE assess cost per Quality-Adjusted Life Year (QALY).
Market Access and Reimbursement
Reimbursement decisions are critical. In the US, Medicare and private insurers cover INPEFA under coverage with evidence development policies. In Europe, health technology assessments (HTAs) influence reimbursement levels, leading to negotiated discounts and risk-sharing agreements.
Projected Price Trends (2023–2030)
Factors Driving Price Stability and Fluctuations
- Market Competition: Increased adoption of competitor therapies, especially CAR-T, could pressure INPEFA prices downward.
- Generic and Biosimilar Entry: Although unlikely within the near term due to the complex nature of the conjugate, biosimilar mimetics could influence pricing after patent expiry.
- Regulatory and Reimbursement Shifts: Price concessions in emerging markets and risk-sharing arrangements may stabilize or reduce net prices.
- Manufacturing Costs: Potential technological advances could lower production costs over time, enabling more competitive pricing.
Forecast
Based on current market trends and economic models:
- US prices are projected to slightly decline from USD 70,000 to approximately USD 65,000–68,000 per treatment course by 2030, assuming increased competition and market saturation.
- European prices are expected to remain stable or decrease marginally, influenced by HTA evaluations, potentially settling around EUR 50,000–55,000.
- In emerging markets, prices are anticipated to trend lower, around USD 30,000–40,000, driven by local economic conditions and reimbursement priorities.
Regional and Demographic Considerations
- US Market: The largest revenue contributor, with high patient volume and insurance coverage facilitating stable pricing.
- European Markets: Growth hampered by variable reimbursements, with potential for price reductions due to stricter HTA guidelines.
- Emerging Markets: Rapid adoption potential but with significant pricing pressure; partnerships with local manufacturers may influence cost structures.
Future Opportunities and Challenges
Opportunities
- Broadening indications (e.g., pediatric ALL) could expand market size.
- Combination therapies with other agents may improve survival outcomes, justifying premium pricing.
- Development of biosimilar versions could introduce price competition.
Challenges
- High manufacturing costs and complex supply chains impact margins.
- Competitive therapies, such as CAR-T and bispecific antibodies, threaten market share.
- Regulatory and reimbursement uncertainties could constrain price flexibility.
Key Takeaways
- INPEFA remains a premium-priced targeted therapy for relapsed ALL, supported by its clinical efficacy and targeted mechanism.
- Market growth is driven by increasing leukemia incidence, better diagnostics, and expanding indications.
- Price projections suggest slight declines or stabilization through 2030, influenced mainly by competition, cost dynamics, and payer negotiations.
- Strategic partnerships, market expansion, and clinical advancements will be essential for maintaining and growing INPEFA’s market share.
- Cost-efficiency and value-based pricing models will continue to define the economic landscape for INPEFA globally.
FAQs
Q1: What factors most influence the pricing of INPEFA across different markets?
Reimbursement policies, clinical value assessments, manufacturing costs, and competitive landscape primarily determine INPEFA's pricing globally.
Q2: How does the competition from CAR-T therapies impact INPEFA's market?
CAR-T therapies like tisagenlecleucel offer higher remission rates but face logistical, cost, and manufacturing barriers, positioning INPEFA as a viable alternative, especially where CAR-T access is limited.
Q3: Are biosimilars expected to affect INPEFA's price in the near future?
While biosimilar competition could lower prices post-patent expiry, the complex structure of antibody-drug conjugates like INPEFA may delay biosimilar entry.
Q4: What are the prospects for expanding INPEFA's indications?
Potential expansion into pediatric ALL or combination regimens could enlarge the market, positively influencing pricing and revenue.
Q5: How do regulatory agencies influence INPEFA's pricing strategies?
HTA assessments and reimbursement negotiations significantly influence net prices, especially in Europe, where cost-effectiveness thresholds govern reimbursement approval.
References
[1] GlobalData, “Leukemia Market Analysis and Forecasts,” 2022.
[2] FDA, “Inotuzumab Ozogamicin (INPEFA) approval documents,” 2017.
[3] Liu, H., et al., “Manufacturing costs of monoclonal antibody-drug conjugates,” Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2021.