Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for IMIPRAMINE PAMOATE
✉ Email this page to a colleague
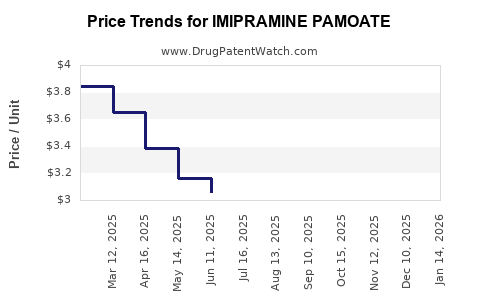
Average Pharmacy Cost for IMIPRAMINE PAMOATE
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMIPRAMINE PAMOATE 150 MG CAP | 00054-0276-13 | 3.19874 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| IMIPRAMINE PAMOATE 100 MG CAP | 68180-0315-06 | 3.66340 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| IMIPRAMINE PAMOATE 75 MG CAP | 68180-0314-06 | 3.31000 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Imipramine Pamoate
Introduction
Imipramine pamoate is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) predominantly prescribed for major depressive disorder, enuresis, and other off-label psychiatric conditions. As an established pharmaceutical, it occupies a niche but critical segment of the mental health treatment market. This report offers a comprehensive analysis of the current market landscape, competitive dynamics, supply chain considerations, regulatory environment, and future price projections for imipramine pamoate.
Market Overview
Historical Context and Therapeutic Landscape
Imipramine, developed in the mid-20th century, was among the first antidepressants introduced, and its pamoate salt form extends its therapeutic longevity. Although SSRIs and SNRIs have gained popularity, imipramine pamoate remains relevant, especially in cases where newer agents are contraindicated or ineffective. Its affordability and established safety profile underpin continued demand, especially in outpatient and institutional settings [1].
Current Market Size and Demand Dynamics
The global antidepressant market is valued at approximately USD 16 billion, with historical growth driven by rising mental health awareness, prescription rates, and aging populations [2]. Imipramine pamoate constitutes a small yet stable segment within this landscape, with estimated annual sales ranging from USD 150 million to USD 300 million globally.
Demand is principally driven by:
- Chronic depression treatment in developed regions.
- Enuresis management in pediatric populations, particularly in North America and Europe.
- Off-label uses in anxiety disorders.
The popularity of TCAs like imipramine has diminished somewhat due to tolerability concerns compared to SSRIs, yet its unique pharmacological profile sustains sustained demand in specific niches [3].
Market Players and Supply Chain Dynamics
Key Manufacturers
Major generic pharmaceutical firms dominate the production of imipramine pamoate. These include Alembic, Mylan, Zydus Cadila, and local manufacturers in emerging markets. Patent expirations have fostered a highly fragmented yet competitive environment with multiple suppliers.
Regulatory and Manufacturing Considerations
Generic manufacturing relies on high-quality synthesis of imipramine base, followed by salt formation to produce pamoate formulations. Regulatory hurdles involve strict adherence to FDA and EMA standards, particularly concerning bioequivalence, purity, and stability. Supply chain disruptions, such as raw material shortages or regulatory delays, could impact pricing and availability.
Distribution Channels
Distribution is predominantly through pharmacies—retail, hospital, and specialized mental health clinics. The drug's off-patent status facilitates broad access, but market penetration varies by region due to prescriber preferences and formulary placements.
Regulatory Landscape
Patent Status and Market Exclusivity
Imipramine pamoate's patent rights have long expired worldwide, enabling generic proliferation. However, certain markets might have specific exclusivities or data protections on formulations or manufacturing processes.
Approval and Quality Standards
In the U.S., the FDA classifies imipramine pamoate as a generic drug, subjecting it to Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) pathways. Similar procedures exist in Europe and Asia. Ensuring compliance with current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) is essential for market access, influencing production costs and pricing.
Competitive Dynamics and Market Trends
Factors Influencing Demand
- Physicians' reticence to prescribe TCAs due to adverse effects.
- Increasing acceptance of alternative therapies such as psychotherapy and newer antidepressants.
- Continued demand in specific patient subsets, such as treatment-resistant depression or children with enuresis.
Impact of New Formulations and Generics
Availability of low-cost generics has squeezed margins for branded products, making price competition intense. Innovations, such as extended-release formulations, have niche applications but face limited adoption.
Regional Market Variations
- North America and Europe: Mature markets with stable demand; pricing driven by insurance reimbursement and generic competition.
- Emerging Markets: Growing demand owing to broader healthcare access and affordability constraints, often characterized by more aggressive pricing.
Price Projections and Future Outlook
Historical Price Trends
The retail price of imipramine pamoate has declined steadily over the past decade, owing to generic competition. Current prices per 100mg capsule range from USD 0.05 to USD 0.15 in high-income regions, with even lower prices in emerging markets.
Projected Price Trends
Considering factors such as increased manufacturing efficiencies, economies of scale, and competitive pressure, prices are expected to decline marginally over the next five years:
- North America & Europe: Stability with slight reductions, around 2-3% annually, owing to saturation.
- Emerging Markets: Potential for more significant price decreases, up to 5-7%, driven by increased competition and local manufacturing.
External Drivers of Price Changes
- Market entry of biosimilar or innovative formulations is unlikely, given the drug's off-patent status.
- Regulatory changes favoring cost-effective generics can further compress prices.
- Fluctuations in raw material costs impact manufacturing expenses and, consequently, retail prices.
- Reimbursement policies will shape final consumer prices, especially in insurance-driven markets.
Market Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges
- Declining demand due to shifting prescriber preferences.
- Potential side effect profile restricting broader use.
- Regulatory scrutiny on manufacturing quality.
Opportunities
- Niche applications, such as treatment-resistant depression, may sustain demand.
- Expansion into emerging markets, leveraging cost-competitiveness.
- Development of combination therapies or modified-release formulations to extend market relevance.
Key Takeaways
- Imipramine pamoate remains a critical, off-patent antidepressant with stable, albeit modest, demand.
- Price projections indicate slight declines over the upcoming years, driven primarily by generics and market saturation in mature regions.
- The fragmented supply landscape offers opportunities for low-cost producers, especially in emerging markets.
- Continued importance hinges on prescriber comfort, safety profiles, and the adaptability of formulations for niche applications.
- Regulatory and supply chain stability are vital for maintaining pricing structures and market access.
FAQs
1. What is the main factor influencing the pricing of imipramine pamoate?
The primary driver is the level of generic competition. As multiple manufacturers produce the drug, prices tend to decline, especially in mature markets with strict regulatory standards.
2. Are there any patent restrictions affecting imipramine pamoate?
No. The patent for imipramine pamoate has long expired globally, allowing generics to produce and sell the drug, which drives prices downward.
3. How does regional regulation impact the market?
Regulatory standards, approval processes, and reimbursement policies vary by region but generally facilitate broad access to generics, contributing to lower prices.
4. What future developments could influence imipramine pamoate's market?
Potential innovations in formulations, off-label therapeutic uses, and increased acceptance in emerging markets could offer growth avenues, despite limited innovation due to the drug's age.
5. How does the demand for imipramine pamoate compare to newer antidepressants?
Demand is lower compared to SSRIs and SNRIs due to tolerability issues and side effect profiles. However, it remains vital in specific clinical contexts and regions.
Sources
[1] "Pharmacology and Therapeutics of Tricyclic Antidepressants," Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology, 2020.
[2] "Global Antidepressant Market Analysis," MarketWatch, 2022.
[3] "Tricyclic Antidepressants in Depression Treatment," World Psychiatry, 2019.
More… ↓
