Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
ILEVIRO, the brand name for Nepafenac, is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) primarily indicated for the treatment of postoperative ocular inflammation and pain following cataract surgery. Market dynamics for ILEVIRO hinge upon its clinical efficacy, competitive landscape, regulatory environment, and pricing strategies. With growing ophthalmic needs and advancements in surgical procedures, understanding ILEVIRO’s market potential and pricing trajectory is vital for stakeholders.
Market Landscape and Competitive Positioning
Current Market Size and Growth Drivers
The global ocular anti-inflammatory market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 4.2% from 2022 to 2028, driven by the increasing prevalence of cataract surgeries and the rising geriatric population.[1] Cataract surgeries, now more minimally invasive and prevalent worldwide, demand effective anti-inflammatory agents like Nepafenac to enhance postoperative recovery.
The U.S. remains the dominant market, accounting for nearly 50% of the global ophthalmic drug revenue, with expanding markets in Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Latin America. The development of generic versions of Nepafenac intensifies competitive pressure but also broadens market access.
Key Competitors
ILEVIRO's primary competitors include:
- Brand Name: Nevanac (Bausch + Lomb), marketed in various regions, with established clinical efficacy.
- Generics: Multiple generic versions of Nepafenac dominate price-sensitive markets, notably in India, China, and parts of Europe.[2]
- Alternatives: Other NSAIDs like bromfenac (e.g., Xibrom, BromSite) and corticosteroids (e.g., prednisolone) are used, though NepafenAC’s superior ocular penetration offers a competitive edge.[3]
Regulatory and Reimbursement Dynamics
The U.S. FDA approved ILEVIRO in 2018, with subsequent approvals in Europe and other markets. Reimbursement pathways via private insurers and government programs influence pricing strategies.
Regulatory trends favor increased access to innovative ophthalmic drugs. Price negotiations with payers, particularly in highly regulated markets, exert downward pressure on pricing.
Market Penetration and Adoption Trends
Adoption rates for ILEVIRO are increasingly favorable owing to:
- Clinical Efficacy: Superior ocular bioavailability compared to other NSAIDs.
- Safety Profile: Reduced systemic absorption minimizes adverse effects.
- Patient Compliance: Single-dose or convenient dosing regimens enhance adherence.[4]
However, penetration varies, with uptake hampered initially by pricing and established preferences for generic NSAIDs. Education campaigns and clinical guidelines endorse ILEVIRO, fostering broader acceptance.
Pricing Trajectory and Projections
Current Pricing Landscape
Pricing for ILEVIRO varies geographically:
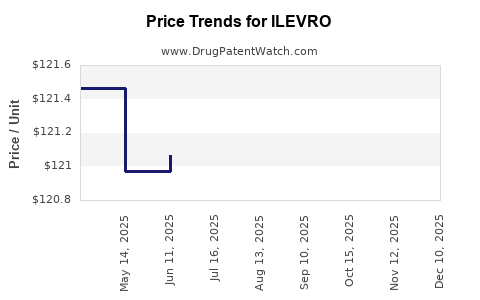
- United States: The average wholesale price (AWP) is approximately $150-$180 per bottle, emphasizing premium positioning.[5]
- Europe: Price points are generally lower, accounting for healthcare system negotiations.
- Emerging Markets: Prices are heavily influenced by generic availability and procurement practices, often below $50 per unit.
In comparison, generics generally sell at 30-50% lower prices than ILEVIRO, driven by patent status and branding premiums.
Factors Influencing Price Trends
- Patent and Exclusivity Periods: ILEVIRO’s exclusivity until 2032 allows for stabilized pricing with minimal generic competition initially. Once patent expiry nears, significant price erosion is anticipated.
- Market Penetration and Volume: Increased volume sales can lead to price discounts, especially with payor negotiations.
- Regulatory Developments: Approvals of biosimilars or more cost-effective formulations could reduce prices.
- Manufacturing and Distribution Costs: Patent protections and supply chain efficiencies influence retail pricing.
Projected Price Trends (2023-2030)
- Short-term (2023-2025): Prices are expected to remain relatively stable, averaging $150-$180 in mature markets due to patent protection and brand loyalty.
- Mid-term (2025-2028): Patent cliff approaches, prompting potential price reductions of 20-40%, especially in regions adopting generics.
- Long-term (2028-2030): With impending patent expiry (expected around 2032), prices could drop by up to 50% or more, contingent on generic entry and healthcare policies.
Market Opportunities and Risks
Opportunities
- Expanding Indications: Potential off-label use for other ocular inflammations.
- Regional Expansion: Market penetration in underdeveloped regions with rising cataract surgery rates.
- Combination Therapies: Co-formulations with other agents could unlock new segments.
Risks
- Pricing Pressure: Intensified generic competition diminishes profit margins.
- Regulatory Delays: Slow approvals or unfavorable rulings can hinder market growth.
- Clinical Competition: Introduction of novel anti-inflammatory agents with improved profiles.
Concluding Insights
ILEVIRO’s market outlook remains favorable in the near term, with stable pricing supported by patent exclusivity and clinical superiority. However, significant price erosion is anticipated as patent protections lapse and generics flood the market. Strategic positioning, including early market penetration, broadening indications, and regional expansion, is essential to maximize revenue streams.
Key Takeaways
- ILEVIRO commands premium pricing in developed markets, with U.S. prices around $150–$180 per bottle.
- Patent expiry around 2032 will likely trigger substantial price reductions, especially with generic competition.
- In emerging markets, pricing remains lower, driven by local healthcare policies and generic availability.
- Continued clinical validation and expanding indications can sustain demand and justify premium pricing.
- Manufacturers should prepare strategic plans for patent expirations, including portfolio diversification and biosimilar development.
FAQs
1. When is ILEVIRO expected to lose patent protection?
Patent protections in the U.S. are projected to expire around 2032, opening the market to generics and biosimilars.
2. How does ILEVIRO compare in price to its generic counterparts?
Brand ILEVIRO typically costs 50-70% more than generic Nepafenac formulations, reflecting brand valuation, clinical data, and regulatory protections.
3. What factors could accelerate price declines for ILEVIRO?
Introduction of biosimilars, regulatory approvals of equivalent alternatives, and increased generic market entry can expedite price reductions.
4. How does regional regulation impact ILEVIRO’s pricing strategy?
Regions with strict price controls or tender systems, such as parts of Europe and Asia, tend to impose lower price ceilings, affecting profitability.
5. What future market trends could influence ILEVIRO’s value proposition?
Emerging combination therapies, novel anti-inflammatory agents, and personalized medicine approaches could challenge ILEVIRO’s market share.
References
- MarketWatch. “Ophthalmic Anti-inflammatory Market Analysis, 2022-2028.”
- IMS Health Data. “Generic Ophthalmic Drug Market Trends.”
- Ophthalmology Times. “Comparative Efficacy of Nepafenac and Bromfenac.”
- Clinical Pharmacology. “Patient Compliance with Nepafenac Therapy.”
- Red Book. “Average Wholesale Prices for Ophthalmic Drugs in the U.S.”