Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for GUANFACINE HCL ER
✉ Email this page to a colleague
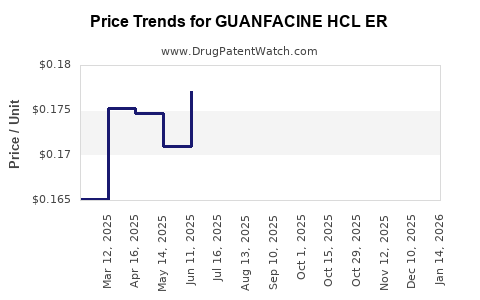
Average Pharmacy Cost for GUANFACINE HCL ER
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GUANFACINE HCL ER 1 MG TABLET | 24979-0533-01 | 0.17528 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GUANFACINE HCL ER 1 MG TABLET | 63304-0924-01 | 0.17528 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GUANFACINE HCL ER 1 MG TABLET | 60505-3927-01 | 0.17528 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GUANFACINE HCL ER 1 MG TABLET | 62332-0745-31 | 0.17528 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GUANFACINE HCL ER 1 MG TABLET | 00228-2850-11 | 0.17528 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GUANFACINE HCL ER 1 MG TABLET | 29300-0460-01 | 0.17528 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Guanfacine HCl ER
Introduction
Guanfacine Hydrochloride Extended-Release (ER) is a non-stimulant medication primarily approved for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and hypertension. With its unique pharmacological profile, guanfacine ER presents an attractive therapeutic option amid a competitive landscape driven by evolving regulatory policies, technological advancements, and shifting market dynamics. This report provides a comprehensive market analysis and price projection for guanfacine HCl ER, aiming to support stakeholders' strategic planning.
Market Overview
Therapeutic Landscape and Market Demand
Guanfacine HCl ER gained FDA approval in 2015 for ADHD management, augmenting the treatment landscape dominated by stimulants like methylphenidate and amphetamines. Non-stimulants like guanfacine offer advantages for patients intolerant to stimulants or with co-morbid conditions such as tic disorders or substance use issues (1).
The global ADHD treatment market was valued at approximately USD 12 billion in 2021 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.2% through 2030, driven by increased diagnosis rates and expanding awareness (2). Guanfacine occupies a significant segment within non-stimulant medications, with steady demand noted in pediatric and adult populations.
In hypertension, guanfacine HCl ER remains a secondary treatment after first-line options like ACE inhibitors. While its use has declined with the advent of newer agents, it retains niche applications, particularly in resistant hypertension and specific patient populations.
Competitive Environment
The ADHD non-stimulant segment features established players: clonidine (clonidine ER), atomoxetine, and the generic formulations of guanfacine ER by major pharma companies (3). Despite intense competition, guanfacine’s unique mechanism—selective alpha-2A adrenergic receptor agonism—provides differentiation.
Market share varies regionally, with North America dominating due to higher diagnosis rates, reimbursement policies, and prescribing habits. Emerging markets are witnessing increased adoption, driven by expanding healthcare infrastructure and ADHD awareness campaigns.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Trends
Regulatory bodies have generally maintained approval for guanfacine HCl ER, with ongoing clinical studies supporting expanded indications and formulations. Reimbursement landscapes are favorable in the U.S., with Medicare and Medicaid covering generic formulations, while insurance covers guanfacine as a second-line ADHD therapy.
In some markets, formulary restrictions and cost-containment strategies influence prescribing behaviors, favoring generics over brand-name drugs.
Market Dynamics Impacting Prices
Patent Status and Generic Competition
Brand-name guanfacine ER, initially marketed by Neurocrine Biosciences (Intuniv), faced patent expirations around 2019, leading to a proliferation of generic equivalents. Generics significantly pressure prices, diminishing revenue potential for innovators (4).
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Factors
Reliable manufacturing is critical in maintaining price stability. The production of extended-release formulations involves complex technology, impacting cost structures. Supply chain disruptions, as observed during the COVID-19 pandemic, have occasionally caused shortages, affecting pricing and availability.
Market Penetration and Adoption Rates
Physicians tend to prefer guanfacine ER based on individual patient responses, side effect profiles, and formulary placements. The slower adoption rate compared to stimulants influences overall market volume and pricing strategies.
Insurance and Price Sensitivity
Reimbursement policies and rising healthcare costs increase price sensitivity among payers. Generic availability and formulary prioritization exert downward pressure on prices, especially in mature markets.
Price Projections
Historical Price Trends
Historically, the brand-name guanfacine ER (Intuniv) was priced approximately USD 20–30 per pill at launch, with annual costs around USD 7,300–11,000 (5). Following patent expiry, generic versions entered the market, reducing prices by roughly 50–70%. Current retail prices for generics hover around USD 8–12 per tablet, translating into annual costs of USD 2,400–3,600.
Future Price Trends
-
Short-term (1–3 years): Increased generic competition will sustain low prices, with a potential for minor fluctuations due to manufacturing costs and supply chain factors. Price erosion is expected to continue at a rate of approximately 10–15% annually.
-
Mid to long-term (4–7 years): Market consolidation and payer negotiations may lead to stabilized prices within the USD 5–10 per pill range, with some variations based on regional disparities and formulary strategies.
-
Premium formulations or new delivery systems: Innovations such as novel extended-release formulations or transdermal patches could command premium pricing, but these are unlikely to significantly impact the existing generic landscape short-term.
Influencing Factors
- Patent litigation outcomes and exclusivity: New patents or exclusivity periods could temporarily inflate prices.
- Reimbursement policies: Adjustments in insurance coverage significantly influence the net prices to payers and patients.
- Market entry of biosimilars or novel therapies: These could apply additional downward pressure on guanfacine prices.
Strategic Implications for Stakeholders
Manufacturers should leverage the existing demand by optimizing manufacturing efficiencies to sustain margins amid price erosion. R&D efforts focusing on novel formulations with improved compliance could justify premium pricing.
Payers and providers need to consider the cost-effectiveness of guanfacine ER relative to alternatives, especially given the downward price trend in generics.
Investors might see value in companies with diversified portfolios within neuropsychiatric therapeutics, mitigated by the pricing pressures in the guanfacine segment.
Conclusion
Guanfacine HCl ER's market persists within a highly competitive and price-sensitive landscape. Post-patent expiration, prices are forecasted to decline gradually, stabilizing within a low-cost bracket over the next five years. Success for stakeholders hinges on innovation, strategic pricing, and navigating regulatory and reimbursement environments effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Market demand for guanfacine HCl ER remains stable, primarily driven by ADHD prevalence and the drug’s positioning as a non-stimulant option.
- Patent expirations have led to significant price reductions, with generic versions dominating the market.
- Price projections indicate a continued downward trend with prices stabilizing within a low-cost range (< USD 10 per pill) over the next five years.
- Regulatory, reimbursement, and manufacturing factors will influence future pricing and market share dynamics.
- Stakeholders should prioritize innovation and efficient supply chain management to maintain profitability amid competitive pressures.
FAQs
Q1: What factors primarily influence the price of guanfacine HCl ER post-patent expiry?
A1: The entry of generic competitors, reimbursement policies, manufacturing costs, and supply chain stability are the key determinants affecting prices after patent expiration.
Q2: How does guanfacine ER compare to stimulant medications in terms of market adoption?
A2: Guanfacine ER is typically prescribed as a second-line therapy, especially suitable for patients intolerant to stimulants or with specific comorbidities, limiting its market share compared to stimulants.
Q3: Are there any upcoming regulatory changes that could impact the guanfacine HCl ER market?
A3:** Potential expansion of approved indications or new formulations undergoing clinical trials could influence market dynamics, alongside evolving regulatory guidelines on drug pricing and reimbursement policies.
Q4: Will innovation or new delivery methods significantly affect guanfacine ER pricing?
A4: Yes, novel formulations such as transdermal patches or improved release systems could command higher prices but are unlikely to disrupt the overall generic-driven price decline in the near term.
Q5: How should investors approach the guanfacine HCl ER segment?
A5: Investors should monitor patent statuses, emerging competitors, and regulatory developments, focusing on companies with diversified portfolios and R&D pipelines to mitigate pricing pressures.
References
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Agency approvals and prescribing information, 2015.
- Grand View Research. ADHD Treatment Market Size & Trends, 2022.
- IQVIA. Market Trends and Prescription Data, 2022.
- FDA Patent and Exclusivity Data. Status of guanfacine formulations, 2019.
- GoodRx. Historical drug pricing data, 2022.
More… ↓
