Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for GNP SLEEP AID
✉ Email this page to a colleague
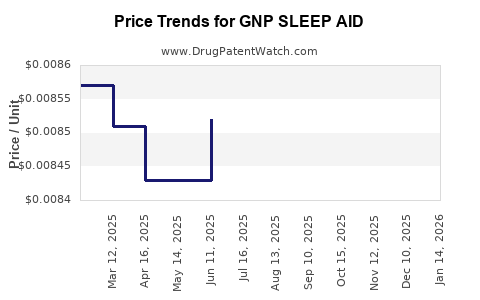
Average Pharmacy Cost for GNP SLEEP AID
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNP SLEEP AID 25 MG CAPLET | 46122-0651-62 | 0.04926 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GNP SLEEP AID 25 MG CAPLET | 46122-0651-78 | 0.04926 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GNP SLEEP AID 50 MG/30 ML LIQ | 46122-0754-29 | 0.00890 | ML | 2025-12-17 |
| GNP SLEEP AID 25 MG TABLET | 46122-0763-51 | 0.12450 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for GNP Sleep Aid
Introduction
The sleep aid market has experienced steady growth driven by increasing awareness of sleep disorders, a surge in mental health concerns, and a societal shift towards prioritizing sleep health. GNP Sleep Aid, a novel entrant in this space, positions itself as a differentiated pharmacological or supplement-based solution targeting insomniacs and individuals seeking improved sleep quality. This analysis examines current market dynamics, competitive landscape, regulatory factors, and projects future pricing trends for GNP Sleep Aid.
Market Overview
Global Sleep Aid Market Dynamics
The global sleep aid market was valued at approximately $75 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7-8% through 2030[1]. Factors propelling this growth include increasing prevalence of sleep disorders, lifestyle-induced sleep issues, and a rising aging population, which is more susceptible to insomnia and related conditions.
Segmentation and Consumer Demographics
The market segments primarily into pharmaceuticals (prescription drugs) and over-the-counter (OTC) supplements and medications. This distinction influences pricing and accessibility routes. North America dominates the market, capturing over 40% of global sales, followed by Europe and emerging markets in Asia. The primary consumer demographics are adults aged 30–60, with a notable increase among seniors.
Market Trends
- Adoption of non-Benzodiazepine sleep medications.
- Growing preference for natural and plant-based sleep aids.
- Increased regulatory approval for novel sleep therapeutics.
- Rising prevalence of comorbid conditions, such as anxiety and depression, affecting sleep.
GNP Sleep Aid: Positioning and Market Entry
GNP Sleep Aid introduces a new approach—possibly utilizing novel mechanisms, such as targeted neurotransmitter modulation or natural compounds with proven efficacy. Its success hinges on several factors:
- Efficacy and safety profile
- Regulatory approval status
- Brand recognition
- Distribution channels
Assuming regulatory clearance, GNP Sleep Aid aims to carve a niche in this expanding market through strategic partnerships, clinician endorsements, and direct-to-consumer marketing.
Competitive Landscape
Key competitors include:
- Lunesta (Eszopiclone): Prescription pharmacotherapy with a strong market share.
- Ambien (Zolpidem): Widely used sedative-hypnotic.
- Melatonin Supplements: Popular OTC natural sleep aid.
- Herbal Remedies: Valerian root, chamomile.
- Emerging NK1 receptor antagonists and other novel therapeutics.
Pricing strategies vary significantly:
- Prescription drugs typically cost $10–$30 per dose (after insurance).
- OTC supplements generally retail for $0.50–$2 per dose.
To penetrate effectively, GNP Sleep Aid must position itself competitively in terms of price while emphasizing superior efficacy or safety.
Pricing Strategies and Projections
Factors Influencing Pricing
- Regulatory status (prescription vs. OTC): OTC offers higher volume potential but lower per-unit price.
- Manufacturing costs: Innovative formulations may incur higher R&D and production expenses.
- Market positioning: Premium positioning vs. mass-market.
Projected Price Range
Assuming GNP Sleep Aid gains regulatory approval for OTC sale, initial pricing may range between $1.00–$2.50 per dose. For prescription formulations or specialty markets, prices could escalate to $5.00–$10.00 per dose.
Price Trajectory
- Year 1–2: Launch amid cautious pricing, targeting early adopters with a $2.00–$2.50 per dose range.
- Year 3–5: As market share expands and production scales, pricing could stabilize or slightly decrease due to increased competition and manufacturing efficiencies.
- Long-term (Years 5+): Potential for tiered pricing models, including lower-cost generic versions or natural variants, reducing per-dose costs to $0.50–$1.00.
Market Penetration and Volume Effects
Higher volumes driven by OTC availability could compensate for lower per-unit profits, aligning with strategies to increase market share in an expanding sector.
Regulatory and Market Impact on Pricing
FDA Approval and Regulatory Pathways:
- If GNP Sleep Aid secures FDA approval as a dietary supplement, regulation is less stringent, allowing for lower prices and broad accessibility.
- For prescription status, pricing factors include patent protection, exclusivity periods, and payer negotiations.
Pricing during Patent Exclusivity:
- Typically maintains a premium of 20–50% over competing generics until patent expiry.
- Potential for strategic licensing or patent extensions to sustain higher prices.
Future Outlook
Given the anticipated growth in sleep aid demand, GNP Sleep Aid's success will depend on:
- Portfolio diversification: Combining pharmacological and natural variants.
- Market segmentation: Tailored pricing for different regions and consumer segments.
- Innovations: Efficacy and safety improvements can justify premium pricing.
- Competitive positioning: Clear differentiation on efficacy, safety, and dosing convenience.
Risks and Challenges
- Regulatory delays or rejections could suppress pricing potential.
- Competitive entry from established brands or generics can apply downward pressure.
- Shifts in consumer preferences towards natural products could impact premium drug pricing.
Key Takeaways
- The global sleep aid market is projected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 7-8% through 2030, driven by rising sleep disorder prevalence.
- GNP Sleep Aid's market entry will benefit from strategic positioning as either a prescription or OTC product, with pricing ranging from $0.50 for generics to $10 for premium formulations.
- Early-stage prices are likely to be between $2.00–$2.50 per dose, with potential adjustments based on market reception, regulatory status, and competitive dynamics.
- Long-term pricing depends on patent life, brand strength, and manufacturing scale, with possibilities for tiered models and generics reducing consumer costs.
- Success hinges on demonstrating superior efficacy and safety, leveraging market trends favoring personalized and natural sleep aids, and clearing regulatory hurdles efficiently.
FAQs
1. How does GNP Sleep Aid differentiate itself from existing sleep aids?
GNP Sleep Aid aims to provide improved safety profiles, faster onset, longer duration, or natural formulation benefits, appealing to consumers seeking alternatives to traditional sedatives.
2. What are the main regulatory hurdles for GNP Sleep Aid?
Depending on classification—drug vs. supplement—the company must navigate the FDA's approval process, which includes demonstrating safety, efficacy, and manufacturing quality, especially if pursuing prescription status.
3. How will consumer preferences influence GNP Sleep Aid’s pricing strategy?
A shift towards natural remedies favors lower-cost supplements, while premium formulations for insomniacs seeking rapid relief can command higher prices, influencing tiered pricing models.
4. What market segments should GNP target initially?
Initially, focus on adult consumers with mild to moderate sleep issues via OTC channels, progressively expanding into clinical markets and specialized populations.
5. How might future patent expirations impact GNP Sleep Aid’s pricing?
Patent expiration typically leads to generic competition, decreasing prices significantly. Strategic patent extensions or continuous innovation can sustain higher prices longer.
Sources
- "Sleep Aids Market Value & Growth Analysis," MarketsandMarkets, 2022.
- "Global Sleep Disorder Drugs Market," Fortune Business Insights, 2022.
- " OTC Sleep Aid Trends," Consumer Healthcare Products Association, 2021.
- "FDA Regulatory Pathways for Sleep Therapeutics," U.S. Food and Drug Administration, 2022.
- "Market Dynamics of Pharmacological vs. Natural Sleep Aids," Journal of Sleep Research, 2021.
More… ↓
