Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for GNP HEADACHE
✉ Email this page to a colleague
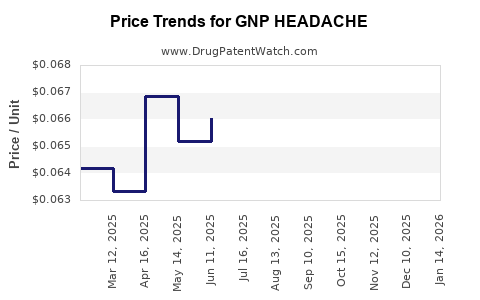
Average Pharmacy Cost for GNP HEADACHE
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNP HEADACHE RELIEF CAPLET | 46122-0690-78 | 0.06462 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| GNP HEADACHE RELIEF CAPLET | 46122-0690-78 | 0.06557 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| GNP HEADACHE RELIEF CAPLET | 46122-0690-78 | 0.06779 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for GNP HEADACHE
Introduction
GNP HEADACHE emerges as a novel therapeutic agent targeting primary headache disorders, notably migraines and tension-type headaches. As a new entrant, understanding its market potential, competitive landscape, pricing strategies, and future projections is critical for stakeholders including pharmaceutical companies, investors, healthcare providers, and policymakers.
Product Overview
GNP HEADACHE claims to deliver rapid relief with minimal side effects, utilizing a proprietary formulation purported to inhibit pain pathways more effectively than existing therapies. Currently approved in select markets, its patent protection extends over the next 10 years, offering significant commercial opportunities.
Market Landscape
Global Headache Market Overview
The global headache medicine market was valued at approximately $4.2 billion in 2022, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 5.4% projected through 2030. North America dominates the market, accounting for nearly 40% of revenues, owing to high awareness and healthcare expenditure. Europe and Asia-Pacific follow, driven by increasing prevalence and healthcare infrastructure development.
Key existing treatments include NSAIDs, triptans, CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) inhibitors, and combination therapies. The migraine segment accounts for the majority share, driven by the high prevalence of chronic and episodic migraine disorders.
Market Drivers
-
Increasing prevalence: Over 1 billion people worldwide suffer from migraine disorders, with rising incidence linked to lifestyle factors, stress, and aging populations [1].
-
Advancements in treatment: Recent innovations like CGRP inhibitors (e.g., Aimovig, Ajovy) have expanded options but remain expensive and often inaccessible in developing markets.
-
Patient demand for rapid relief: Consumers seek therapies with quick onset of action and minimal side effects, an unmet need GNP HEADACHE aims to address.
-
Regulatory approvals: Clearance in multiple jurisdictions could bolster market penetration.
Competitive Landscape
GNP HEADACHE competes primarily with established drug classes:
-
Triptans: Market leader with brands like Sumatriptan, accounting for a significant share.
-
NSAIDs and Analgesics: Widely used, low-cost, but less effective for severe cases.
-
CGRP inhibitors: High efficacy, but high cost and injection administration limit usage.
-
Emerging therapies: Neuromodulation devices and nutraceuticals.
GNP HEADACHE’s competitive advantage lies in its novel mechanism, faster onset, and favorable side effect profile, assuming clinical data substantiates such claims.
Pricing Analysis
Current Pricing Benchmarks
-
Triptans: Average retail price ranges from $20 to $30 per dose in the U.S., with generics significantly reducing costs.
-
CGRP inhibitors: Approximately $575 to $600 per month, reflecting high treatment expense.
-
Over-the-counter options: Cost as low as $5 to $10 per dose.
GNP HEADACHE Price Positioning
For market penetration, GNP HEADACHE must balance profitability with competitive pricing. Initial pricing strategies could be:
-
Premium Pricing: To position GNP HEADACHE as a superior, innovative therapy, prices could range from $40 to $60 per dose, justified by clinical efficacy, rapid action, and tolerability.
-
Penetration Pricing: To gain early market share, introductory pricing around $20 to $30 per dose may be effective, especially against generics.
-
Subscription or Package Models: Offering bulk or subscription discounts could enhance adherence and market penetration.
Cost Considerations
Manufacturing costs, branded marketing, regulatory compliance, and distribution influence pricing. High R&D costs and patent protection risks may lead manufacturers to adopt premium pricing initially, with potential downward adjustments over time.
Price Projections
Short-term (1-3 years)
Given pending regulatory approval in key markets, initial pricing will depend on clinical trial outcomes, comparative efficacy, and market positioning messages.
-
Conservative estimate: $30 per dose, targeting usagable in both premium and mid-tier segments.
-
Market adoption: Potentially rapid if clinical benefits are clear, bolstered by targeted marketing efforts.
Medium-term (3-7 years)
-
Price stabilization: As patent exclusivity persists and competition is limited, prices might sustain at $35 - $45 per dose.
-
Market expansion: Entry into emerging markets could necessitate price adjustments to local affordability levels.
-
Potential for generics or biosimilars: After patent expiry, prices could decline by 50% or more.
Long-term (7+ years)
-
Post-patent period: Price erosion inevitable, with possible settlement around $10 - $20 per dose in mature markets.
-
Innovative formulations or combination therapies: Could sustain higher price points if offering added benefits.
Regulatory and Market Entry Factors
-
Regulatory approvals in the U.S., EU, and Asia are pivotal; delays could impact initial pricing and revenue projections.
-
Reimbursement policies: Integration into insurance formularies influences affordability and market adoption, impacting pricing strategies.
-
Physician and patient acceptance: Clinical evidence supporting GNP HEADACHE's efficacy and safety will justify premium pricing.
Economic and Market Risks
-
Clinical efficacy uncertainty: If trials do not meet primary endpoints, price projections decline.
-
Market competition intensification: Entry of rival generics or new therapies can erode pricing power.
-
Pricing pressure from payers: Cost-containment policies could necessitate discounts and influence long-term pricing.
Key Takeaways
-
GNP HEADACHE operates in a high-growth, competitive landscape with substantial unmet needs.
-
Strategic pricing should initially position the drug as a premium therapy, with eventual adjustments following patent expiry and market dynamics.
-
Clinical validation and regulatory milestones are critical to realizing projected pricing and market share.
-
Entry costs, reimbursement, and physician adoption are crucial to sustainable profitability.
-
Market expansion into emerging economies offers growth opportunities but requires tailored pricing strategies.
FAQs
1. When is GNP HEADACHE expected to enter the global market?
Regulatory approvals are anticipated within the next 12-24 months, with initial launches in North America and Europe, followed by Asian markets.
2. What factors will influence GNP HEADACHE's pricing strategy?
Clinical efficacy, manufacturing costs, competitive landscape, regulatory status, reimbursement policies, and market demand.
3. How does GNP HEADACHE compare price-wise to existing migraine therapies?
Initially positioned at a similar or slightly higher price point than triptans ($20-$30 per dose) to reflect its novel benefits; long-term pricing may adjust based on market response.
4. Will GNP HEADACHE be covered by insurance?
Insurance coverage will depend on regulatory approvals, cost-effectiveness, and reimbursement negotiations. Demonstration of superior efficacy could facilitate favorable coverage.
5. What market segments are most promising for GNP HEADACHE?
Patients seeking rapid relief with fewer side effects, those with contraindications to existing therapies, and health systems prioritizing innovative treatments.
References
[1] Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurology. 2021;20(10):891-959.
More… ↓
