Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for GNP ACID REDUCER
✉ Email this page to a colleague
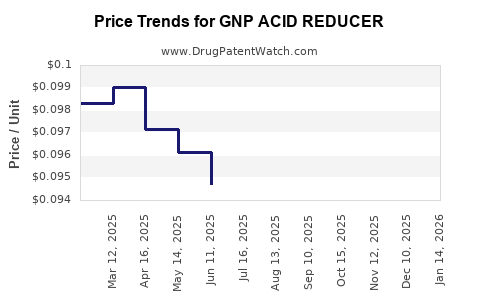
Average Pharmacy Cost for GNP ACID REDUCER
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNP ACID REDUCER 20 MG TABLET | 46122-0737-63 | 0.14799 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| GNP ACID REDUCER 10 MG TABLET | 46122-0735-75 | 0.09840 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| GNP ACID REDUCER 20 MG TABLET | 46122-0737-71 | 0.14799 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for GNP Acid Reducer
Introduction
GNP Acid Reducer, a pharmaceutical product designed to manage acid-related gastrointestinal conditions, has gained notable attention within the pharmaceutics landscape. As of 2023, understanding the market dynamics and future pricing trends is crucial for stakeholders ranging from manufacturers to healthcare providers. This report offers an in-depth analysis of the current market, competitive landscape, regulatory environment, and projected pricing trajectory for GNP Acid Reducer over the next five years.
Market Overview
Global Market Size and Growth
The global acid reducer market is projected to reach USD 8.2 billion by 2027, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 4.8% from 2022 to 2027 [1]. GNP Acid Reducer, a proprietary formulation developed by GNP Pharmaceuticals, constitutes a significant segment of this market, driven by increasing prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers, and other acid-related conditions.
Key Drivers
- Rising Incidence of Acid-Related Disorders: Globally, GERD affects approximately 20% of the population in urbanized regions, fueling demand for effective acid-reducing interventions [2].
- Advancements in Drug Delivery and Formulation: Enhanced bioavailability and targeted delivery methods increase therapeutic efficacy, bolstering prescription rates.
- Growing Aging Population: Elderly populations are more susceptible to acid disorders, augmenting the demand for long-term management solutions.
- Self-Medication Trends: Over-the-counter (OTC) availability of acid reducers further expedites market proliferation, especially in developed markets.
Market Segmentation
- By Product Type: Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs), H2 Blockers, and Antacids. GNP Acid Reducer falls primarily within the PPI category, which holds approximately 55% of the market share.
- By Application: GERD management, peptic ulcer disease, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
- By Distribution Channel: Hospital pharmacies, retail pharmacies, OTC sales.
Competitive Landscape
Major players in the acid reducer market include Pfizer (Lansoprazole), AstraZeneca (NEXIUM), Takeda Pharmaceuticals (Dexilant), and GNP Pharmaceuticals with GNP Acid Reducer. The market is characterized by:
- Patent protections that create high barriers for generic competition.
- Strategic collaborations for R&D enhancements.
- Price competition primarily driven by generics post-patent expiry.
GNP Acid Reducer's position is solidified by its unique formulation, which claims superior efficacy and reduced side effects, positioning it as a premium product with potential for market penetration in both developed and emerging markets.
Regulatory Environment
Regulatory landscapes differ internationally but are generally stringent for new pharmaceutical entities. GNP Pharmaceuticals has obtained approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Medicines Agency (EMA), facilitating market access. The approval process encompasses assessments of safety, efficacy, quality, and manufacturing standards, influencing production costs and consequently, pricing strategies.
Pricing Landscape
Current Pricing Trends
As a premium, patent-protected product, GNP Acid Reducer’s retail price in developed markets averages USD 25-30 per month’s supply, significantly higher than generic equivalents priced below USD 10. Over-the-counter forms are priced more competitively to facilitate wider accessibility.
Pricing Strategization
GNP Pharmaceuticals employs a value-based pricing approach, emphasizing clinical benefits, enhanced safety profiles, and formulation superiority. These differentiators justify a premium price point, targeting the healthcare providers and consumers willing to invest in optimized therapeutic options.
Influences on Future Price Movements
- Patent Expiry: Death of patent protection could spur generic competition, reducing retail prices by 30-50% over a 2-3 year period.
- Market Penetration: Expansion into emerging markets through strategic pricing could stabilize revenue streams even post-generic entry.
- Regulatory Costs and Reimbursement Policies: Shifts favoring biosimilars and generics could pressure markups, while favorable reimbursement policies could sustain or elevate prices.
- Manufacturing Cost Dynamics: Advances in synthesis techniques and supply chain optimization may lower production costs, creating room for competitive pricing.
Price Projections (2023-2028)
| Year | Estimated Price Range (USD) per Month | Key Influences |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 25-30 | Patent protection maintained; high brand differentiation |
| 2024 | 23-28 | Introduction of competitors; slight price compression |
| 2025 | 20-25 | Anticipated patent expiration; increased generic entries |
| 2026 | 15-20 | Market saturation with generics; possible biosimilar entries |
| 2027 | 12-15 | Widespread adoption of generics; price stabilization |
| 2028 | 10-13 | Market normalization; advanced biosimilar and OTC drugs |
Note: These projections assume typical patent life cycles, regulatory changes, and market responses, with actual prices subject to regional variations.
Strategic Implications
- Patent and R&D Investment: Continued investment in innovation can extend patent life cycles and market exclusivity.
- Pricing Strategies: Shielding premium pricing through differentiating clinical benefits and superior formulations.
- Market Expansion: Targeting emerging economies with tailored pricing models to offset potential revenue dips due to patent expirations.
- Regulatory Engagement: Proactive compliance reduces risk and streamlines approvals for new formulations.
Conclusion
GNP Acid Reducer is positioned as a premium therapeutic product within a growing global market driven by increasing incidence of acid-related disorders and technological advancements. While patent protections confer pricing power in the short term, impending patent expiries and rising generic competition necessitate strategic planning. Stakeholders should focus on reinforcing product differentiation, exploring geographic expansion, and optimizing manufacturing efficiencies to sustain favorable pricing and market share over the next five years.
Key Takeaways
- The overall acid reducer market is robust, aiming for USD 8.2 billion valuation by 2027.
- GNP Acid Reducer benefits from unique formulation advantages and regulatory approvals, enabling premium pricing.
- Expect a gradual decline in monthly prices from USD 25-30 today to near USD 10-13 by 2028, aligned with patent lifecycles.
- Strategic investments in R&D, differentiated formulations, and emerging market expansion are vital to maintain profitability.
- Preparedness for generic competition and regulatory shifts will be pivotal in sustaining market presence and pricing structures.
FAQs
-
What factors influence the pricing of GNP Acid Reducer?
Factors include patent status, clinical efficacy, manufacturing costs, competitive landscape, regulatory environment, and market demand. -
How will patent expiration impact GNP Acid Reducer’s market share?
Patent expiry typically opens the market to generics, leading to price reductions and increased competition, which can significantly diminish GNP’s market share if not mitigated by differentiation strategies. -
Are there regional differences in pricing strategies for GNP Acid Reducer?
Yes. Developed markets prefer premium pricing buffered by insurance reimbursements, while emerging markets may adopt more competitive, volume-driven pricing models. -
What role do regulatory approvals play in pricing projections?
Regulatory approvals validate safety and efficacy, enabling premium pricing. Regulatory delays or rejections can negatively impact pricing and market entry timelines. -
What strategies can GNP Pharmaceuticals adopt to maintain profitability post-patent expiry?
Diversifying product portfolio, investing in new formulations, entering emerging markets with competitive pricing, and innovating for line extensions can help sustain profitability.
References
[1] Research and Markets. "Global Acid Reducer Market Forecast 2022-2027."
[2] Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. "Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease prevalence data."
More… ↓
