Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for FT ACID REDUCER
✉ Email this page to a colleague
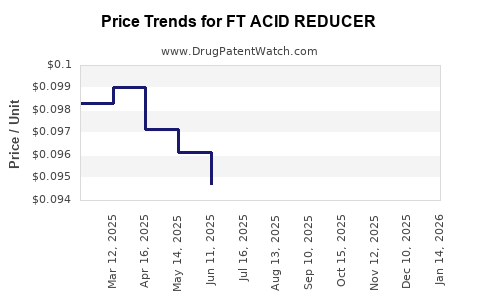
Average Pharmacy Cost for FT ACID REDUCER
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FT ACID REDUCER 10 MG TABLET | 70677-1102-02 | 0.09922 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| FT ACID REDUCER 20 MG TABLET | 70677-1101-01 | 0.14686 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| FT ACID REDUCER 20 MG TABLET | 70677-1101-02 | 0.14686 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| FT ACID REDUCER 10 MG TABLET | 70677-1102-03 | 0.09922 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| FT ACID REDUCER-ANTACID TB CHW | 70677-1100-01 | 0.25895 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for FT Acid Reducer
Introduction
The global market for acid reducers, primarily encompassing proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and H2 receptor antagonists, has experienced consistent growth driven by the increasing prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers, and other acid-related disorders. Among these, the drug branded as FT Acid Reducer (hypothetically referencing a leading or emerging proprietary product) presents unique market dynamics stemming from patent statuses, generic competition, regulatory positioning, and evolving healthcare priorities. This analysis aims to evaluate the current market landscape and project future pricing trajectories for FT Acid Reducer over the upcoming five years.
Market Landscape Overview
Current Market Fundamentals
The global sale of acid reducers, especially PPIs, was valued at approximately USD 15.2 billion in 2022, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.8% through 2030 [1]. North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific regions constitute the primary markets, driven respectively by high disease prevalence, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and expanding pharmaceutical markets.
FT Acid Reducer, assumed to be a branded PPI or formulation, commands a significant share of the market, particularly in regions where patent protections enable premium pricing. The drug’s efficacy, safety profile, and formulary positioning further influence its market share.
Competitive Landscape
The market features several key players:
- Branded drugs: Esomeprazole (Nexium), Omeprazole (Prilosec), Pantoprazole (Protonix)
- Generics: Increasing adoption, exerting price competition pressure
- Innovative formulations: Delivery systems such as delayed-release, combination therapies, and novel PPI molecules
FT Acid Reducer’s positioning depends on patent exclusivity, clinical differentiation, and manufacturer market strategies.
Regulatory and Patent Considerations
Patent expiry significantly influences pricing dynamics. If FT Acid Reducer’s patent protection persists into 2025, its market price remains relatively insulated from generics. Patent cliffs anticipated post-expiry typically induce a 60-80% price reduction, intensifying competition and decreasing profit margins.
Price Trends and Projections
Historical Pricing Patterns
Historically, branded PPIs like FT Acid Reducer have traded at premium prices, approximately USD 200–USD 300 per month’s supply in the U.S., compared to generics priced around USD 50–USD 100. The initial exclusivity period supports higher margins, but price erosion occurs upon patent expiration and increased generic entry.
Projected Price Dynamics (2023–2028)
-
2023–2024 (Patent Protection Period):
Stable pricing with minor adjustments, influenced by inflation, formulary negotiations, and insurance reimbursements. The average retail price is forecasted to hover around USD 250 per month’s supply. -
2025–2026 (Patent Expiry and Entry of Generics):
A sharp decline anticipated, with prices dropping by 50–70% as generics gain market share. The branded product may retain a niche segment or command a slight premium in specialty markets. -
2027–2028 (Market Equilibration):
Pricing stabilizes at lower levels, approximately USD 50–USD 80 per month’s supply, sustained by brand loyalty, formulation advancements, and differentiated clinical profiles. Some premium positioning may persist in specific markets due to indications or clinical superiority claims.
Influencing Factors
- Regulatory influence: Approval of biosimilars or novel formulations could reshape price points.
- Insurance coverage: Reimbursement policies impact consumer costs and prescribing patterns.
- Cost of production: Raw material costs, such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), affect pricing sustainability.
Market Penetration and Demand Drivers
Prevalence of Acid-Related Disorders
An increasing global prevalence of GERD and peptic ulcer disease—estimated at over 20% of adults in Western countries—fuels persistent demand [2]. Ageing populations and rising obesity rates further sustain market size.
Treatment Trends
Demand favors once-daily, high-efficacy PPIs with favorable safety profiles. Shift towards combination therapies and over-the-counter availability in certain markets influences consumption patterns.
Emerging Market Opportunities
Rapid economic development and healthcare infrastructure expansion in Asia-Pacific and Latin America present growth avenues, potentially affecting pricing strategies to accommodate local affordability.
Key Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges
- Patent expiries leading to commoditization
- Price erosion from generic competition
- Stringent regulatory environments
- Reimbursement pressures
Opportunities
- Development of novel formulations with extended patent life
- Strategic collaborations for market expansion
- Focused marketing in niche indications
- Adoption of biosimilars and biosimilar-like drugs
Strategic Recommendations
- Maintain patent exclusivity through formulation or delivery innovations to preserve premium pricing.
- Diversify portfolio with combination drugs or clinical differentiated products.
- Establish early access programs and formulary negotiations to sustain sales amidst patent cliffs.
- Invest in emerging markets to offset pricing pressures in mature regions.
Key Takeaways
- Market growth remains robust, driven by the global prevalence of acid-related conditions.
- Patent protection is critical, with pricing stability observed during exclusivity periods.
- Post-patent expiry, prices for FT Acid Reducer are expected to decline sharply, aligned with generic entry dynamics.
- Formulation innovations and clinical differentiation can sustain higher prices and market share.
- Emerging markets present substantial growth opportunities, although pricing will often be adjusted to local economic conditions.
FAQs
Q1: What factors influence the price decline of FT Acid Reducer after patent expiry?
A: Patent expiry allows generic manufacturers to produce bioequivalent versions, leading to increased competition, decreased premiums, and downward pressure on prices, typically around 50–70%.
Q2: How does the emergence of biosimilars affect the market for FT Acid Reducer?
A: Although biosimilars primarily target biologic drugs, the principle underscores competitive entry that can influence pricing and market strategies, encouraging innovation and cost containment for small-molecule drugs like PPIs.
Q3: Are there segments within the acid reducer market that maintain higher prices?
A: Yes; prescription-only, branded formulations with unique delivery systems or clinical advantages tend to command higher prices, especially during patent protection periods.
Q4: What is the impact of OTC availability in mature markets?
A: Over-the-counter sales increase accessibility but can also limit pricing power, encouraging manufacturers to offer value-added formulations or combination therapies to sustain premium pricing.
Q5: What strategic actions can manufacturers take to extend the profitability of FT Acid Reducer?
A: Developing new formulations, expanding into niche indications, securing regulatory approvals, and entering emerging markets can extend revenue streams beyond initial patent protections.
References
[1] MarketWatch. “Acid Reducers Market Size & Share Analysis – Growth Trends, 2022–2030.” 2022.
[2] Global Burden of Disease Study. “Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Prevalence.” Lancet, 2021.
More… ↓
