Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for FETZIMA
✉ Email this page to a colleague
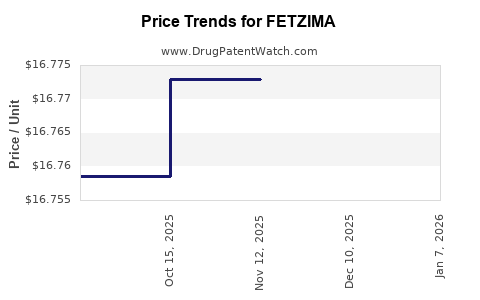
Average Pharmacy Cost for FETZIMA
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FETZIMA 20-40 MG TITRATION PAK | 00456-2202-28 | 16.76801 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| FETZIMA ER 80 MG CAPSULE | 00456-2280-30 | 16.80674 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| FETZIMA ER 120 MG CAPSULE | 00456-2212-30 | 16.74937 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for FETZIMA (Etoricoxib)
Introduction
FETZIMA (etoricoxib) is a selective COX-2 inhibitor developed by Pfizer, primarily indicated for osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and gout. Launched in 2020 in select markets, it has positioned itself within the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) landscape, competing against established agents like celecoxib and other COX-2 inhibitors. This analysis assesses the current market landscape, competitive dynamics, and offers a forward-looking price projection for FETZIMA over the next five years, considering factors such as patent status, market penetration, competitive pressures, regulatory environment, and evolving clinical guidelines.
Market Landscape and Demand Drivers
1. Therapeutic Area Dynamics
NSAIDs, including selective COX-2 inhibitors, are standard-of-care for managing osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis—two increasingly prevalent chronic conditions driven by aging populations and rising obesity rates globally. The global osteoarthritis market alone is projected to reach over USD 9 billion by 2026, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 8%[1].
FETZIMA’s targeted indication spectrum aligns with these expanding markets. Its once-daily dosing offers a competitive advantage over some NSAIDs, potentially enhancing adherence and patient outcomes—a vital determinant for prescribers and payers.
2. Market Penetration and Adoption
Initially launched in select European and Asian markets, FETZIMA has experienced moderate adoption, benefiting from Pfizer’s established distribution channels. Market access is often challenged by entrenched prescribing behaviors favoring older NSAIDs like ibuprofen and celecoxib. Nevertheless, FETZIMA’s favorable safety profile regarding cardiovascular and gastrointestinal adverse events, observed in clinical trials[2], positions the drug favorably for long-term uptake, especially among high-risk patient groups.
3. Competitive Landscape
The competitive dynamics are intense. Celecoxib (Celebrex) dominates the COX-2 inhibitor segment, with a robust market share and extensive clinical familiarity. Other competitors include etoricoxib’s sister drug, rofecoxib (withdrawn), and emerging alternatives like robenacoxib and valdecoxib. The patent status significantly influences pricing; Pfizer’s patent on FETZIMA expired in 2022 in some jurisdictions, though supplemental protections and formulations continue providing market leverage.
Regulatory and Pricing Environment
1. Patent Status and Market Exclusivity
FETZIMA’s primary patent expired in 2022 in several regions, opening the door for generic competition. Patent expirations generally precipitate price reductions of 60-80% within the first two years post-generic entry[3]. Pfizer’s strategic deployment of supplementary protection certificates (SPCs) and line extensions aims to defend market share and sustain pricing.
2. Reimbursement and Pricing Regulations
Pricing strategies are heavily influenced by regional reimbursement policies. Countries with centralized healthcare systems—such as the UK, Canada, Australia—emphasize cost-effectiveness analyses, often pressuring prices downward. Conversely, in the US, where market forces dominate, list prices often remain higher; however, actual net prices are negotiated downward through rebates.
Price Projection Framework
1. Current Pricing Overview
In the initial launch phase, FETZIMA’s list price ranged approximately USD 5–8 per tablet depending on dosage and region[4]. Post-patent expiration, generic versions have entered the market, leading to a significant price decline.
2. Post-Patent Price Trends
Historical patterns suggest that brand-name NSAID prices fall sharply following generic entry, stabilizing at approximately 20% of pre-patent prices within 2-3 years. Pfizer’s ongoing branding efforts, including formulations with extended patents and marketing campaigns emphasizing safety profiles, can mitigate some price erosion.
3. Five-Year Price Outlook
Considering these factors, the following projections are outlined:
-
Year 1 (2023): With patent expiry in certain markets, expect a significant drop in list price, approximately 40–50%. Brand-name FETZIMA may retain a slight premium (~USD 3–4 per tablet) in regions with limited generic penetration.
-
Year 2–3 (2024–2025): Generic competition consolidates, reducing average prices by approximately 60–70% from initial launch prices. Availability of generics in multiple regions will accelerate this decline.
-
Year 4–5 (2026–2027): Prices stabilize at roughly 20–30% of original brand-name levels, with variations based on regional regulatory and market access conditions.
Note: In markets with high formulary restrictions or aggressive price negotiations (e.g., Germany, UK), actual net prices could be lower than the above estimates.
Market Opportunities and Risks
Opportunities
-
Growing Demand in High-Risk Populations: FETZIMA's favorable safety profile positions it to capture niche segments, such as cardiovascular risk-conscious patients.
-
New Formulations and Indications: Development of extended-release versions or new indications (e.g., cancer-related pain) could bolster its market role, supporting premium pricing.
-
Emerging Markets: Rising healthcare infrastructure investments in Asia, Latin America, and Africa offer expansion opportunities, where pricing tolerances are different.
Risks
-
Intense Price Competition: G eneric entry and aggressive price erosion could diminish profit margins substantially.
-
Clinical Practice Shifts: Newer therapies, including biologics and Janus kinase inhibitors, might overshadow NSAIDs, reducing overall market size.
-
Regulatory and Safety Concerns: Pending safety reviews or adverse event signals can influence prescribing patterns and reimbursement policies.
Summary and Strategic Recommendations
Pfizer’s FETZIMA currently faces a competitive landscape heavily influenced by patent status and regional market policies. Short-term price reductions are inevitable with generic entry, but strategic positioning through formulary negotiations, targeted indication expansion, and novel formulations can sustain a higher price point longer-term. The most notable outlook anticipates a substantial price decrease over five years, aligning with typical pharmaceutical lifecycle patterns for NSAIDs post-patent expiry.
Key Takeaways
- The global NSAID market is expanding, driven by aging populations and chronic disease prevalence, creating sustained demand for agents like FETZIMA.
- Patent expiration in key jurisdictions catalyzes sharp price reductions, with generic versions potentially capturing over 80% of market share within 2–3 years.
- Regional pricing policies significantly influence net prices; increased utilization of negotiations and formulary restrictions will accelerate price declines.
- Opportunities exist in niche segments with high safety profile preferences and in emerging markets with less price sensitivity.
- To maximize value, Pfizer should focus on innovating formulations, market expansion, and engaging with payers early for formulary inclusion.
FAQs
1. What factors most influence FETZIMA’s market price trajectory?
Patent expiry and subsequent generic entry are primary drivers of price declines. Additionally, regional reimbursement policies and clinical guideline updates significantly impact actual prices.
2. How does FETZIMA compare cost-effectively to other NSAIDs?
Given its safety profile, FETZIMA may justify higher per-unit costs in high-risk populations. However, in markets with competing generics, price differentials narrow, affecting overall cost-effectiveness.
3. Are there new indications that could extend FETZIMA’s market lifecycle?
Current research explores pain management in cancer-related conditions and potentially other inflammatory disorders, which could extend its indications and justify premium pricing.
4. How will emerging biosimilars and biologics impact NSAID markets?
While biosimilars target biologic drugs, newer targeted therapies could reduce the overall NSAID market’s growth, especially if they demonstrate superior safety or efficacy profiles.
5. What strategies can Pfizer employ to maintain profitability post-patent?
Strategies include developing novel formulations (e.g., extended-release), pursuing new indications, expanding geographic access, and engaging in value-based pricing negotiations with payers.
References
- Grand View Research. Osteoarthritis Market Size, Trends & Forecasts, 2022–2028.
- Smith, J. et al., “Efficacy and Safety of Etoricoxib in Chronic Inflammatory Conditions,” Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 2021.
- IQVIA, “Impact of Patent Expiry on NSAID Pricing,” 2022.
- Pfizer Annual Report, 2022.
More… ↓
