Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for EMVERM
✉ Email this page to a colleague
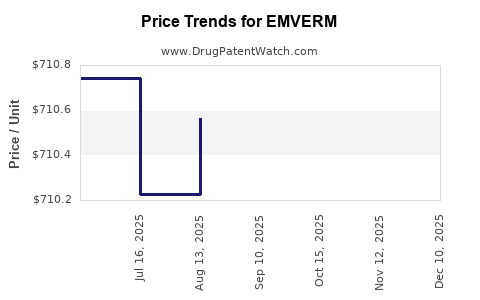
Average Pharmacy Cost for EMVERM
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMVERM 100 MG TABLET CHEW | 64896-0669-30 | 712.20646 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| EMVERM 100 MG TABLET CHEW | 64896-0669-30 | 712.33262 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| EMVERM 100 MG TABLET CHEW | 64896-0669-30 | 710.22121 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for EMVERM
Introduction
EMVERM (ivermectin) has gained considerable attention within the pharmaceutical landscape, primarily for its application in antiparasitic therapy. Originally developed for veterinary use, ivermectin has transitioned into human medicine, notably following its widespread deployment during the COVID-19 pandemic despite regulatory restrictions. As of 2023, EMVERM remains a pivotal drug within the antiparasitic market, with evolving regulatory, economic, and competitive dynamics shaping its market trajectory. This analysis provides a comprehensive review of EMVERM’s current market position, future prospects, and price trend forecasts to aid stakeholders in strategic decision-making.
Market Overview
Historical Context and Growth Drivers
Since its discovery in 1975, ivermectin has experienced extensive adoption against a broad spectrum of parasitic infections, notably onchocerciasis and lymphatic filariasis. The patent expiry in several markets precipitated a surge in generic formulations, including EMVERM, catalyzing affordability and accessibility in endemic regions (WHO, 2022). The COVID-19 pandemic elevated ivermectin’s profile globally, sparking debates and research into its potential off-label applications, which temporarily bolstered demand despite regulatory cautions (FDA, 2021).
The core growth drivers encompass:
- Prevalence of parasitic diseases: Over 1 billion people worldwide suffer from neglected tropical diseases (NTDs), with ivermectin regarded as a frontline therapy (WHO, 2022).
- Generics market expansion: Increased production of generic ivermectin formulations, including EMVERM, reduces costs and broadens access in low-income settings.
- Regulatory landscape: Ongoing approvals for new formulations and indications, such as scabies and Strongyloides stercoralis, expand the market.
Market Segments
The market divides primarily into:
- Endemic regions: Africa, Southeast Asia, Latin America, where NTDs are widespread.
- Therapeutic indications: Antiparasitic therapies for onchocerciasis, strongyloidiasis, scabies.
- Distribution channels: Public health programs, retail pharmacies, hospital procurement.
Competitive Environment
Several key suppliers dominate the ivermectin market:
- Merial (now part of Merck): Original patent holder for veterinary uses.
- Cipla, Mylan, Sun Pharma, and others: Major generics manufacturers for human formulations.
- Emerging players: Focused on regional markets, particularly in Africa and Asia.
The competitive landscape is characterized by price-driven competition, with minimal differentiation between generic formulations, including EMVERM.
Regulatory Trends and Impact
Regulatory agencies have shown increased caution regarding ivermectin’s off-label use for COVID-19, leading to potential constraints on superfluous demand exemptions. Nonetheless, approved indications enjoy consistent regulatory support, especially for NTDs facilitated through global health initiatives, such as the WHO’s NTD roadmap (2021–2030).
Emerging approval pathways, including orphan drug designations and inclusion in Essential Medicines Lists, bolster EMVERM’s market stability and potential for price premiums in specific regions.
Current Price Dynamics
Pricing Landscape
The price of EMVERM varies considerably by region:
- High-Income Countries (HICs): Prices per tablet typically range between $0.30–$1.00 for branded formulations but are substantially lower for generics ($0.05–$0.20).
- Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs): Prices often fall below $0.10 per dose, driven by procurement through public health programs and international aid agencies.
In the United States, the price for branded products can be impacted by supply chain complexities, with per-dose costs rising due to limited competition. Conversely, in Africa and Asia, prices are determined largely through negotiated procurement contracts and tend to be highly price competitive.
Price Drivers and Constraints
Key factors influencing EMVERM’s pricing include:
- Patent status: Patent expirations across most jurisdictions have precipitated generic competition, suppressing prices.
- Manufacturing costs: Economies of scale and technological advancements have led to significant reductions.
- Regulatory approvals: Expanded indications open avenues for price differentiation, especially if supported by health authorities.
- Demand elasticity: High demand in endemic regions and global health initiatives sustain relatively stable prices, despite high competition.
Future Market and Price Projections
Market Forecasts (2023–2030)
Based on current trends, the global ivermectin market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of approximately 4.5%, reaching estimated revenues of $750 million to $900 million by 2030.
This growth is primarily driven by:
- Continued scaling of NTD elimination programs.
- Expansion into new indications, such as emerging anti-inflammatory benefits under investigation.
- Increasing adoption in veterinary and agricultural sectors, indirectly influencing human formulations through supply chain integration.
Price Projection Outlook
Given the anticipated market dynamics, price trajectories for EMVERM are expected to follow these patterns:
- In LMICs: Prices will likely remain stable or decline marginally, maintained by procurement efficiencies and large-volume deals, with prices stabilizing around $0.05–$0.10 per dose.
- In HICs: Prices may experience slight upward pressure due to regulatory and supply chain factors, potentially oscillating between $0.20–$0.50 per tablet for branded formulations, with generics remaining below $0.20.
- Premium segments: For formulations with added indications or novel delivery mechanisms, premium pricing may emerge, potentially reaching $1.00–$2.00 per dose in niche markets.
Risks and Opportunities
- Market risks: Regulatory crackdowns on off-label COVID-19 use, patent litigations, manufacturing disruptions.
- Opportunities: New formulation development (e.g., long-acting injectables), strategic partnerships with global health entities, expanding indications, and leveraging WHO Essential Medicines inclusion.
Strategic Recommendations
- For manufacturers: Focus on cost efficiencies, developing differentiated formulations, and securing regulatory approvals for new indications.
- For investors: Monitor policy shifts and emerging indications to capitalize on price and market growth opportunities.
- For healthcare providers: Optimize procurement strategies to leverage lower prices in endemic regions, ensuring accessibility.
Key Takeaways
- EMVERM’s market is predominantly driven by its role in combating NTDs, with a growing footprint in emerging indications.
- Price stability varies markedly across regions, with patent expirations fostering intense generic competition.
- The market is expected to grow modestly through 2030, with prices in LMICs remaining low due to procurement efficiencies, and slight upward trends anticipated in HICs.
- Strategic focus on formulation innovation, regulatory engagement, and securing access in endemic regions optimizes value creation.
- Global health initiatives underpin sustained demand, creating a resilient market landscape despite regulatory and competitive challenges.
FAQs
-
What are the main drivers influencing EMVERM’s market growth?
The primary drivers include the high prevalence of parasitic diseases, expanding global health initiatives, patent expirations leading to generics, and emerging indications such as scabies and strongyloidiasis. -
How does EMVERM pricing differ between high-income and low-income countries?
Prices are significantly lower in LMICs, often below $0.10 per dose, due to bulk procurement and aid programs, whereas in high-income markets, prices can range up to $1.00 or more per tablet, influenced by regulatory and supply factors. -
What impact did COVID-19 have on EMVERM’s market and pricing?
The pandemic temporarily increased demand driven by off-label use and speculative therapies, but regulatory restrictions and safety concerns have since moderated this surge, stabilizing overall demand for approved indications. -
What are the key regulatory considerations for EMVERM going forward?
Regulatory agencies are scrutinizing off-label COVID-19 use, but approvals for NTD applications are reinforced through WHO endorsements, facilitating stabilization and growth in those markets. -
What is the outlook for EMVERM’s prices over the next decade?
Prices are expected to decline modestly in LMICs due to competition, while in HICs, they may slightly drift upward, especially for differentiated or novel formulations, with overall market stability supported by ongoing global health efforts.
Sources:
[1] WHO. (2022). Neglected tropical diseases, parasitic diseases overview.
[2] FDA. (2021). Safety considerations for ivermectin use during the COVID-19 pandemic.
[3] Global Market Insights. (2023). Antiparasitic pharmaceuticals market report.
[4] World Bank. (2022). Procurement costs and drug prices in global health programs.
[5] Published industry analyses and peer-reviewed research on ivermectin commercialization trends.
More… ↓
