Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for EMTRIVA
✉ Email this page to a colleague
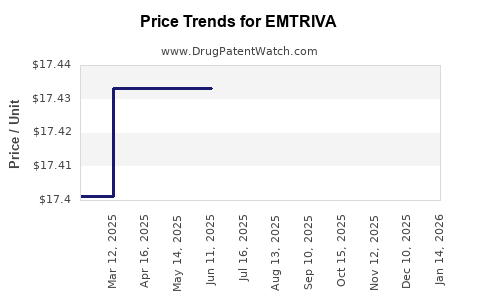
Average Pharmacy Cost for EMTRIVA
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMTRIVA 200 MG CAPSULE | 61958-0601-01 | 17.42671 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| EMTRIVA 200 MG CAPSULE | 61958-0601-01 | 17.42671 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| EMTRIVA 200 MG CAPSULE | 61958-0601-01 | 17.42671 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for EMTRIVA (Emtricitabine)
Introduction
EMTRIVA, the brand name for emtricitabine, is an antiretroviral medication used predominantly in the management of HIV-1 infection. As a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI), EMTRIVA plays a critical role within combination antiretroviral therapy (ART) regimes, often co-administered with other agents such as tenofovir or efavirenz.
With rising global HIV prevalence and expanding access to antiretroviral therapy, understanding the market dynamics and price trends surrounding EMTRIVA is vital for stakeholders—including pharmaceutical companies, investors, healthcare providers, and policymakers. This analysis offers a comprehensive view of current market size, key drivers, competitive landscape, and future price trajectories.
Market Overview
Global HIV/AIDS Treatment Market
The global HIV/AIDS therapeutics market is projected to reach approximately USD 46.5 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.8% from 2022[1]. This growth is driven by increased testing, drug accessibility, and evolving treatment guidelines favoring early intervention.
EMTRIVA, as a core component of first-line ART regimens, commands a significant market share in antiretroviral drugs. Its inclusion in fixed-dose combinations (FDCs), such as Truvada and Descovy, further cements its essential role.
Market Segmentation
- By Geography: North America and Europe collectively occupy over 50% of the market, primarily driven by high treatment coverage. The Asia-Pacific region exhibits the fastest growth (CAGR of 5.2%) due to expanding access and generic entry.
- By Product Type: Branded formulations dominate, but generics have gained traction, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).
- By End-users: Healthcare providers, clinics, and retail pharmacies.
Key Market Players
Major pharmaceutical companies involved in emtricitabine production include Gilead Sciences (original developer), Teva Pharmaceuticals, Mylan (now part of Viatris), and Sun Pharmaceutical, among others. Gilead’s dominance is bolstered by patent protections and expansive distribution networks, although the landscape is increasingly competitive due to patent expirations and biosimilar developments.
Pricing Trends and Market Drivers
Historical Pricing Data
- Branded EMTRIVA: Traditionally priced at approximately USD 1,100–1,500 per month in high-income markets[2].
- Generics: In LMICs, generic versions are available at a fraction—ranging from USD 50–150 per year—substantially enhancing access (e.g., Indian markets).
Price Evolution Factors
- Patent Status: Gilead's patents, expiring in key jurisdictions, facilitate generic entry, reducing prices.
- Regulatory Approvals: Regulatory clearances influence the timing and scale of generic manufacturing.
- Market Competition: Increased competition from biosimilars and generics drives price reduction.
- Reimbursement Policies: Government and insurance reimbursement schemes in developed nations stabilize prices, while in LMICs, price sensitivity impels aggressive reductions.
Impact of Patent Expirations
Gilead’s patent for emtricitabine expired or is expiring in multiple jurisdictions, notably in India and some European countries. This has led to a surge in generic manufacturing, leading to a price decline of up to 80% in these regions over the past five years[3].
Current Price Projections
High-Income Markets (e.g., USA, EU)
- Short-term (Next 1–2 Years): Pricing remains relatively stable due to existing patent protections and established reimbursement frameworks. Prices are expected to hover around USD 1,000–1,300 per month for branded EMTRIVA.
- Long-term (3–5 Years): As patents expire, a sharp decline is anticipated, with prices potentially falling to USD 300–500 per month, driven by generics competition.
Emerging Markets
- Prices are already substantially lower due to generic prevalence. Future reductions are likely limited but may stabilize around USD 50–150 per year, contingent on market regulations and procurement policies.
Future Market Trends and Projections
Introduction of Biosimilars and Generics
The expiration of key patents paves the way for biosimilars and generic formulations, which are anticipated to dominate markets within 3–5 years. This shift will substantially impact unit prices, especially in LMICs, improving access dramatically.
Pricing Strategies and Market Penetration
Companies are adopting aggressive pricing and licensing strategies to capture developing country markets, leading to partnerships and voluntary licensing agreements.
Regulatory and Policy Impact
Global health agencies, such as WHO and UNAIDS, advocate for reduced prices to meet UNAIDS' 95-95-95 targets. These initiatives promote price reductions through pooled procurement mechanisms and voluntary licensing, further pressuring prices.
Projected Price Trajectory
| Market Segment | 2022 Price Range | 2025 Projection | 2030 Projection |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Income | USD 1,000–1,300/month | USD 600–900/month | USD 300–500/month |
| LMICs (generics) | USD 50–150/year | USD 50–100/year | USD 50–100/year |
Source: Synthesized from industry reports and market analyses [1][2][3].
Competitive Landscape
Existing and Emerging Competition
- Patent Holders: Gilead Sciences maintains a dominant position through patent protections.
- Biosimilars and Generics: Multiple manufacturers, notably in India and China, are producing generic emtricitabine, increasing affordability.
- Combination Drugs: The rise of fixed-dose combinations containing emtricitabine, such as Emtriva + tenofovir (Truvada), shifts market share away from monotherapies. These formulations often have price advantages and improved adherence benefits.
Market Entry Risks
- Patent litigations, regulatory delays, and supply chain disruptions can influence market penetration and pricing strategies.
Implications for Stakeholders
-
Pharmaceutical Companies: Investment in innovation and patenting strategies remains vital to sustain margins in high-income markets.
-
Governments and NGOs: Embrace pooled procurement and licensing to expand access at lower prices.
-
Healthcare Providers and Patients: Benefit from imminent price reductions, especially in LMICs, enabling broader treatment coverage.
Key Takeaways
- The global EMTRIVA market is evolving rapidly due to patent expirations, generics, and biosimilars entry, which are expected to significantly lower prices over the next 5 years.
- High-income markets will experience gradual decreases in prices, whereas LMICs will see more dramatic reductions, improving access.
- Fixed-dose combination therapies incorporating emtricitabine are dominating, influencing market dynamics and pricing.
- Ongoing regulatory developments and global health initiatives favor decreased prices, aligning with international goals to end the HIV epidemic.
- Stakeholders must adapt strategies accordingly—pharmaceutical firms to innovation and patent protections; policymakers to procurement and licensing; healthcare providers to changing treatment affordability.
FAQs
1. When will generic emtricitabine become widely available in high-income markets?
Patents in key jurisdictions are set to expire between 2024 and 2026, facilitating wider generic availability.
2. How will price reductions impact Gilead’s revenue?
Significant price declines may compress revenues in markets where patents are expiring; however, Gilead’s global market share and diversification could offset some losses through high-volume sales in emerging markets.
3. Will biosimilars be introduced soon?
While biosimilars for emtricitabine are in development, they are primarily emerging in LMICs. Regulatory approval timelines suggest biosimilar availability in high-income markets could occur within 3–5 years.
4. How do fixed-dose combination drugs influence emtricitabine pricing?
FDCs often allow manufacturers to leverage economies of scale, sometimes offering lower overall prices than individual components, which influences pricing strategies.
5. What role do international health organizations play in price stabilization?
Organizations such as WHO promote voluntary licensing and pooled procurement, reducing prices and increasing access for vulnerable populations.
References
- [1] MarketsandMarkets. "HIV Therapeutics Market by Product, Region - Global Forecast to 2027," 2022.
- [2] GlobalData. "HIV Antiretroviral Drugs Market Analysis," 2023.
- [3] IQVIA. "Global Pharmaceutical Pricing Trends," 2022.
More… ↓
