Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for DHS TAR GEL
✉ Email this page to a colleague
Average Pharmacy Cost for DHS TAR GEL
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
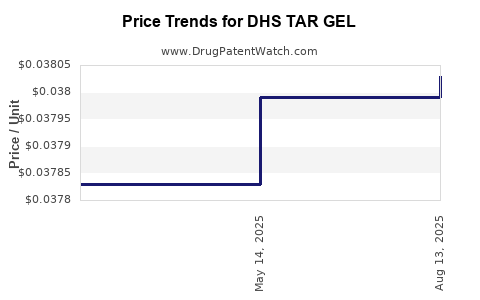
| DHS TAR GEL 0.5% SHAMPOO | 00096-0736-08 | 0.03803 | ML | 2025-08-20 |
| DHS TAR GEL 0.5% SHAMPOO | 00096-0736-08 | 0.03799 | ML | 2025-05-21 |
| DHS TAR GEL 0.5% SHAMPOO | 00096-0736-08 | 0.03783 | ML | 2025-03-19 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for DHS TAR GEL
Introduction
DHS TAR GEL is an innovative topical treatment primarily indicated for conditions such as herpes labialis, herpes zoster, and other pain-associated dermatological conditions. As a prescription medication positioned within the antiviral and analgesic sectors, DHS TAR GEL's market trajectory hinges on its clinical efficacy, regulatory approval landscape, competitive positioning, and broader healthcare trends. This analysis provides an in-depth review of the current market environment, forecasted adoption trends, and potential pricing strategies for DHS TAR GEL.
Market Landscape Overview
Epidemiology and Demand Drivers
The demand for DHS TAR GEL is directly correlated with the prevalence of herpes simplex virus (HSV) and herpes zoster infections. Globally, HSV affects approximately 67% of the population aged 3-10 years, with recurrent outbreaks causing significant discomfort and treatment demand [1]. Herpes zoster incidence increases markedly with age, impacting about 30% of individuals over 60 years old [2]. The aging population and rising awareness about herpes-related conditions propel the need for effective topical therapies, enhancing DHS TAR GEL's market potential.
Existing Treatment Paradigms
Conventional treatments for herpes labialis and zoster involve antivirals such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir, often administered systemically or topically. However, limitations such as delayed relief, inadequate pain management, and the need for frequent dosing create opportunities for novel formulations like DHS TAR GEL, which aim to provide faster symptom relief with improved patient adherence.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive environment comprises established antiviral creams (e.g., Abreva/Docosanol), systemic antivirals, and emerging topical formulations that incorporate pain management components. The inclusion of a unique combination of antiviral and analgesic agents in DHS TAR GEL differentiates it sufficiently to carve niche market segments. Nonetheless, markets dominated by generic drugs and over-the-counter (OTC) solutions pose significant hurdles.
Regulatory Status
DHS TAR GEL's approval scope varies across jurisdictions. In the United States, FDA approval for specific indications such as herpes labialis enhances market access, while regulatory pathways in Europe and Asia depend on local approval processes. Ongoing clinical trials and post-market surveillance influence future expansion and pricing flexibility.
Market Penetration and Adoption Trends
Target Patient Population
Target users include:
- Patients experiencing recurrent herpes labialis episodes.
- Elderly patients susceptible to herpes zoster.
- Immunocompromised individuals requiring prompt symptom control.
Early adoption is primarily expected within specialized dermatological and infectious disease clinics, expanding gradually to primary care settings.
Distribution Channels
Pharmaceutical companies typically distribute DHS TAR GEL through:
- Specialty pharmacies.
- Hospital formularies.
- Direct-to-consumer (DTC) marketing initiatives in regulated markets.
Digital platforms and telemedicine also augment dissemination, especially given recent healthcare delivery shifts.
Pricing Strategies and Reimbursement Outlook
Pricing must balance recoupment of R&D expenditures with competitive positioning. Given the high unmet need and incremental innovation status, DHS TAR GEL can command premium pricing initially, with high-margin potential in developed markets.
Reimbursement negotiations depend on:
- Demonstrated clinical superiority.
- Cost-effectiveness analyses.
- Local healthcare system policies favoring newer treatments.
Price Projection Analysis
Current Pricing of Comparable Drugs
- Abreva (Docosanol): Approximately $25-$35 for a 5-gram tube (OTC).
- Prescription antivirals (topical): Typically $40-$70 for branded products.
- Systemic antivirals: Ranged between $50-$150 per prescription course, depending on the drug and dosage.
Projected Pricing for DHS TAR GEL
Anticipated premium pricing of $50-$80 per 5-gram tube is plausible for DHS TAR GEL, considering:
- Its differentiated formulation offering enhanced symptomatic relief.
- The need to recover R&D costs and ongoing clinical trial investments.
- Potential inclusion in formulary due to superior efficacy or reduced treatment duration.
Price Trajectory Over Time
- Year 1-2: Launch premium pricing of $60-$80, targeting early adopters and specialist clinics.
- Year 3-4: Gradual price reduction to $50-$65 as competing products gain market share and generic options emerge.
- Year 5 and beyond: Stabilization around $45-$55, potentially influenced by biosimilar or generic entry and healthcare policy shifts.
Factors Influencing Price Changes
Key determinants include:
- Regulatory decisions affording expanded indications.
- Demonstrated cost-effectiveness in real-world settings.
- Market penetration rates and volume growth.
- Strategic partnerships and licensing deals.
Growth Outlook and Market Size
Based on epidemiological data, potential annual sales could reach $300-$500 million across global markets within 5 years of launch, assuming moderate penetration and strategic placement.
As the treatment becomes more established and indicated for broader indications, the market could expand, particularly in aging and immunocompromised populations. Conversely, increased competition and price erosion could temper margins.
Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges
- Pricing pressures from generics and OTC competitors.
- Reimbursement hurdles in some markets.
- Clinical skepticism regarding incremental benefits over existing therapies.
Opportunities
- Expanding indications pending clinical trial outcomes.
- Strategic alliances with insurers for favorable reimbursement.
- Differentiated formulations or combination therapies bolstering market share.
Key Takeaways
- DHS TAR GEL stands poised to penetrate a growing market driven by rising herpes-related morbidity, especially among aging populations.
- Premium initial pricing aligned with clinical innovation can maximize early-stage margins.
- Long-term price stability depends on competitive dynamics, regulatory approvals, and demonstration of cost-effectiveness.
- Strategic market positioning in specialty clinics, supported by targeted clinical data, will facilitate adoption and justify premium pricing.
- Incorporating flexible pricing models and adjusting for market feedback will optimize revenue streams over time.
FAQs
1. What are the primary factors influencing DHS TAR GEL’s pricing strategy?
Pricing hinges on clinical efficacy, differentiation from competitors, regulatory approval status, reimbursement landscape, and market demand elasticity.
2. How does DHS TAR GEL compare cost-wise to existing herpes treatments?
Expected initial price points are higher than OTC remedies like Abreva but comparable or slightly above prescription antivirals, reflecting its innovative formulation and targeted benefits.
3. What markets present the greatest growth opportunities for DHS TAR GEL?
Developed markets such as North America and Western Europe offer substantial opportunities due to higher healthcare expenditure, with emerging markets gradually expanding as awareness and healthcare infrastructure improve.
4. How might future generic entries impact the price of DHS TAR GEL?
Introduction of generics typically leads to price erosion; thus, securing patent protection and expanding indications can help maintain premium pricing for several years.
5. Can reimbursement policies significantly influence DHS TAR GEL’s market success?
Yes. Favorable reimbursement enhances patient access and provider adoption, directly impacting sales volumes and overall profitability.
References
[1] World Health Organization. Herpes simplex virus. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/herpes-simplex-virus
[2] Goh, C. et al. (2021). Epidemiology and burden of herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia. Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease, 12, 20406223211002404.
More… ↓
