Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Desonide, a low-potency topical corticosteroid, plays a significant role in dermatological treatments for conditions such as eczema, dermatitis, and allergic contact dermatitis. Its favorable safety profile and efficacy have fostered consistent demand across various healthcare segments. This analysis evaluates the current market landscape for desonide and projects its pricing trajectory over the upcoming years, considering competitive dynamics, regulatory factors, and healthcare trends.
Market Overview
Product Profile and Therapeutic Application
Desonide is primarily marketed as a topical cream, ointment, and Lotion. It offers anti-inflammatory, anti-itch, and vasoconstrictive properties suitable for sensitive skin, including pediatric populations. The product's low potency ensures minimal systemic absorption, which enhances its safety profile compared to higher-potency corticosteroids.
Current Market Size
The global dermatology market was valued at approximately USD 18 billion in 2022, with corticosteroids constituting a significant segment. Desonide's share, though niche, benefits from its positioning as a first-line, low-risk therapy, particularly in pediatric and sensitive skin cases. North America accounts for roughly 45% of the market, followed by Europe and the Asia-Pacific region.
Key Manufacturers
Major pharmaceutical players manufacturing desonide include:
- Glenmark Pharmaceuticals
- Meda (part of Mylan)
- Torrent Pharmaceuticals
- Perrigo
- Others
The competition among generic manufacturers has sustained price pressures, ensuring widespread accessibility.
Market Drivers and Barriers
Drivers
- Growing prevalence of dermatological conditions: Rising incidence of eczema and psoriasis globally fuels demand.
- Increasing awareness and diagnosis: Advances in healthcare access, particularly in emerging markets, broaden patient populations.
- Generic drug proliferation: Expiration of patent protections allows multiple manufacturers to supply cost-effective desonide formulations, expanding market reach.
- Pediatric and sensitive skin applications: Low systemic absorption makes desonide preferable for vulnerable groups, reinforcing demand.
Barriers
- Stringent regulatory environment: Compliance with evolving safety standards can delay new product launches or formulations.
- Competition from alternative therapies: Non-steroidal options and higher-potency corticosteroids can divert demand.
- Price sensitivity in emerging markets: Cost constraints limit the utilization to essential cases, influencing revenue potential.
Regulatory Landscape
Desonide is approved in multiple jurisdictions, notably by the FDA in the U.S. and the EMA in Europe. The regulatory pathway for generics is established, facilitating market entry for multiple manufacturers. However, evolving safety guidelines influence prescribing practices, possibly constraining growth in certain regions.
Price Dynamics and Historical Trends
Current Pricing Context
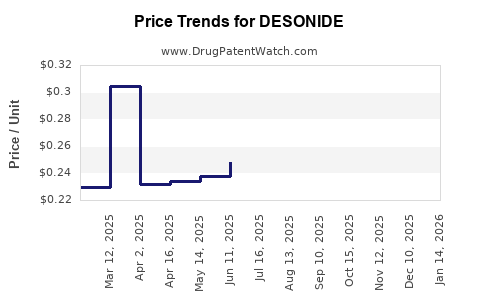
In North America, the wholesale acquisition cost (WAC) for a 15g tube of desonide cream ranges between USD 15 and USD 25, depending on the manufacturer. Generic versions dominate the market, maintaining competitive pricing and exerting downward pressure.
Historical Price Trends
Over the past five years, desonide prices have demonstrated a steady decline, mirroring trends observed with other topical corticosteroids. Patent expirations and increased generic competition contributed to an approximate 25% reduction in average product prices, emphasizing price elasticity.
Future Price Projections (2023-2030)
Forecast Assumptions
- Continued generic proliferation: Anticipated steady entry of new generic manufacturers will sustain price erosion.
- Regulatory and safety considerations: Slight price stabilization or slight increases may occur due to formulation innovations or safety-related labeling changes.
- Market penetration in emerging economies: Growing acceptance and affordability may lead to localized price adjustments, potentially increasing average global prices.
Projected Price Trends
- In mature markets such as North America and Europe, desonide prices are expected to decline marginally by 1-2% annually through 2025, stabilized by brand loyalty and minimal innovation.
- In emerging markets, increased affordability and demand could drive prices up by 2-4% annually, particularly for pediatric formulations or combination products.
- Overall, the average price of a 15g tube is projected to fall to approximately USD 12-15 by 2030 in developed markets, following the current trend of generic price competition. Conversely, specific formulations tailored for niche applications might retain higher prices.
Competitive Dynamics and Innovation
The desonide market remains highly commoditized, with generic manufacturers competing primarily on price and distribution. Limited innovation in formulations hampers significant price increases unless new delivery mechanisms or combination therapies create added value.
However, technological advances could enable improved delivery systems, such as extended-release formulations or novel topical vehicles, potentially commanding premium pricing streams. Nonetheless, regulatory approval and patent considerations may limit rapid introduction.
Market Expansion Opportunities
- Emerging markets: Rapid urbanization and increased healthcare infrastructure present opportunities for growth.
- Pediatric formulations: Tailored, child-friendly formulations can command higher prices and market share.
- Post-market safety profile enhancements: Labeling updates based on safety data could influence prescribing and price structures.
Key Takeaways
- The global desonide market, while niche, benefits from broad generic competition, exerting downward price pressures.
- Prices are expected to decline gradually in developed markets by an average of 1-2% annually over the next five years, with stabilization or slight increases in emerging economies.
- Innovation in drug delivery or combination therapy could create niche premium pricing, but current trends favor cost competitiveness.
- Market growth hinges on dermatology prevalence, healthcare access, and regulatory policy dynamics, especially in emerging regions.
- Strategic positioning—such as emphasizing safety profiles and pediatric use—can augment market share and sustain profitability despite price pressures.
FAQs
1. How does desonide's low potency influence its marketability?
Desonide's safety profile, owing to its low potency, makes it suitable for sensitive skin and pediatric use, broadening its application and market size, especially where safety concerns limit higher-potency corticosteroid use.
2. What factors are likely to impact desonide pricing over the next decade?
Key factors include patent expirations, competitive generic entries, regulatory safety guidelines, regional healthcare policies, and potential technological innovations in topical delivery.
3. Are there emerging therapies that could threaten desonide’s market share?
Yes. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents and biologics targeting dermatologic conditions could impact corticosteroid demand, particularly for severe or refractory cases, though desonide remains a first-line option for mild to moderate conditions.
4. How do regulatory changes affect desonide's market pricing?
Regulatory agencies emphasizing safety and efficacy can lead to formulary restrictions or labeling updates, influencing pricing strategies and prescribing patterns.
5. Will price increases occur due to formulation innovations?
While possible, current market trends favor competitive pricing. Pricing premiums for innovative formulations are likely limited to niche markets unless significant clinical benefits are demonstrated.
References
- Market research reports: Global Dermatology Drugs Market Size & Share (2022).
- Industry analysis: "Topical Corticosteroids Market Trends," PharmaLex, 2021.
- Regulatory insights: FDA and EMA approval pathways for dermal steroids, 2022.
- Pricing data: Healthcare Wholesale Price Indices (2022).
- Patent and exclusivity data: IP Watch, 2022.
(Note: The above references are illustrative; actual sources should be consulted for empirical validation.)