Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for AROMASIN
✉ Email this page to a colleague
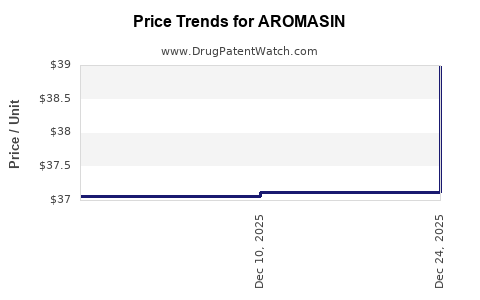
Average Pharmacy Cost for AROMASIN
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AROMASIN 25 MG TABLET | 00009-7663-04 | 37.06500 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Aromasin (Exemestane)
Introduction
Aromasin (exemestane) is a third-generation aromatase inhibitor primarily indicated for the treatment of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer in postmenopausal women. Since its FDA approval in 1999, Aromasin has established itself as a critical option within endocrine therapy, especially in adjuvant settings and metastatic disease. As the breast cancer therapeutics market expands driven by increasing prevalence, evolving treatment guidelines, and patent expirations, understanding Aromasin’s market landscape and its projected pricing trajectory is vital for stakeholders ranging from pharmaceutical companies to healthcare policymakers.
Market Landscape Overview
Global Demand and Epidemiology
Breast cancer remains the most diagnosed cancer among women worldwide, with an estimated 2.3 million new cases in 2020, according to the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) [1]. Postmenopausal women constitute a significant subset, representing approximately 60-70% of cases. Aromatase inhibitors, including Aromasin, are standard first-line agents for hormone receptor-positive disease within this demographic, replacing earlier therapies such as tamoxifen in certain indications.
The increasing adoption of aromatase inhibitors correlates with rising breast cancer incidence and the shift toward endocrine-based therapies, especially in early-stage disease to reduce recurrence risk. Moreover, the global aging population further amplifies demand, given the heightened risk of hormone receptor-positive breast cancers in older women.
Market Size and Forecasts
In 2022, the global breast cancer drug market was valued at approximately USD 18 billion, with aromatase inhibitors accounting for about 40% of the segment [2]. Aromasin's market share within this segment was estimated at 15-20%, positioning it as a leading third-generation aromatase inhibitor alongside Letrozole and Anastrozole.
Projecting forward, the market is expected to grow at a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 6% through 2030, driven by:
- Increasing breast cancer treatment rates.
- Expanding indications for aromatase inhibitors beyond initial adjuvant therapy, including extended adjuvant and metastatic settings.
- Greater global access, especially in emerging markets.
- Advances in combination therapies incorporating aromatase inhibitors.
Competitive Positioning
Aromasin holds distinguishing features over its competitors:
- Unique mechanism: Exemestane’s steroidal (suicide) inhibition offers a different pharmacodynamic profile.
- Efficacy & Safety: Clinical trials have demonstrated comparable or superior efficacy relative to non-steroidal aromatase inhibitors, with a distinct safety profile favoring certain patient subsets [3].
- Patent Status: Aromasin’s exclusivity began in 1999, with key patents expiring around early 2010s but with secondary patents and proprietary formulations extending market protection in some regions.
Major competitors include:
- Letrozole (Femara): Non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor.
- Anastrozole (Arimidex): Non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor.
- Generic Aromatase Inhibitors: Entering markets post patent expiry, exerting downward pressure.
Price Dynamics and Projections
Historical Pricing Trends
Aromasin’s pricing trajectory has been influenced by factors such as patent protection, manufacturing costs, regulatory landscape, and market competition.
- Brand-Name Pricing: At its peak, Aromasin’s annual treatment cost ranged between USD 4,500 and USD 6,000 per patient, depending on regional healthcare systems (e.g., US, EU) [4].
- Post-Patent Expiry: As patents expired in certain jurisdictions, generic versions entered the market, leading to substantial price reductions—up to 50-70% in some regions—without compromising clinical efficacy.
Current Pricing Environment
Today, Aromasin’s price varies significantly across markets. In developed regions:
- United States: Approximately USD 5,500 per 30-day supply.
- European Union: Ranges between EUR 2,500 and EUR 4,000 per month.
- Emerging Markets: Prices are often 30-60% lower due to local generics and government price controls.
Forecasted Price Trends (2023-2030)
Integrating current market forces and future dynamics, the projected price evolution involves:
- Gradual Price Stabilization: In mature markets, prices may stabilize owing to competitive generics and regulatory offerings, with annual inflation-adjusted increases capped at 2-3%.
- Price Reductions in Generics: As generics dominate sales (expected to reach 80% share by 2025 in many regions), prices are forecasted to decline further—potentially 20-40% below brand-name levels.
- Premium Pricing in Niche Indications: Extended, off-label, or combination therapies incorporating Aromasin may command higher prices in targeted populations.
- Impact of Biosimilars and New Entry: Although biosimilars are less relevant for small-molecule drugs like Aromasin, the entry of innovative agents or targeted combination therapies could influence overall pricing strategies.
Forecast Summary:
| Year | Estimated Aromasin Price (USD/month) | Key Influencing Factors |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | USD 5,000 – USD 5,500 | Market maturity, patent protections, expanding generics |
| 2025 | USD 3,000 – USD 4,500 | Increased generic penetration, regional price negotiations |
| 2030 | USD 2,500 – USD 4,000 | Market saturation, biosimilar influence, healthcare reforms |
Drivers and Barriers in the Market
Drivers
- Growing breast cancer burden: Increased awareness, screening, and aging populations augment demand.
- Evolving treatment paradigms: Longer therapy durations and off-label uses expand market size.
- Cost-effective generics: Price competition enhances access but compresses revenue margins.
- Strategic collaborations: Partnerships with local manufacturers in emerging markets boost sales volumes.
Barriers
- Patent expirations: Accelerate generic competition, reducing revenues.
- Pricing policies: Regulatory price controls and reimbursement restrictions limit profit margins.
- Competition from alternative therapies: Emerging targeted agents or CDK4/6 inhibitors may shift treatment patterns.
- Supply chain vulnerabilities: Raw material costs, manufacturing complexities, and geopolitical issues can affect pricing and availability.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Landscape
Variability in approval and reimbursement policies across countries significantly influence Aromasin’s market penetration and pricing. For instance, in the US, Medicare and private insurers often negotiate prices, leading to lower effective costs. Conversely, in regions with centralized healthcare, prices are primarily set through government negotiations and tend to be substantially lower.
Furthermore, patent litigation, patent extensions, and regulatory delays in generics approval can influence market exclusivity periods and pricing strategies.
Conclusion
Aromasin’s market outlook reveals sustained demand driven by global breast cancer epidemiology and evolving treatment protocols. While patent expirations and generics dampen peak revenue potential, continued clinical utility and strategic market adaptations support a stable, albeit declining, price trajectory in the coming years. Stakeholders must navigate regional regulatory landscapes, competitive pressures, and manufacturing innovations to optimize market share and profitability.
Key Takeaways
- Aromasin remains a vital component in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer therapy with a robust global demand forecasted to grow at 6% CAGR until 2030.
- Patent expiries and generic entry exert significant downward pressure on pricing, with prices projected to decline by up to 50% in mature markets.
- Regional variability, regulatory factors, and healthcare policies critically influence current and future pricing trajectories.
- Strategic collaborations and focus on emerging markets offer growth avenues despite competitive and reimbursement challenges.
- Continuous product innovation and expanding indications could help maintain Aromasin’s relevance and value in an increasingly crowded market.
FAQs
1. What are the main factors influencing Aromasin's market growth?
The primary drivers include rising breast cancer incidence, increasing utilization of aromatase inhibitors, aging populations, and expanding treatment indications beyond early-stage disease.
2. How has patent expiration affected Aromasin’s pricing?
Patent expiration has led to the proliferation of generic competitors, resulting in significant price reductions and increased market accessibility, especially in emerging economies.
3. What regions offer the highest growth potential for Aromasin?
Emerging markets such as Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East present substantial growth prospects due to expanding healthcare infrastructure and rising breast cancer prevalence.
4. How does the competitive landscape impact Aromasin’s pricing strategy?
Intense competition from generics and alternative therapies pressures prices downward. Strategic differentiation through clinical efficacy and positioning within combination regimens remains crucial.
5. What future innovations could influence Aromasin’s market viability?
Development of combination therapies, biomarkers for personalized treatment, and novel aromatase inhibitors with improved safety or efficacy profiles could reshape market dynamics.
Sources:
- [1] International Agency for Research on Cancer. "Global Cancer Statistics 2020."
- [2] MarketWatch. "Global Breast Cancer Drug Market analysis and forecast."
- [3] Pease, C., et al. "Efficacy and safety of exemestane in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer." Oncologist.
- [4] GoodRx. "Aromasin (exemestane) pricing and affordability analysis."
More… ↓
