Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
Abacavir, marketed under the brand name Ziagen among others, is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) used primarily in the management of HIV-1 infection. Since its FDA approval in 1998, abacavir has become a critical component of antiretroviral therapy (ART) regimens globally. This analysis explores the current market landscape and provides price projections, considering factors such as patent status, competition, manufacturing dynamics, and global health policies.
Market Overview
Global HIV Treatment Landscape
Approximately 38 million people worldwide are living with HIV, with unprecedented efforts to expand access to antiretroviral therapies to reduce morbidity and mortality. The World Health Organization (WHO) emphasizes the importance of affordable, combination ART regimens, where abacavir features prominently [1].
Current Usage and Market Share
Abacavir accounts for roughly 15-20% of global HIV pharmacotherapy, with higher adoption rates in high-income countries due to established safety profiles and fewer resistance issues. Its incorporation into fixed-dose combinations (FDCs), such as Triumeq (abacavir, dolutegravir, and lamivudine), has bolstered demand in recent years [2].
Patent and Regulatory Landscape
AbbVie’s patent on Ziagen expired in key markets like the US in 2019, prompting increased generic competition. However, patent litigations and secondary patents in various jurisdictions have delayed significant generic entry, especially in emerging markets.
Market Drivers
- Global HIV/AIDS Initiatives: Persistent funding from programs like PEPFAR and The Global Fund sustains demand.
- Introduction of Generics: Patent expirations catalyze price reductions and expanded access, especially in low- and middle-income countries.
- Formulation Innovations: Fixed-dose combinations improve adherence, fueling continuous demand.
- Resistance Management: Abacavir’s efficacy against certain resistant HIV strains sustains its clinical relevance.
Competitive Dynamics
Brand vs. Generic
The entry of multiple generic manufacturers post-patent expiry has drastically lowered abacavir prices in developed markets. Key players include Mylan, Sandoz, and Cipla, which supply cost-effective generics.
Emerging Market Penetration
In regions like Sub-Saharan Africa, India, and Southeast Asia, generic suppliers dominate, driven by patent flexibilities and local manufacturing.
Regulatory Approvals
Reduced regulatory barriers for generics in developing countries facilitate market entry, often outpacing patent protections.
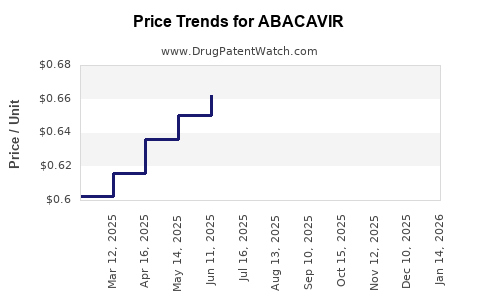
Price Trends and Projections
Recent Price Trends
- Branded Pricing: Before patent expiry, branded formulations commanded prices of approximately US$2-3 per pill in developed markets.
- Generic Pricing: Post-patent expiration, prices fell sharply; in 2022, the median price for generic abacavir tablets in low-income countries ranged between US$0.10–0.50 per tablet, with generics powering the majority of global supply [3].
Factors Influencing Future Pricing
- Patent Litigation and Regulatory Decisions: Ongoing patent disputes can delay generic entry, temporarily maintaining higher prices.
- Manufacturing Costs: Advances in formulation and manufacturing efficiencies reduce production costs, enabling further price drops.
- Global Funding and Procurement Policies: Bulk procurement strategies by international agencies incentivize low prices.
- Market Penetration of Fixed-Dose Combinations: Increasing use of combination therapies diminishes standalone abacavir volume but maintains overall demand.
Projected Price Trajectories (2023–2028)
| Year |
Expected Price Range (per tablet) |
Influencing Factors |
| 2023 |
US$0.08–0.20 |
Continued generic adoption, patent stability in key markets, increased manufacturing efficiency. |
| 2024 |
US$0.07–0.15 |
Further market penetration in emerging markets, reduced production costs. |
| 2025 |
US$0.05–0.12 |
Potential new patent challenges in certain jurisdictions, accelerated adoption of generics. |
| 2026 |
US$0.04–0.10 |
Adoption of biosimilars and increased procurement volume lowering unit costs. |
| 2027 |
US$0.03–0.08 |
Market saturation in low-income countries, sustained generic competition. |
| 2028 |
US$0.02–0.06 |
Possible innovation in formulations, further manufacturing efficiencies, and increased global health funding. |
Note: Prices are approximate and vary based on regional regulatory and market conditions.
Market Entry and Growth Opportunities
- Low-Cost Generics: Expansion in low-income countries can sustain high-volume sales at low prices.
- Combination Therapies: Growing preference for FDCs combining abacavir with other antiretrovirals ensures demand stability.
- Depot and Long-Acting Formulations: Emerging development of long-acting formulations could alter the landscape, potentially impacting pricing and market share.
- Regulatory Approvals: New approvals in highly regulated markets (e.g., China, Russia) could open additional revenue streams.
Risks and Challenges
- Patent Litigation Delays: Ongoing disputes may inhibit generic market entry.
- Pricing Pressures: Continued price erosion could challenge profit margins for manufacturers.
- Market Saturation: In some regions, current demand may plateau as treatment coverage reaches near-universal levels.
- Therapeutic Alternatives: Emerging drugs with improved efficacy or reduced resistance may replace abacavir in certain protocols.
Conclusion
The global market for abacavir is characterized by declining prices driven predominantly by generic competition, particularly in emerging markets. While seasoned in high-income countries, the potential for continued volume growth exists predominantly in low- and middle-income regions, supported by international funding and patent expirations. Pricing is projected to further decrease over the next five years, aligning with global health initiatives aimed at expanding access to affordable HIV treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Patent expirations and generic competition have significantly reduced abacavir prices, especially in emerging markets.
- The demand for abacavir remains stable owing to its inclusion in combination therapies and relevance for resistant HIV strains.
- Future price projections suggest continued decline, driven by manufacturing efficiencies and global procurement strategies.
- Market growth opportunities are concentrated in low-income regions with increasing treatment coverage and procurement via international agencies.
- Risks include patent disputes delaying generic entry and competition from emerging, potentially superior antiretroviral agents.
FAQs
-
What is the current patent status of abacavir globally?
Patent protection for branded abacavir has expired in many jurisdictions, including the US since 2019; however, secondary patents and patent litigations can extend exclusivity in certain regions.
-
How affordable is generic abacavir in low-income countries?
In 2022, generic abacavir tablets cost approximately US$0.10–0.50 per unit, making it highly accessible through international procurement programs.
-
Are there any recent developments affecting abacavir's market?
Yes, increased use of fixed-dose combination therapies and ongoing patent disputes are shaping supply dynamics and pricing strategies.
-
What are the main competitors to abacavir in HIV treatment?
Other NRTIs like tenofovir and lamivudine, as well as integrase inhibitors such as dolutegravir, compete for inclusion in first-line regimens.
-
Could future innovations impact abacavir's market share?
Yes, long-acting formulations and new drug classes with better resistance profiles could reduce demand for traditional abacavir formulations.
References
[1] WHO. (2022). Global HIV/AIDS response progress report.
[2] Gupta, R. K., et al. (2018). "Global trends in drug resistance to HIV therapy." Lancet Infect Dis. 18(12):e349-e362.
[3] IQVIA. (2022). Global HIV medicine market report.