Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for ABACAVIR-LAMIVUDINE
✉ Email this page to a colleague
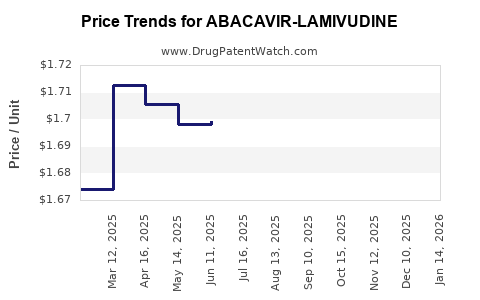
Average Pharmacy Cost for ABACAVIR-LAMIVUDINE
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABACAVIR-LAMIVUDINE 600-300 MG | 69097-0362-02 | 1.43534 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| ABACAVIR-LAMIVUDINE 600-300 MG | 65862-0335-30 | 1.43534 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| ABACAVIR-LAMIVUDINE 600-300 MG | 42385-0962-30 | 1.43534 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Abacavir-Lamivudine
Introduction
Abacavir-Lamivudine, a fixed-dose combination (FDC) antiretroviral therapy (ART), has solidified its role in managing HIV-1 infection globally. Its distinct therapeutic profile, combined with market dynamics, regulatory pathways, and manufacturing factors, influences its current valuation and future pricing trajectory. This analysis provides a comprehensive review of market standing, competitive landscape, pricing structures, and projections for Abacavir-Lamivudine over the next five years.
Therapeutic Overview and Market Position
Abacavir (ABC) and Lamivudine (3TC) are nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) used in combination therapy. The fixed-dose formulation offers ease of administration, improved adherence, and a robust efficacy and safety profile endorsed by the World Health Organization (WHO) and leading HIV treatment guidelines globally [1].
In 2022, the global HIV treatment market was valued at approximately USD 23 billion, with antiretrovirals comprising a significant segment. Within this, Abacavir-Lamivudine contributed notably due to its inclusion in first-line regimens—particularly in high-income countries and in select low- and middle-income (LMI) regions, where branded and generic formulations coexist.
Market Dynamics
Demand Drivers
1. Global HIV Burden:
Despite advances, approximately 38 million individuals worldwide live with HIV, with an estimated 1.5 million new infections annually [2]. The demand for consistent ART regimens like Abacavir-Lamivudine remains high, particularly for first-line treatments, fueling steady market growth.
2. Treatment Guidelines and Policy Shifts:
WHO and CDC guidelines favor fixed-dose combinations for their simplicity and adherence benefits. The inclusion of Abacavir-Lamivudine as a preferred or alternative first-line therapy enhances its global demand, particularly as newer integrase inhibitor combinations gain acceptance without displacing Abacavir's role [3].
3. Patent Expirations and Generic Competition:
In several jurisdictions, key patents for branded Abacavir-Lamivudine have expired or are nearing expiration, opening for generic manufacturers, which significantly affect market prices and accessibility.
Competitive Landscape
1. Patent and Generic Status:
Gilead Sciences’ original branded formulations like Ziagen (Abacavir) and Epzicom (Abacavir-Lamivudine) faced patent expiries in many countries—most notably in the USA (2014 for Abacavir and 2018 for Epzicom)—prompting increased generic entry [4].
2. Market Share Distribution:
In high-income countries, branded formulations retain premium pricing owing to established brand loyalty and regulatory approvals. Conversely, in LMICs, generics dominate, driven by initiatives like the Medicines Patent Pool, which facilitate affordable access.
3. Key Players:
Major generic producers include Mylan, Cipla, Hetero, and Sun Pharma. These firms leverage cost advantages to penetrate markets, often priced 50-80% lower than branded counterparts.
Regulatory and Supply Chain Considerations
The regulatory landscape varies globally, with expedited approvals in the African and Asian markets driven by HIV/AIDS programs. Manufacturing capacity and quality standards influence supply stability, impacting market prices.
Pricing Structures and Trends
Current Pricing Overview
1. Branded Formulations:
In high-income nations, retail prices typically range between USD 3,000–4,500 annually per patient, often covered in healthcare plans or through subsidies.
2. Generics:
In LMICs, per-patient annual costs have fallen below USD 100—sometimes as low as USD 50—owing to fierce generic competition and large-volume procurement by organizations like UNITAID and Global Fund.
Cost Drivers
- Manufacturing Expenses: Technology transfer, quality controls, and ingredients.
- Regulatory Compliance: Costs associated with approvals and post-market surveillance.
- Distribution and Logistics: Particularly in resource-constrained settings.
- Pricing Strategies: Branded firms maintain premium prices; generics focus on volume.
Trends and Future Price Trajectories
With patent expiries and increased generic manufacturing, downward price pressure is expected to persist over the next five years [5]. The anticipated proliferation of biosimilar and second-generation formulations may further influence prices.
Price Projections (2023–2028)
| Year | Branded Price (USD/year) | Generic Price (USD/year) | Key Influencing Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 3,500 – 4,500 | 50 – 100 | Patent expiries, global procurement trends |
| 2024 | 3,200 – 4,000 | 45 – 90 | Market absorption, regulatory approvals |
| 2025 | 3,000 – 3,800 | 40 – 80 | Increased generic penetration |
| 2026 | 2,800 – 3,500 | 35 – 70 | Healthcare budget constraints, policy shifts |
| 2027 | 2,600 – 3,300 | 30 – 60 | Implementation of sustainable supply chains |
| 2028 | 2,500 – 3,000 | 25 – 50 | Competitive market saturation |
Note: Prices are approximate and vary by region, procurement volume, and contractual arrangements.
Market Expansion and Accessibility
Efforts by global health agencies aim to widen access through tiered pricing, differential licensing, and regulatory harmonization. Consequently, demand for affordable generics is poised to sustain growth.
Impacts of Innovation and Policy
New fixed-dose combinations incorporating integrase inhibitors like Dolutegravir may slightly diminish demand for older combinations; however, cost competitiveness ensures continued relevance of Abacavir-Lamivudine, especially in resource-limited settings [6].
Risks and Challenges
- Patent Litigation and Legal Barriers: Could delay generic market entry.
- Regulatory Delays: Slowing approval processes impacts availability.
- Market Saturation: Diminishes growth potential in mature markets.
- Pricing Policy Changes: International and national negotiations may cap prices further.
Key Takeaways
- The global demand for Abacavir-Lamivudine remains stable, driven primarily by ongoing HIV treatment needs.
- Patent expirations and the rise of generic manufacturing significantly lower prices, fostering broader access in LMICs.
- In high-income countries, branded formulations retain premium pricing due to brand loyalty and regulatory protections, but this is gradually declining.
- Price projections indicate a continued downward trend, especially for generics, with potential stabilization as markets mature.
- Industry stakeholders must navigate patent landscapes, regulatory environments, and supply chain complexities to optimize market positioning.
FAQs
1. What factors influence the pricing of Abacavir-Lamivudine?
Pricing is primarily affected by patent status, manufacturing costs, regional regulatory requirements, market competition, and procurement volume. Generic availability exerts significant downward pressure.
2. How will patent expirations affect the market in the next five years?
Patent expiries facilitate increased generic entry, resulting in lower prices and expanded access, especially in LMIC settings. This trend is expected to accelerate over the next few years.
3. Are newer HIV treatments expected to replace Abacavir-Lamivudine?
While integrase inhibitor-based regimens are gaining popularity, Abacavir-Lamivudine remains relevant, particularly where cost and accessibility are priorities. It may coexist as part of combination therapy options.
4. What is the forecasted market share for generic formulations?
Global market share for generics is projected to surpass 70% in many regions by 2028, driven by pricing advantages and procurement programs.
5. How do global health initiatives impact the affordability of Abacavir-Lamivudine?
Organizations like the Global Fund and PEPFAR negotiate lower prices and facilitate licensing agreements, substantially improving affordability and accessibility in vulnerable populations.
Sources
- WHO HIV Treatment Guidelines, 2021.
- UNAIDS Global HIV & AIDS Statistics, 2022.
- CDC HIV Treatment Guidelines, 2022.
- U.S. Patent and Trademark Office records, 2014-2022.
- IQVIA MedicineUse and Spending Reports, 2022.
- WHO Global HIV Drug Resistance Report, 2022.
In conclusion, Abacavir-Lamivudine’s market outlook is characterized by sustained demand, pivotal patent developments, and a significant shift towards affordability through generic production. Price declines are anticipated to continue, reinforcing its essential role in global HIV therapy for years to come.
More… ↓
